House of Nationalities
| House of Nationalities အမျိုးသားလွှတ်တော် Amyotha Hluttaw | |
|---|---|
| 2nd Amyotha Hluttaw | |
 | |
| Type | |
| Type |
Upper house of the Pyidaungsu Hluttaw |
| History | |
| Founded | 31 January 2011 |
| Preceded by | People's Assembly (1974-1988) |
| Leadership | |
Deputy Speaker | |
| Structure | |
| Seats | 224 MPs |
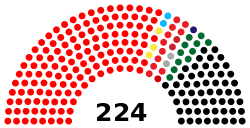 | |
Amyotha Hluttaw political groups |
NLD (135) |
| Elections | |
Amyotha Hluttaw last election | 8 November 2015 |
| Meeting place | |
|
| |
| Pyidaungsu Hluttaw Complex, Naypyidaw | |
| Website | |
|
www | |
 |
| This article is part of a series on the politics and government of Myanmar |
|
|
|
The House of Nationalities (Burmese: အမျိုးသားလွှတ်တော်, IPA: [ʔəmjóðá l̥ʊʔtɔ̀] Amyotha Hluttaw) is the upper house of the Pyidaungsu Hluttaw, the bicameral legislature of Myanmar (Burma). It consists of 224 member of which 168 are directly elected and 56 appointed by the Myanmar Armed Forces. The last elections to the Amyotha Hluttaw were held in November 2015.[1] At its second meeting on 3 February 2016, Mahn Win Khaing Than and Aye Thar Aung were elected Speaker and Deputy Speaker of the Amyotha Hluttaw and Speaker and Deputy Speaker of the Pyidaungsu Hluttaw as a whole.[2]
Composition
House of Nationalities (Amyotha Hluttaw) consists of 224 members including with the 168 directly elected and 56 appointed by the Myanmar Armed Forces. The representatives are elected in equal numbers of 12 representatives from each state or region inclusive of relevant Union territories and including one representative from each Self-Administered Division or Self-Administered Zone.[3]
| Amyothahluttaw (Upper House) | Total |
|---|---|
| Amyotha Hluttaw Representatives | 168 |
| Representatives of Army | 56 |
2016-present
| Amyotha Hluttaw elections, 2015[4] | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Party | Seats | Net gain/loss | Seats % | Votes % | Votes | +/− | |||
| NLD | 135 | |
60.27 | ||||||
| USDP | 11 | |
4.91 | ||||||
| ANP | 10 | |
4.46 | ||||||
| SNLD | 3 | |
1.34 | ||||||
| TNP | 2 | |
0.89 | ||||||
| ZCD | 2 | |
0.89 | ||||||
| MNP | 1 | |
0.45 | ||||||
| NUP | 1 | |
0.45 | ||||||
| PNO | 1 | |
0.45 | ||||||
| Independent | 2 | |
0.89 | ||||||
| AMRDP | 0 | |
0 | ||||||
| SNDP | 0 | |
0 | ||||||
| Others | 0 | |
0 | ||||||
| Military appointees | 56 | |
25.00 | – | – | 0 | |||
| Total | 224 | 100 | |||||
| Amyotha Hluttaw by Regions and States, 2015 | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Region/State | NLD | USDP | ANP | SNLD | ZCD | PNO | TNP | MNP | NUP | Independent | Total |
| Kachin State | 10 | 1 | 1 | 12 | |||||||
| Kayah State | 9 | 2 | 1 | 12 | |||||||
| Kayin State | 10 | 2 | 12 | ||||||||
| Chin State | 9 | 1 | 2 | 12 | |||||||
| Mon State | 11 | 1 | 12 | ||||||||
| Rakhine State | 1 | 1 | 10 | 12 | |||||||
| Shan State | 3 | 3 | 3 | 1 | 2[5] | 12 | |||||
| Sagaing Region | 12 | 12 | |||||||||
| Tanintharyi Region | 12 | 12 | |||||||||
| Bago Region | 12 | 12 | |||||||||
| Magway Region | 12 | 12 | |||||||||
| Mandalay Region | 10 | 2 | 12 | ||||||||
| Yangon Region | 12 | 12 | |||||||||
| Ayeyarwady Region | 12 | 12 | |||||||||
| Total | 135 | 11 | 10 | 3 | 2 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 2 | 168 |
2015 results are as of 20 November 2015. Military appointees are not included in the Amyotha Hluttaw by Regions and States, 2015 table.[6]
2011–2016
| Party | Seats[7] | % | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Union Solidarity and Development Party | 129 | 57.59 | |
| Rakhine Nationalities Development Party | 7 | 3.13 | |
| National Unity Party | 5 | 2.23 | |
| National Democratic Force | 4 | 1.79 | |
| All Mon Region Democracy Party | 4 | 1.79 | |
| Chin Progressive Party | 4 | 1.79 | |
| Shan Nationalities Democratic Party | 3 | 1.33 | |
| Phalon-Sawaw Democratic Party | 3 | 1.33 | |
| Chin National Party | 2 | 0.89 | |
| Pa-O National Organisation | 1 | 0.45 | |
| Kayin People's Party | 1 | 0.45 | |
| Taaung (Palaung) National Party | 1 | 0.45 | |
| Wa Democratic Party | 1 | 0.45 | |
| Unity and Democracy Party of Kachin State | 1 | 0.45 | |
| Kayin State Democracy and Development Party | 1 | 0.45 | |
| Independent | 1 | 0.45 | |
| Military appointees | 56 | 25.00 | |
| Total | 224 | 100 | |
| Date | Constituency | Old MP | Party | New MP | Party | Note |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| August 2011 | Rangoon Division No. 3 | Phone Myint Aung | NDF | Phone Myint Aung | NNDP | Changed party membership[8] |
| December 2011 | Rangoon Region No. 4 | Myat Nyana Soe | NDF | Myat Nyana Soe | NLD | Changed party membership[9] |
| 28 January 2012 | Sagaing Division No. 2 | Bogyi aka Aung Ngwe | USDP | – | – | Deceased[10] |
| Party | Seats won | Change | Seats before | Seats after[11] | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Union Solidarity and Development Party | 1 | | 128 | 123 | |
| Rakhine Nationalities Development Party | 0 | | 7 | 7 | |
| National Unity Party | 0 | | 5 | 5 | |
| National League for Democracy | 4 | | 1 | 5 | |
| National Democratic Force | 0 | | 2 | 2 | |
| New National Democracy Party | 0 | | 1 | 1 | |
| All Mon Region Democracy Party | 0 | | 4 | 4 | |
| Chin Progressive Party | 0 | | 4 | 4 | |
| Shan Nationalities Democratic Party | 1 | | 3 | 4 | |
| Phalon-Sawaw Democratic Party | 0 | | 3 | 3 | |
| Chin National Party | 0 | | 2 | 2 | |
| Pa-O National Organization | 0 | | 1 | 1 | |
| Kayin People's Party | 0 | | 1 | 1 | |
| Taaung (Palaung) National Party | 0 | | 1 | 1 | |
| Wa Democratic Party | 0 | | 1 | 1 | |
| Unity and Democracy Party of Kachin State | 0 | | 1 | 1 | |
| Kayin State Democracy and Development Party | 0 | | 1 | 1 | |
| Independent | 0 | | 1 | 1 | |
| Vacant | 0 | | 1 | 1 | |
| Military appointees | – | – | 56 | 56 | |
| Total | 6 | | 224 | 224 | |
| Date | Constituency | Old MP | Party | New MP | Party | Note |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 5 February 2013 | Rangoon Division No. 6 | Tin Shwe | NDF | – | – | Became a Deputy Minister[10] |
| 2013 | Arakan State No. 4 | Maung Sa Pru | RNDP | – | – | Deceased[10] |
References
- ↑ "Myanmar election commission publishes election final results". Xinhuanet. 17 November 2010.
- ↑ "Burma's parliament opens new session". BBC News. 31 January 2011.
- ↑ 2008 Constitution, Myanmar. Pg. Article 141 (a)
- ↑ "Announcement 93/2015". Union Election Commission. Retrieved 20 November 2015.
- ↑ "Announcement 95/2015". Union Election Commission. Retrieved 26 November 2015.
- ↑ "Announcement 93/2015". Union Election Commission. Retrieved 20 November 2015.
- ↑ "Burma's 2010 Elections: A comprehensive report" (PDF). Burma Fund UN Office. 2011-01-31. Retrieved 2015-11-26.
- ↑ "New political party says it wants to work for a peaceful Burma". Mizzima. 2011-08-24. Retrieved 2015-11-24.
- ↑ "NDF MPs rejoin NLD". Mizzima. 2012-04-09. Retrieved 2015-11-24.
- 1 2 3 "National Assembly - Overview - Parliament Watch". ALTSEAN Burma. Retrieved 2015-11-24.
- ↑ "National Assembly - Overview - Parliament Watch". ALTSEAN Burma. Archived from the original on 2012-07-19.