Hillegom
| Hillegom | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Municipality | |||
|
Hillegom city hall | |||
| |||
.svg.png) Location in South Holland | |||
| Coordinates: 52°17′N 4°35′E / 52.283°N 4.583°ECoordinates: 52°17′N 4°35′E / 52.283°N 4.583°E | |||
| Country | Netherlands | ||
| Province | South Holland | ||
| Government[1] | |||
| • Body | Municipal council | ||
| • Mayor | Jan Broekhuis (VVD) | ||
| Area[2] | |||
| • Total | 13.48 km2 (5.20 sq mi) | ||
| • Land | 12.92 km2 (4.99 sq mi) | ||
| • Water | 0.56 km2 (0.22 sq mi) | ||
| Elevation[3] | 1 m (3 ft) | ||
| Population (May 2014)[4] | |||
| • Total | 21,090 | ||
| • Density | 1,632/km2 (4,230/sq mi) | ||
| Demonym(s) | Hillegommer | ||
| Time zone | CET (UTC+1) | ||
| • Summer (DST) | CEST (UTC+2) | ||
| Postcode | 2180–2182 | ||
| Area code | 0252 | ||
| Website |
www | ||
Hillegom (![]() pronunciation ) is a town and municipality in the western Netherlands, in the province of South Holland. The municipality covers an area of 13.48 km2 (5.20 sq mi) of which 0.56 km2 (0.22 sq mi) is water. Hillegom is part of an area called the Duin- en Bollenstreek ("Dune and Bulb Region"). As such, a large portion of the local economy was traditionally geared to the cultivation of bulb flowers. It is bordered by the municipalities of Bloemendaal, Bennebroek (to the north), Haarlemmermeer (to the east), Lisse (to the south), and Noordwijkerhout (to the west).
pronunciation ) is a town and municipality in the western Netherlands, in the province of South Holland. The municipality covers an area of 13.48 km2 (5.20 sq mi) of which 0.56 km2 (0.22 sq mi) is water. Hillegom is part of an area called the Duin- en Bollenstreek ("Dune and Bulb Region"). As such, a large portion of the local economy was traditionally geared to the cultivation of bulb flowers. It is bordered by the municipalities of Bloemendaal, Bennebroek (to the north), Haarlemmermeer (to the east), Lisse (to the south), and Noordwijkerhout (to the west).
The name Hillegom is derived from the abbey named Hijlighem (Old Frankish for "Holy Home"). This abbey no longer exists. The current Lord of Hillegom is Jan Six X.[5][6]
History
Hillegom was formed on the eastern edge of the coastal dunes where the old Leiden to Haarlem route crossed the Hillegommerbeek (Hillegom's Creek), not far from the shores of the Haarlemmermeer (Haarlem's Lake). Places with the suffix "-heim" (or variant spellings) usually developed before the year 1000 and therefore it is assumed that this may apply to Hillegom as well. In 1150 the abbot of Egmond had the rights to naming priests in Hillegom, indicating that a church or chapel existed there. In 1248 the count Willem II gave the Chapel of Hijllinghem and all its buildings to the Abbot of Egmond.
In the middle of the 14th century, Hillegom gained some prominence when the counts of Holland convened there 3 times for council. In 1369, there were 46 houses with a population of 283, growing to 67 houses and 412 people in 1477.

During the Eighty Years' War, Hillegom found itself several times between the opposing Spanish and Dutch Rebel armies, resulting in its near destruction in 1577. But after the middle of the 17th century, the area became prosperous through the cultivation of fruits and vegetables, growing on the sandy soil of fields dug out the dunes.
In 1722, the rich Amsterdam merchant Jan Six II bought the fiefdom Hillegom and built improvements, including a stone bridge over the Hillegommerbeek and a pump in the village square as well as paving a portion of the main road. In 1749, he purchased Het Hof (The Courtyard), an estate in the centre of Hillegom. At this time, there were many other estates of rich merchants and stadtholders in Hillegom, such as Bethlehem, Oostende, Horstendael, Weeresteyn, Treslong, Duin en Weg, Meer en Dorp, Het Hof, Lapinenburg and Elsbroek (many of these names survive as neighborhood names). The population grew to 930 in 1732 and to 1050 in 1795.
But during the 19th century, the beauty of the area and its estates slowly began to disappear. Developers bought the estates, cut down the forests, and excavated the sand dunes to create fields for bulb flower cultivation. This process accelerated in 1904 when a lime-sand brick factory was built just south of Hillegom, which needed large amounts of sand. By the early 1920s, all estates had disappeared, except for Het Hof which became Hillegom's town hall. This same period saw the rapid growth of the bulb flower industry and Hillegom's population, up to 8800 in 1916.
Hillegom's convenient location led to another rapid growth period during the 1960s, 70s, and 80s, when many new neighborhoods were built to accommodate families working in either Haarlem, Amsterdam, or Leiden. Its economy became less dependent on the bulb flower trade and more diversified with the establishment of a few business parks.
Demographics
.png)
Population on January 1:
- 1899: 5,361
- 1930: 10,812
- 1960: 14,789
- 1970: 16,963
- 1980: 17,937
- 1990: 19,885
- 2000: 20,664
- 2004: 20,588
- 2006: 20,317
- 2011: 20,627
- Source: Statistics Netherlands

Transportation
Historically, much of the town's transportation was done by water, either canals or streams.
The Hillegommerbeek (Hillegom's Creek) was used to transport goods from the town to Haarlemmermeer (Haarlem's Lake) and, after its reclamation, to the Ringvaart. Several docks and wharfs still line the creek and canal.
The Leidsevaart (Leiden Canal) was completed in 1657 and runs between Leiden and Haarlem just west of Hillegom. This canal has fallen in disuse because of its many non-operable bridges.
Hillegom is served by Provincial Roads 207, 208, and 442.
Railway
Hillegom is served by Hillegom railway station, with direct connections to Haarlem in the north and Leiden and The Hague southward.
Tourism and attractions
The most interesting time to visit is during the spring when the fields around Hillegom are in a colourful bloom. At this time a flower parade, the Bloemencorso, travels through its main streets.
Hillegom is also home to the Den Hartogh Ford Museum, which has the world's largest collection of Ford automobiles. It has over 200 classic cars, all from before World War II.
Notable persons from Hillegom
- John Blankenstein (1949 - 2006), soccer referee
- Dick van Egmond (born 1961), soccer referee
- Bart de Graaff (1967 - 2002), television personality and producer, founder and chairman of BNN
- Schelto van Heemstra (1879 - 1960), Queen's commissioner
- Jesse Huta Galung (born 1985), professional tennis player
- Rogier Koordes (born 1972), former footballer
- Frénk van der Linden (born 1957), journalist
- Constantijn Muysken (1843 - 1922), architect
- Rien van Nunen (1912 - 1975), actor
- Thea de Roos-van Rooden (born 1949), historian and former politician
- Annemarie Spilker (born 1980), photographer
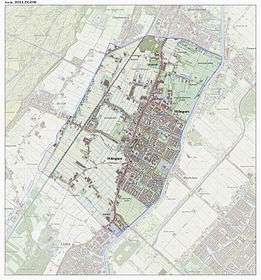
Neighborhoods
- Centrum
- Elsbroek
- De Marel
- Meer en Dorp I and II
- Patrimonium
- Treslong
- De Zanderij
- Hofzicht
- Weerestein
- Amerikabuurt
- Hillegom Zuid
- Vossepolder (under construction)
References
- ↑ "Leden college van B&W" [Members of the board of mayor and aldermen] (in Dutch). Gemeente Hillegom. Retrieved 30 July 2013.
- ↑ "Kerncijfers wijken en buurten" [Key figures for neighbourhoods]. CBS Statline (in Dutch). CBS. 2 July 2013. Retrieved 12 March 2014.
- ↑ "Postcodetool for 2181EC". Actueel Hoogtebestand Nederland (in Dutch). Het Waterschapshuis. Retrieved 30 July 2013.
- ↑ "Bevolkingsontwikkeling; regio per maand" [Population growth; regions per month]. CBS Statline (in Dutch). CBS. 26 June 2014. Retrieved 24 July 2014.
- ↑ "Six van Hillegom". Hillegom Promotie (in Dutch). Retrieved 17 November 2014.
- ↑ "Hillegom". Bollenstreek (in Dutch). Retrieved 17 November 2014.
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Hillegom. |
- Official website
- History of Hillegom (in Dutch)
 |
Bloemendaal (NH) |  | ||
| Noordwijkerhout | |
Haarlemmermeer (NH) | ||
| ||||
| | ||||
| Lisse |