George Hayter
| Sir George Hayter | |
|---|---|
 Self Portrait painted in 1843 (Private collection) | |
| Born |
George Hayter 17 December 1792 St. James's, London, England |
| Died |
18 January 1871 (aged 78) Marylebone, London, England |
| Nationality | English |
| Education | Royal Academy Schools |
| Known for | Painter |
| Notable work |
The Trial of Queen Caroline in the House of Lords 1820 The First Meeting of the Reformed House of Parliament 1833 State Portrait of HM Queen Victoria 1838 The Coronation of HM Queen Victoria 1838 The Marriage of Queen Victoria 1840 The Christening of the Prince of Wales 1842 |
| Awards | Knight Bachelor, Knight of the Lion and the Sun of Persia, Member of the Academies of St. Luke (Rome), Bologna, Parma, Florence and Venice |
| Patron(s) | HM Queen Victoria, King Leopold I of the Belgians, 6th Duke of Bedford, 6th Duke of Devonshire |
Sir George Hayter (17 December 1792 – 18 January 1871) was a notable English painter, specialising in portraits and large works involving in some cases several hundred individual portraits. Queen Victoria appreciated his merits and appointed Hayter her Principal Painter in Ordinary and also awarded him a Knighthood 1841.
Early life

Hayter was the son of Charles Hayter (1761–1835), a miniature painter and popular drawing-master and teacher of perspective who was appointed Professor of Perspective and Drawing to Princess Charlotte and published a well-known introduction to perspective and other works.
Initially tutored by his father, he went to the Royal Academy Schools early in 1808, but in the same year, after a disagreement about his art studies, ran away to sea as a Midshipman in the Royal Navy. His father secured his release, and they came to an agreement that Hayter should assist him while pursuing his own studies.[1]
In 1809 he secretly married Sarah Milton, a lodger at his father's house (he was 15 or 16, she 28), the arrangement remaining secret until around 1811.[1] Together they had three children Georgiana, Leopold and Henry.
At the Royal Academy Schools he studied under Fuseli, and in 1815 was appointed Painter of Miniatures and Portraits by Princess Charlotte. Hayter was awarded the British Institution’s premium for history painting for the Prophet Ezra (1815; Downton Castle), purchased by Richard Payne Knight.
Around 1816 his wife left him, for reasons which are not apparent. He subsequently began a relationship with Louisa Cauty, daughter of Sir William Cauty, with whom he lived openly for the next decade and who bore him two children, Angelo and Louisa (despite not having sought a divorce from his first wife).[1]
Travel to Italy

Encouraged by his patron, John Russell, 6th Duke of Bedford, he travelled to Italy to study in 1816. There he met Canova, whose studio he attended while painting his portrait, where he absorbed Canova’s classical style. He is also believed to have learned sculpture from Canova at this time. Canova was Perpetual Principal of the Accademia di San Luca (Rome's premier artistic institution) and doubtless put Hayter forward for honorary membership on the strength of his painting ‘The Tribute Money’ which was very favourably received in Rome. Hayter thereby became the Academy's youngest ever member.
Historical Portraiture

Returning to London in 1818, Hayter practised as a portrait painter in oils and history painter. Dubbed ‘The Phoenix’ by William Beckford, Hayter showed a pomposity that irritated his fellow artists, but he mixed freely with many aristocratic families. His unconventional domestic life (separated from his wife, yet living with his mistress) set him apart from official Academy circles: he was never elected to the Royal Academy.

Hayter was most productive and innovative during the 1820s. George Agar-Ellis (later Lord Dover) commissioned the Trial of Queen Caroline in the House of Lords in 1820 (exh. Cauty’s Great Rooms, 80-82 Pall Mall, 1823; London, National Portrait Gallery); painted on a large scale (2.33×2.66 m), Hayter’s first (and most successful) contemporary history painting revealed a taste for high drama effectively realised. In the Trial of William, Lord Russell, in the Old Bailey in 1683 (1825; Woburn Abbey) Hayter celebrated John Russell’s ancestry, in a work reminiscent of fashionable tableaux vivants of the country-house set.
Return to the Continent
In 1826 Hayter settled in Italy. The Banditti of Kurdistan Assisting Georgians in Carrying off Circassian Women (untraced), completed in Florence for John Proby, 1st Earl of Carysfort (exhibited British Institution 1829), demonstrated Hayter’s assimilation of the style and exotic subject-matter of contemporary French Romantic art.
In 1827 his mistress, Louisa Cauty, died after poisoning herself with arsenic. Although it was apparently an accident, in a bid for attention, it was widely assumed that he had driven her to suicide, and he was forced by the scandal to move from Florence to Rome.[1]
By late 1828 he was in Paris, where his portraits of English society members (some exhibited at the Salon in 1831) were stylistically akin to the work of recent French portrait painters such as François Gérard.
Royal Patronage

In 1831 Hayter returned to England. His grandiose plan to paint the first sitting after the passage of the Reform Bill resulted in his painting 'Moving the Address to the Crown on the Opening of the First Reformed Parliament in the Old House of Commons, 5 February 1833' (1833–43; London, N.P.G.), for which he executed nearly 400 portrait studies in oil. Hayter was an ardent supporter of the reform movement and this painting was not commissioned but to all intents and purposes a labour of love. It occupied him for ten years with no guarantee of financial reward. This is one of the last images executed of the interior of the old House of Commons before its destruction in the fire of 1834. The painting was finally purchased by the government for the nation in 1854, 20 years after it was started.
Having painted the young Princess Victoria (1832–3; destr.; oil sketch, Brit. Royal Col.), Hayter was not a surprising choice as the new Queen’s 'Portrait and Historical Painter'. But on the death of Sir David Wilkie in 1841 Hayter's appointment as Principal Painter in Ordinary to the Queen caused some annoyance at the Royal Academy as this appointment had historically been the preserve of the President, then Sir Martin Archer Shee. In 1842 Hayter was knighted. He painted several royal ceremonies including Queen Victoria’s coronation of 1838 and marriage of 1840 and also the Christening of the Prince of Wales of 1843 (all Brit. Royal Col.). He also painted several royal portraits including his most well known work the State Portrait of the new Queen Victoria. Several versions of this portrait were done, with the assistance of the artist's son Angelo, to be sent as diplomatic gifts. Hayter's active period at court was short-lived however, because Albert preferred German painters such as F. X. Winterhalter.
Several significant examples of Hayter's works from this period remain a part of the Royal Collection, and both the State Portrait and Wedding painting are among those displayed to the public at Buckingham Palace. There is also a full-scale version of the State Portrait in the National Portrait Gallery and smaller copy at Holyrood House.
Hayter's later years

By the mid-1840s Hayter’s portrait style was considered old-fashioned. He adjusted his type of history painting to suit the more literal taste of the early Victorian era (e.g. Wellington Viewing Napoleon’s Effigy at Madame Tussaud’s; destr. 1925; engraving, 1854). Hayter also painted several large religious paintings including two depicting important Reformist events, 'Bishop Latimer Preaching at Paul's Cross' and 'The Martyrdom of Bishops Ridley and Latimer' (exh. 1855), both of which were given to the Art Museum, Princeton University, USA in 1984. He also produced fluent landscape watercolours (many of Italian views), etchings (he published a volume in 1833), decorative designs and sculpture. The contents of Hayter’s studio were auctioned at Christie’s, London, on 19 April 1871.
His younger brother, John (1800–95), was also an artist, known chiefly as a portrait draughtsman in chalks and crayons and his younger sister Anne worked as a miniaturist. Some sources say that the influential printmaker Stanley William Hayter was a direct descendant from John Hayter,[2] although others say the ancestor was Sir George Hayter himself.[1] However the family tree of John and George Hayter published in Crisps Visitations shows no possible link to SW Hayter.[3] What is known for certain is that the French painter and writer, Jean René Bazaine was a great great grandson of George Hayter, through his eldest daughter Georgiana Elizabeth, who married Pierre-Dominique Bazaine older brother of Marshal Bazaine.[4]
See also
References
- 1 2 3 4 5 Barbara Coffey Bryant, "Hayter, Sir George (1792–1871)", Oxford Dictionary of National Biography, Oxford University Press, 2004 accessed 7 June 2007
- ↑
- Innovation in printmaking: Obituary of Mr S W Hayter, The Times, London, May 7, 1988
- ↑ Visitation of England and Wales, Volume 17 1911, ed. Frederick Arthur Crisp, reprinted 1997 by Heritage Books Inc.
- ↑ Jean Bazaine: Couleurs et Mots: le cherche midi éditeur, 1997 (entretiens avec Paul Ricœur et Henri Maldiney)
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to George Hayter. |
Further reading
- R. Ormond: Early Victorian Portraits, 2 vols, London N.P.G. cat. (London, 1973)
- Drawings by Sir George and John Hayter (exh. cat. by B. Coffey [Bryant], London, Morton Morris, 1982) [incl. checklist of prints]
- R. Walker: Regency Portraits, 2 vols, London N.P.G. cat. (London, 1986)
- O. Millar: The Victorian Pictures in the Collection of Her Majesty the Queen, 2 vols (Cambridge, 1992)
- B. Bryant: ‘Sir George Hayter’s Drawings at Duncombe Park: Family Ties and a “Melancholy Event”’, Apollo, cxxxv (1992), pp. 240–50 [incl. newly pubd letter of 1827]
Gallery
 Princess Victoria painted 1833
Princess Victoria painted 1833 Detail from State Portrait of Queen Victoria 1837
Detail from State Portrait of Queen Victoria 1837 State Portrait of Queen Victoria 1837
State Portrait of Queen Victoria 1837 Christening of the Prince of Wales in St.George's Chapel, Windsor 25 Jan 1842
Christening of the Prince of Wales in St.George's Chapel, Windsor 25 Jan 1842 Coronation of Queen Victoria 28 June 1838
Coronation of Queen Victoria 28 June 1838 Marriage of Victoria and Albert, 10 February 1840
Marriage of Victoria and Albert, 10 February 1840 Queen Victoria seated on the throne in the House of Lords 1838
Queen Victoria seated on the throne in the House of Lords 1838.jpg) Queen Victoria seated on the throne in the House of Lords 1838 (copy commissioned by Madamme Tussauds)
Queen Victoria seated on the throne in the House of Lords 1838 (copy commissioned by Madamme Tussauds) Queen Victoria taking the Coronation Oath
Queen Victoria taking the Coronation Oath The Trial of Queen Caroline in the House of Lords 1820 (188 portraits), completed 1823
The Trial of Queen Caroline in the House of Lords 1820 (188 portraits), completed 1823 Queen Caroline, wife of George IV during her trial 1820
Queen Caroline, wife of George IV during her trial 1820 The Trial of William Lord Russell in 1683, painted 1825
The Trial of William Lord Russell in 1683, painted 1825 The House of Commons sitting for the first time following the passing of the Reform Act 5 February 1833 (375 portraits)
The House of Commons sitting for the first time following the passing of the Reform Act 5 February 1833 (375 portraits) Robert Jenkinson, 2nd Earl of Liverpool and Prime Minister, 1823 (for Trial of Queen Caroline picture)
Robert Jenkinson, 2nd Earl of Liverpool and Prime Minister, 1823 (for Trial of Queen Caroline picture) General Thomas Graham, 1st Baron Lynedoch 1823
General Thomas Graham, 1st Baron Lynedoch 1823

 Duchess of Kent (mother of Queen Victoria), 1835
Duchess of Kent (mother of Queen Victoria), 1835 Antonio Canova painted in 1817
Antonio Canova painted in 1817%2C_Windsor_1837.jpg) Queen Louise of Belgium, Windsor 1837
Queen Louise of Belgium, Windsor 1837- Portrait of a young lady in an interior 1826
.jpeg) Portrait of a Lady, Naples 1828
Portrait of a Lady, Naples 1828 Lady Stuart de Rothesay and her daughters, Paris 1830
Lady Stuart de Rothesay and her daughters, Paris 1830 Lord Stuart de Rothesay, British Ambassador to France, Paris 1830
Lord Stuart de Rothesay, British Ambassador to France, Paris 1830 The Hon. Charlotte and The Hon. Louisa Stuart, daughters of Baron Stuart de Rothesay, Paris 1830
The Hon. Charlotte and The Hon. Louisa Stuart, daughters of Baron Stuart de Rothesay, Paris 1830_1830_(Paris).jpg) Charlotte, Countess de la Bourdonnaye (1795-1875) Paris 1830
Charlotte, Countess de la Bourdonnaye (1795-1875) Paris 1830 Saith Satoor and Ali Hassan Bey, 1831. Saith Satoor was the protégé of Prince Abbas Mirza, Crown Prince of Persia
Saith Satoor and Ali Hassan Bey, 1831. Saith Satoor was the protégé of Prince Abbas Mirza, Crown Prince of Persia0.jpg) Sofia Kiselyova, daughter of Count Stanislav Potocki 1831
Sofia Kiselyova, daughter of Count Stanislav Potocki 1831
_society_beauty_and_author_by_GH%2C_Chatsworth_Coll..jpg) The Hon. Mrs. Caroline Norton, society beauty and author, 1832
The Hon. Mrs. Caroline Norton, society beauty and author, 1832
 Charles Grey, 2nd Earl Grey Prime Minister 1830-1834
Charles Grey, 2nd Earl Grey Prime Minister 1830-1834 Lord Melbourne Prime Minister 1834, 1835-1841
Lord Melbourne Prime Minister 1834, 1835-1841 Robert Lawrence Pemberton of Bainbridge House with his mother
Robert Lawrence Pemberton of Bainbridge House with his mother Anne Elphinstone 1835
Anne Elphinstone 1835 Lady Elizabeth Harcourt, eldest daughter of 2nd Earl of Lucan and wife of George Harcourt
Lady Elizabeth Harcourt, eldest daughter of 2nd Earl of Lucan and wife of George Harcourt%2C_7th_Earl_of_Sandwich_as_a_Young_Man_Hinchingbrooke_House_1832_GH.jpg) John Montagu, 7th Earl of Sandwich (1811–1884), 7th Earl of Sandwich
John Montagu, 7th Earl of Sandwich (1811–1884), 7th Earl of Sandwich John Spencer, 3rd Earl Spencer (1782-1845)
John Spencer, 3rd Earl Spencer (1782-1845)
 Lady Louisa Stuart at the age of ninety-three, sketch in oils
Lady Louisa Stuart at the age of ninety-three, sketch in oils.jpg) John Russell, 6th Duke of Bedford (1766-1839)
John Russell, 6th Duke of Bedford (1766-1839) John Russell, 6th Duke of Bedford (1766-1839)
John Russell, 6th Duke of Bedford (1766-1839)
 Francis Baring, 1st Baron Northbrook (1833) for House of Commons picture
Francis Baring, 1st Baron Northbrook (1833) for House of Commons picture
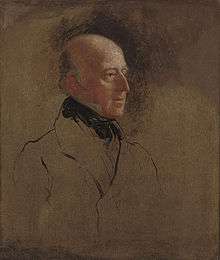 Admiral Sir Edward Codrington 1835
Admiral Sir Edward Codrington 1835

 Thomas Brunton in 1832 (inventor of studded-link, marine chain cable), friend of the artist
Thomas Brunton in 1832 (inventor of studded-link, marine chain cable), friend of the artist William Wilberforce (1759–1833)
William Wilberforce (1759–1833)_by_George_Hayter.jpg) The Duke of Wellington (1839), for the House of Commons picture
The Duke of Wellington (1839), for the House of Commons picture_by_Sir_George_Hayter.jpg)
 Rt Hon John Johnson, Lord Mayor of London 1845
Rt Hon John Johnson, Lord Mayor of London 1845 Sir James Robertson-Bruce 2nd Bt painted in 1820
Sir James Robertson-Bruce 2nd Bt painted in 1820 Mrs Ellen Robertson-Bruce painted in 1820
Mrs Ellen Robertson-Bruce painted in 1820 Portrait of a boy
Portrait of a boy The Angels Ministering to Christ, painted in 1849
The Angels Ministering to Christ, painted in 1849 Hemsted Park, three studies with trees and storm clouds, 1856
Hemsted Park, three studies with trees and storm clouds, 1856
| Court offices | ||
|---|---|---|
| Preceded by Sir David Wilkie |
Principal Painter in Ordinary to the Queen 1841–1871 |
Succeeded by James Sant |