Hvaler
| Hvaler kommune | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Municipality | |||
|
Marina on Hvaler | |||
| |||
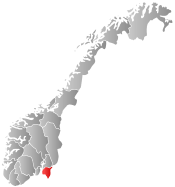
 Hvaler within Østfold | |||
| Coordinates: 59°3′23″N 11°1′20″E / 59.05639°N 11.02222°ECoordinates: 59°3′23″N 11°1′20″E / 59.05639°N 11.02222°E | |||
| Country | Norway | ||
| County | Østfold | ||
| Administrative centre | Skjærhalden | ||
| Government | |||
| • Mayor (2007) | Eivind N. Borge (Frp) | ||
| Area | |||
| • Total | 90 km2 (30 sq mi) | ||
| • Land | 89 km2 (34 sq mi) | ||
| Area rank | 393 in Norway | ||
| Population (2004) | |||
| • Total | 3,694 | ||
| • Rank | 241 in Norway | ||
| • Density | 41/km2 (110/sq mi) | ||
| • Change (10 years) | 9.8 % | ||
| Demonym(s) | Hvalersokning[1] | ||
| Time zone | CET (UTC+1) | ||
| • Summer (DST) | CEST (UTC+2) | ||
| ISO 3166 code | NO-0111 | ||
| Official language form | Bokmål | ||
| Website |
www | ||
|
| |||
Hvaler is a municipality that is a group of islands in the southwestern part of Østfold county, Norway. The administrative centre of the municipality is the village of Skjærhalden, on the island of Kirkeøy. The only police station in the municipality is located in Skjærhalden. Hvaler was established as a municipality on 1 January 1838 (see formannskapsdistrikt).
Name
The name is the plural form of hval which means "whale". The form and shape of the islands are resembling a pod of whales. Prior to 1889, the name was spelled Hvaløerne.
Coat-of-arms
The coat-of-arms is from modern times. They were granted on 9 December 1983. The arms show a silver-colored boat on a blue background. This boat is the type that was typical in the 13th century. This was chosen since this island municipality has been dependent on boats for all its history, and because fisheries and sailing have been the main economic activities for many centuries.[2]
Culture
Hvalerdrakten is the traditional costume or bunad for women in Hvaler. The bodice and skirt are blue or black and are made from 100% wool. The shirt is white and made from 100% cotton. There are several symbolic expressions in the embroideries and the accompanying silver brooches. The embroidered flowers are characteristic to the islands' flora and symbolize the different islands that constitute the municipality. All the silver that belongs to the costume is portraying the locally famous Hvalerbåten (The Boat of Hvaler) and herring, which has been an important commodity to the islands through the ages. All patterns used in this costume have been patented. Since 1999 hvalerdrakten have been manufactured by Hvalerdraktstua AS.[3]

Hvaler Church
Hvaler Church (Hvaler Kirke) is a medieval era church, probably begun about ca. 1000-1100. Hvaler Church is the main church of the archipelago. It is located on Kirkeøy in the extreme south of the parish. It is a stone church with a rectangular nave and narrow choir and apse. The pulpit is from the 1600s. In 1750 the church received a new altar which in 1759 was supplemented with an altarpiece mounted on the altar. Between 1953 and 1955 the church went through a thorough restoration led by antiquarian Håkon Christie in connection with the church's restoration. The J. H. Jorgensen organ is from 1955.[4]
Geography
South of Skjærhalden lies a chain of a few inhabitable islands as well as several hundreds of smaller islands and rocks. The bigger islands are named, clockwise, Nordre Sandøy, Søndre Sandøy, Hærføl, Søndre Lauer, and Nordre Lauer. Another smaller island is Tisler. On all of these islands, with the exception of Søndre Lauer, summer houses fill the landscape. The islands of Søndre Sandøy and Hærføl are the two only islands that have local shops and roads which support car traffic.
Nordre Sandøy, situated on the north end of this chain of islands in southern Hvaler is one of the largest islands with a distinct flora and fauna diversity. Although equipped with a good stretch of roads, car traffic is forbidden there and no commercial activity whatsoever exists. In many ways, this gives its population (mostly summertime vacationers) a greater feeling of isolation from the average Norwegian's hectic life and it acts as a buffer against pollution. Nordre Sandøy is thought to have been one of the bases of Peter Tordenskjold during his time as a privateer. One of the bays on the island is named "Tordenskjoldsbukta" (Norwegian: Bay of Tordenskjold). The remains of two dead pirates have been found on the island. Legend has it that he buried some of his treasure on the island. In 1987, a local boy, Simon Rene Magnussen, found three old golden coins while scuba diving in the area.
| Ancestry | Number |
|---|---|
| | 35 |
| | 21 |
| | 16 |
References
- ↑ "Navn på steder og personer: Innbyggjarnamn" (in Norwegian). Språkrådet. Retrieved 2015-12-01.
- ↑ Norske Kommunevåpen (1990). "Nye kommunevåbener i Norden". Retrieved 2008-12-15.
- ↑ http://www.hvalerdraktstua.no/
- ↑ Sigrid Marie Christie, Håkon Christie. "Hvaler kirke". Norges Kirker. Retrieved October 1, 2016.
- ↑ "Immigrants and Norwegian-born to immigrant parents, by immigration category, country background and percentages of the population". ssb.no. Retrieved 29 June 2015.
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Hvaler. |
| Look up Hvaler in Wiktionary, the free dictionary. |
- Municipal fact sheet from Statistics Norway
Wikivoyage has a travel guide for Østfold. - Koster/Yttre Hvaler