Georgia State Route 300
| ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Georgia-Florida Parkway | ||||||||||
 | ||||||||||
| Route information | ||||||||||
| Maintained by GDOT | ||||||||||
| Length: | 106.0 mi[1] (170.6 km) | |||||||||
| Existed: | 1983[2] – present | |||||||||
| Major junctions | ||||||||||
| South end: |
| |||||||||
|
| ||||||||||
| North end: |
| |||||||||
| Location | ||||||||||
| Counties: | Thomas, Mitchell, Dougherty, Worth, Crisp | |||||||||
| Highway system | ||||||||||
| ||||||||||
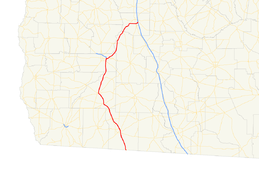
State Route 300 (SR 300, also called the Georgia–Florida Parkway), is a 116-mile-long (187 km) state highway in the southern part of the U.S. state of Georgia. Its southern terminus is at the Florida state line, concurrent with US 19/SR 57 south of Thomasville in Thomas County. Its northern terminus is at SR 90 in Cordele in Crisp County, Georgia. It also has an interchange with Interstate 75 (I-75), also in Cordele.
This is the second state route in Georgia to carry the SR 300 designation. The earlier one, in a different part of the state, was much shorter, running from Monticello to a point 20.3 miles (32.7 km) northeast of Monticello (and about 6 miles (9.7 km) north of Eatonton), and existed from the 1960s[3][4] to the 1980s.[5][6]
SR 300 was the basis for a proposed connector route for I-75, Interstate 175 that would have connected Albany and Cordele on a more easterly routing.[7][8][9]
Route description
Florida to Albany
SR 300 begins at the Florida state line, where it is concurrent with US 19 and unsigned SR 57. On the Florida side of the state line, US 19 is known as the Florida–Georgia Parkway. At the state line, SR 57 ends, and SR 3 and SR 300 begin. US 19/SR 3/SR 300 head northwest until they enter Thomasville. In the city, they intersect US 84/SR 38, which head east to Valdosta. Here, they join the conurrency. Also, this intersection marks the eastern terminus of US 84 Business/SR 38 Business. Farther to the northwest, the five routes intersect US 319/SR 35, where US 84/SR 38 depart to the west, along with SR 3 Alternate. In Meigs, SR 111 intersects the concurrency, along with the northern terminus of SR 3 Alternate. In Camilla, the highways have intersections with SR 37 and SR 112, and curve to make a slight jog to the northeast until they reach Albany.
Albany to Cordele
Most of the route of SR 300 in Albany is on the Liberty Expressway, a freeway-grade bypass of the city's downtown to the northeast. In the southeastern part of the city is an intersection with SR 133, which joins the concurrency, and the eastern terminus of SR 234. Nearly 2 miles (3.2 km) later, the concurrency intersects US 19 Business/US 82 Business/SR 520 Business, where US 19 Business has its southern terminus. Slightly later is US 82/SR 520. They join the US 19/SR 3/SR 133 concurrency, while US 82/SR 300/SR 520 head east for just over 1.5 miles (2.4 km), where SR 300 splits off to the northeast. It travels through rural areas until it reaches the Cordele area. Just before entering Cordele proper is SR 300 Connector and US 41/SR 7. Upon entering Cordele, the route meets an interchange with I-75 and meets its northern terminus, an intersection with SR 90.[1]
History
Former State Route 300
| |
|---|---|
| Location: | Monticello–north of Eatonton |
| Length: | 20.3 mi[10] (32.7 km) |
| Existed: | 1960[3][4]–1982[5][6] |
The former SR 300 was a route between Monticello and US 129/US 441/SR 24, near the Rock Eagle State 4-H Club Center north of Eatonton. It was established in 1960.[3][4] Later that year, a small portion at the eastern terminus was paved.[4][11] By 1967, the section from its western terminus to the intersection with SR 142 was paved.[12][13] In 1970, the entire length of the highway was paved.[14][15] By 1983, the highway was decommissioned and given to local authority.[5][6]
| County | Location | mi[10] | km | Destinations | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Jasper | Monticello | 0.0 | 0.0 | Western terminus | |
| Putnam | Oconee National Forest | 10.5 | 16.9 | ||
| 20.3 | 32.7 | Eastern terminus | |||
| 1.000 mi = 1.609 km; 1.000 km = 0.621 mi | |||||
Current routing
The roadway that would eventually become the current SR 300 was established in 1920 as SR 3 from Thomasville to Albany, via Camilla.[16][17]
By October 1926, nearly all of the aforementioned route was paved.[17][18] By October 1929, SR 3 was extended southwest to where US 319 currently crosses the state line. US 19 was designated along this route to Thomasville, and then its current route from Thomasville to Albany.
SR 35 was designated along a portion of highway that is the current route of US 19 from the Florida state line to Thomasville.[18][19] By 1935, nearly all of the northern half of the section of SR 35 between the Florida state line and Thomasville was paved.[20][21] Prior to the beginning of 1936, nearly all of that section of SR 35 was paved.[22][23] By July, the rest of that section was paved.[23][24]
In March 1937, the section of SR 300 that currently runs from Albany to Cordele was established as a northern extension of SR 133.[25][26] By October the routings of the portions of US 19 southwest of Thomasville was shifted to its current routing, while SR 3 stayed on its original routing.[27][28] The following August, a small portion of SR 133 southwest of Cordele was paved.[29][30]
By 1944, a very brief section of SR 133 northeast of Albany was paved.[31][32] In early 1946, approximately half of the length of SR 133 between Warwick and Cordele was paved.[33][34]
In early 1948, all of SR 133 was redesignated as SR 257. The section of SR 257 from Albany to the intersection with SR 32 and the section from Lake Blackshear to Cordele were paved.[34][35] In 1950, nearly all of SR 257 was paved.[36][37] By 1952, the entire roadway that would eventually become SR 300 was paved.[37][38]
In early 1982, the Georgia–Florida Parkway was approved to be designated along the entire stretch of what is now SR 300.[39] By the next year, all of SR 257 was redesignated as SR 300 and the designation was applied to the rest of its current route.[5][6] Later that year, the routings of SR 3 and SR 35 south of Thomasville were swapped.[6][40]
Interstate 175
| |
|---|---|
| Location: | Albany–Cordele |
| Existed: | 1975–1978[41] |
Interstate 175 (I-175) was a proposed auxiliary route of I-75. Most of the route would have paralleled the current route of SR 300 (then numbered as SR 257). This highway would have connected the city of Albany to the Interstate Highway System via I-75, had it actually been built.[7] I-175 was approved by AASHTO in 1975 to travel east from Albany. It would then curve to the northeast, and travel on a routing that would have been located farther to the east than SR 257.[8][9] If I-175 had been built, it would have had the hidden designation of State Route 412.[41]
Major intersections
| County | Location | mi[1] | km | Destinations | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Florida state line | 0.0 | 0.0 | Continuation into Florida concurrent with unsigned SR 57; southern terminus of SR 3 | ||
| Thomas | Thomasville | 12.3 | 19.8 | Eastern terminus of US 84 Business/SR 38 Business; southern end of US 84/SR 38 | |
| 13.7 | 22.0 | Western terminus of SR 122 | |||
| 14.2 | 22.9 | Former northern terminus of US 319 Bus. | |||
| 15.3 | 24.6 | Northern end of US 84/SR 38 concurrency; southern end of SR 3 Alternate | |||
| | 17.7 | 28.5 | Southern terminus of SR 202 | ||
| Ochlocknee | 24.0 | 38.6 | |||
| | 31.4 | 50.5 | Northern terminus of SR 3 Alternate | ||
| Mitchell | Pelham | 36.9 | 59.4 | ||
| Camilla | 45.0 | 72.4 | |||
| 45.1 | 72.6 | ||||
| Baconton | 55.8 | 89.8 | Northern terminus of SR 93 | ||
| Dougherty | Albany | 67.5 | 108.6 | Southern end of SR 133 concurrency; eastern terminus of SR 234 | |
| 69.4 | 111.7 | Southern terminus of US 19 Business | |||
| 70.1 | 112.8 | Northern end of US 19/SR 3 & SR 133 concurrencies; southern end of US 82/SR 520 concurrency | |||
| 71.8 | 115.6 | Northern end of US 82/SR 520 concurrency | |||
| Worth | | 84.3 | 135.7 | ||
| Warwick | 92.7 | 149.2 | Northern terminus of SR 313 | ||
| Lake Blackshear | 93.9 | 151.1 | Unnamed bridge over Lake Blackshear | ||
| Crisp | | 101 | 163 | Southern terminus of SR 300 Connector | |
| | 105 | 169 | |||
| Cordele | 106 | 171 | |||
| 108 | 174 | Northern terminus | |||
1.000 mi = 1.609 km; 1.000 km = 0.621 mi
| |||||
Bannered route
| |
|---|---|
| Location: | Southwest of Cordele |
| Length: | 3.4 mi[42] (5.5 km) |
State Route 300 Connector (SR 300 Connector) is a 3.4-mile-long (5.5 km) connector route of the SR 300 mainline that exists entirely within Crisp County. It follows Old Albany Highway from an intersection with SR 300 southwest of Cordele and travels northeast until it meets its northern terminus, an intersection with US 280/SR 30 west of the city.[42]
The entire route is in Crisp County.
| Location | mi[42] | km | Destinations | Notes | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| | 0.0 | 0.0 | Southern terminus | ||
| | 3.4 | 5.5 | Northern terminus | ||
| 1.000 mi = 1.609 km; 1.000 km = 0.621 mi | |||||
See also
-
.svg.png) Georgia (U.S. state) portal
Georgia (U.S. state) portal -
 U.S. Roads portal
U.S. Roads portal
References
- 1 2 3 Google (June 8, 2013). "Route of SR 300" (Map). Google Maps. Google. Retrieved June 8, 2013.
- ↑ Georgia Department of Transportation (1983). Official Highway and Transportation Map (PDF) (Map) (1983–84 ed.). Scale not given. Atlanta: Georgia Department of Transportation. Retrieved July 22, 2016.
- 1 2 3 Georgia State Highway System (PDF) (Map). Cartography by GSHD. Georgia State Highway Department. July 1, 1957. Retrieved June 8, 2013.
- 1 2 3 4 Georgia State Highway System (PDF) (Map). Cartography by GSHD. Georgia State Highway Department. June 1, 1960. Retrieved June 8, 2013.
- 1 2 3 4 Georgia State Highway System (PDF) (Map). Cartography by GSHD. Georgia State Highway Department. January 1, 1982. Retrieved June 8, 2013.
- 1 2 3 4 5 Georgia State Highway System (PDF) (Map). Cartography by GSHD. Georgia State Highway Department. January 1, 1983. Retrieved June 8, 2013.
- 1 2 "Southwest Georgia Interstate Study: Final Report" (PDF). Georgia Department of Transportation. December 2009. Retrieved June 7, 2013.
- 1 2 Georgia State Highway System (PDF) (Map). Cartography by GSHD. Georgia State Highway Department. January 1, 1976-7. Retrieved June 8, 2013. Check date values in:
|date=(help) - 1 2 Georgia State Highway System (PDF) (Map). Cartography by GSHD. Georgia State Highway Department. January 1, 1977-8. Retrieved June 8, 2013. Check date values in:
|date=(help) - 1 2 Google (August 10, 2013). "Route of Former SR 300" (Map). Google Maps. Google. Retrieved August 10, 2013.
- ↑ Georgia State Highway System (PDF) (Map). Cartography by GSHD. Georgia State Highway Department. June 1, 1960. Retrieved June 8, 2013.
- ↑ Georgia State Highway System (PDF) (Map). Cartography by GSHD. Georgia State Highway Department. January 1, 1966. Retrieved June 8, 2013.
- ↑ Georgia State Highway System (PDF) (Map). Cartography by GSHD. Georgia State Highway Department. January 1, 1967. Retrieved June 8, 2013.
- ↑ Georgia State Highway System (PDF) (Map). Cartography by GSHD. Georgia State Highway Department. January 1, 1970. Retrieved June 8, 2013.
- ↑ Georgia State Highway System (PDF) (Map). Cartography by GSHD. Georgia State Highway Department. January 1, 1971. Retrieved June 8, 2013.
- ↑ Georgia State Highway System (PDF) (Map). Cartography by GSHD. Georgia State Highway Department. January 1, 1920. Retrieved June 8, 2013.
- 1 2 Georgia State Highway System (PDF) (Map). Cartography by GSHD. Georgia State Highway Department. September 23, 1921. Retrieved June 8, 2013.
- 1 2 Georgia State Highway System (PDF) (Map). Cartography by GSHD. Georgia State Highway Department. October 1, 1926. Retrieved June 8, 2013.
- ↑ Georgia State Highway System (PDF) (Map). Cartography by GSHD. Georgia State Highway Department. October 1, 1929. Retrieved June 8, 2013.
- ↑ Georgia State Highway System (PDF) (Map). Cartography by GSHD. Georgia State Highway Department. October 1, 1934. Retrieved June 8, 2013.
- ↑ Georgia State Highway System (PDF) (Map). Cartography by GSHD. Georgia State Highway Department. January 1, 1935. Retrieved June 8, 2013.
- ↑ Georgia State Highway System (PDF) (Map). Cartography by GSHD. Georgia State Highway Department. October 1, 1935. Retrieved June 8, 2013.
- 1 2 Georgia State Highway System (PDF) (Map). Cartography by GSHD. Georgia State Highway Department. January 1, 1936. Retrieved June 8, 2013.
- ↑ Georgia State Highway System (PDF) (Map). Cartography by GSHD. Georgia State Highway Department. July 1, 1936. Retrieved June 8, 2013.
- ↑ Georgia State Highway System (PDF) (Map). Cartography by GSHD. Georgia State Highway Department. January 1, 1937. Retrieved June 8, 2013.
- ↑ Georgia State Highway System (PDF) (Map). Cartography by GSHD. Georgia State Highway Department. April 1, 1937. Retrieved June 8, 2013.
- ↑ Georgia State Highway System (PDF) (Map). Cartography by GSHD. Georgia State Highway Department. July 1, 1937. Retrieved June 8, 2013.
- ↑ Georgia State Highway System (PDF) (Map). Cartography by GSHD. Georgia State Highway Department. October 1, 1937. Retrieved June 8, 2013.
- ↑ Georgia State Highway System (PDF) (Map). Cartography by GSHD. Georgia State Highway Department. August 1, 1938. Retrieved June 8, 2013.
- ↑ Georgia State Highway System (PDF) (Map). Cartography by GSHD. Georgia State Highway Department. September 1, 1938. Retrieved June 8, 2013.
- ↑ Georgia State Highway System (PDF) (Map). Cartography by GSHD. Georgia State Highway Department. January 1, 1943. Retrieved June 8, 2013.
- ↑ Georgia State Highway System (PDF) (Map). Cartography by GSHD. Georgia State Highway Department. January 1, 1944. Retrieved June 8, 2013.
- ↑ Georgia State Highway System (PDF) (Map). Cartography by GSHD. Georgia State Highway Department. January 1, 1945. Retrieved June 8, 2013.
- 1 2 Georgia State Highway System (PDF) (Map). Cartography by GSHD. Georgia State Highway Department. November 7, 1946. Retrieved June 8, 2013.
- ↑ Georgia State Highway System (PDF) (Map). Cartography by GSHD. Georgia State Highway Department. February 28, 1948. Retrieved June 8, 2013.
- ↑ Georgia State Highway System (PDF) (Map). Cartography by GSHD. Georgia State Highway Department. April 1, 1949. Retrieved June 8, 2013.
- 1 2 Georgia State Highway System (PDF) (Map). Cartography by GSHD. Georgia State Highway Department. August 1, 1950. Retrieved June 8, 2013.
- ↑ Georgia State Highway System (PDF) (Map). Cartography by GSHD. Georgia State Highway Department. January 1, 1952. Retrieved June 8, 2013.
- ↑ "Georgia-Florida Parkway — Designated" (PDF). General Assembly of the State of Georgia. April 14, 1982. Retrieved June 8, 2013.
- ↑ Georgia State Highway System (PDF) (Map). Cartography by GSHD. Georgia State Highway Department. January 1, 1984. Retrieved June 8, 2013.
- 1 2 Georgia Department of Transportation (January 1977). Official Highway Map (PDF) (Map) (1977–78 ed.). Scale not given. Atlanta: Georgia Department of Transportation. Retrieved July 12, 2016.
- 1 2 3 Google (August 10, 2013). "Route of SR 300 Connector" (Map). Google Maps. Google. Retrieved August 10, 2013.
External links
-
 Media related to Georgia State Route 300 at Wikimedia Commons
Media related to Georgia State Route 300 at Wikimedia Commons - Georgia Roads (Routes 281 - 300)
- Georgia State Route 300 on State-Ends.com
- Interstate 175 Georgia on Kurumi.com
