List of geometers
"Geometer" redirects here. For the moth family, see geometer moth.

One of the oldest surviving fragments of Euclid's Elements, found at Oxyrhynchus and dated to circa AD 100 (P. Oxy. 29). The diagram accompanies Book II, Proposition 5.[1]
A geometer is a mathematician whose area of study is geometry.
Some important geometers and their main fields of work, chronologically listed are:
800 BC to 1 BC
Further information: History of geometry
 Pythagoras |
 Euclid |
 Archimedes | |
 Eratosthenes |
 Thales |
 Plato |
 Mozi |
- Baudhayana (fl. c. 800 BC) - Euclidean geometry, geometric algebra
- Manava (ca. 750 BC–690 BC) - Euclidean geometry
- Thales of Miletus (c. 624 BC–c. 546 BC) - Euclidean geometry
- Pythagoras (c. 570 BC–c. 495 BC) - Euclidean geometry, Pythagorean Theorem
- Zeno of Elea (ca. 490 BC–ca. 430 BC) - Euclidean geometry
- Hippocrates of Chios (born c. 470–died 410 BC) - first systematically organized Stoicheia Elements (geometry textbook)
- Mozi (ca. 470 BC–ca. 391 BC)
- Plato (427–347 BC)
- Theaetetus (c. 417 BC–369 BC)
- Autolycus of Pitane (360–c. 290 BC) - astronomy, spherical geometry
- Euclid (fl. 300 BC) - Elements, Euclidean geometry (sometimes called the "father of geometry")
- Apollonius of Perga (ca. 262 BC–ca. 190 BC) - Euclidean geometry, conic sections
- Archimedes (c. 287 BC–c. 212 BC) - Euclidean geometry
- Eratosthenes (c. 276 BC–c. 195/194 BC) - Euclidean geometry
- Katyayana (c. 3rd century BC) - Euclidean geometry
1–1400 AD
 Hero of Alexandria |
 Omar Khayyam |
 Vergilius of Salzburg |
 Abu'l-Wáfa |
 Ibn Maḍāʾ |
- Hero of Alexandria (c. AD 10–70) - Euclidean geometry
- Pappus of Alexandria (c. AD 290–c. 350) - Euclidean geometry, projective geometry
- Hypatia of Alexandria (c. AD 370–c. 415) - Euclidean geometry
- Brahmagupta (597–668) - Euclidean geometry, cyclic quadrilaterals
- Vergilius of Salzburg (c.700–784) - Irish bishop of Aghaboe, Ossory and later Salzburg, Austria; antipodes, and astronomy.
- Al-Abbās ibn Said al-Jawharī (c. 800–c. 860)
- Thabit ibn Qurra (826–901) - analytic geometry, non-Euclidean geometry, conic sections
- Abu'l-Wáfa (940–998) - spherical geometry, non-Euclidean geometry
- Alhazen (965–c. 1040)
- Omar Khayyam (1048–1131) - algebraic geometry, conic sections
- Ibn Maḍāʾ (1116–1196)
1401–1800 AD
 Leonardo da Vinci |
 Johannes Kepler |
 Girard Desargues |
 René Descartes |
 Blaise Pascal |
 Isaac Newton |
 Leonhard Euler |
 Carl Gauss |
 August Möbius |
 Nikolai Lobachevsky |
 John Playfair |
 Jakob Steiner |
- Piero della Francesca (1415–1492)
- Leonardo da Vinci (1452–1519) - Euclidean geometry
- Jyesthadeva (c. 1500–c. 1610) - Euclidean geometry, cyclic quadrilaterals
- Marin Getaldić (1568–1626)
- Johannes Kepler (1571–1630) - (used geometric ideas in astronomical work)
- Girard Desargues (1591–1661) - projective geometry; Desargues' theorem
- René Descartes (1596–1650)) - invented the methodology of analytic geometry, also called Cartesian geometry after him
- Blaise Pascal (1623–1662) - projective geometry
- Giordano Vitale (1633–1711)
- Philippe de La Hire (1640–1718) - projective geometry
- Isaac Newton (1642–1727) - 3rd-degree algebraic curve
- Giovanni Ceva (1647–1734) - Euclidean geometry
- Giovanni Gerolamo Saccheri (1667–1733) - non-Euclidean geometry
- Leonhard Euler (1707–1783)
- Tobias Mayer (1723–1762)
- Johann Heinrich Lambert (1728–1777) - non-Euclidean geometry
- Gaspard Monge (1746–1818) - descriptive geometry
- John Playfair (1748–1819) - Euclidean geometry
- Lazare Nicolas Marguerite Carnot (1753–1823) projective geometry
- Joseph Diaz Gergonne (1771–1859 ) projective geometry; Gergonne point
- Carl Friedrich Gauss (1777–1855) - Theorema Egregium
- Louis Poinsot (1777–1859)
- Siméon Denis Poisson (1781–1840)
- Jean-Victor Poncelet (1788–1867) - projective geometry
- August Ferdinand Möbius (1790–1868) - Euclidean geometry
- Nikolai Ivanovich Lobachevsky (1792–1856) - hyperbolic geometry, a non-Euclidean geometry
- Germinal Dandelin (1794–1847) - Dandelin spheres in conic sections
- Jakob Steiner (1796–1863) - champion of synthetic geometry methodology, projective geometry, Euclidean geometry
1801–1900 AD
 Julius Plücker |
 Arthur Cayley |
 Bernhard Riemann |
 Richard Dedekind |
Max Noether |
 Felix Klein |
 Henri Poincaré |
 Evgraf Fedorov |
 Alicia Boole Stott |
 Albert Einstein |
 Buckminster Fuller |
 M. C. Escher |
- Karl Wilhelm Feuerbach (1800–1834) - Euclidean geometry
- Julius Plücker (1801–1868)
- János Bolyai (1802–1860) - hyperbolic geometry, a non-Euclidean geometry
- Christian Heinrich von Nagel (1803–1882) - Euclidean geometry
- Johann Benedict Listing (1808–1882) - topology
- Ludwig Otto Hesse (1811-1874) - algebraic invariants and geometry
- Pierre Ossian Bonnet (1819–1892) - differential geometry
- Arthur Cayley (1821–1895)
- Delfino Codazzi (1824–1873) - differential geometry
- Bernhard Riemann (1826–1866) - elliptic geometry (a non-Euclidean geometry) and Riemannian geometry
- Julius Wilhelm Richard Dedekind (1831–1916)
- Ludwig Burmester (1840–1927) - theory of linkages
- Edmund Hess (1843–1903)
- Albert Victor Bäcklund (1845–1922)
- Max Noether (1844–1921) - algebraic geometry
- Henri Brocard (1845–1922) - Brocard points
- William Kingdon Clifford (1845–1879) - geometric algebra
- Pieter Hendrik Schoute (1846–1923)
- Felix Klein (1849–1925)
- Sofia Vasilyevna Kovalevskaya (1850–1891)
- Evgraf Fedorov (1853–1919)
- Henri Poincaré (1854–1912)
- Luigi Bianchi (1856–1928) - differential geometry
- Alicia Boole Stott (1860–1940)
- Hermann Minkowski (1864–1909) - non-Euclidean geometry
- Henry Frederick Baker (1866–1956) - algebraic geometry
- Élie Cartan (1869–1951)
- Dmitri Egorov (1869–1931) - differential geometry
- Veniamin Kagan (1869–1953)
- Raoul Bricard (1870–1944) - descriptive geometry
- Ernst Steinitz (1871–1928) - Steinitz's theorem
- Marcel Grossmann (1878–1936)
- Albert Einstein (1879–1955) - non-Euclidean geometry
- Oswald Veblen (1880–1960) - projective geometry, differential geometry
- Emmy Noether (1882–1935) - algebraic topology
- Harry Clinton Gossard (1884–1954)
- Arthur Rosenthal (1887–1959)
- Buckminster Fuller (1895–1983)
- Helmut Hasse (1898–1979) - algebraic geometry
- Maurits Cornelis Escher (1898–1972) - artist who used geometrical ideas extensively
1901–present
 H. S. M. Coxeter |
 Ernst Witt |
 Benoît Mandelbrot |
 Branko Grünbaum |
 Michael Atiyah |
.jpg) J. H. Conway |
 William Thurston |
 Mikhail Gromov |
 George W. Hart |
 Shing-Tung Yau |
 Károly Bezdek |
.jpg) Grigori Perelman |
- William Vallance Douglas Hodge (1903–1975)
- Patrick du Val (1903–1987)
- Beniamino Segre (1903–1977) - combinatorial geometry
- Samuel L. Greitzer (1905–1988) - founding chairman of USA Mathematical Olympiad
- J. C. P. Miller (1906–1981)
- André Weil (1906–1998) - Algebraic geometry
- H. S. M. Coxeter (1907–2003) - theory of polytopes, non-Euclidean geometry, projective geometry
- J. A. Todd (1908–1994)
- Daniel Pedoe (1910–1998)
- Shiing-Shen Chern (1911–2004) - differential geometry
- Ernst Witt (1911–1991)
- Rafael Artzy (1912–2006)
- Aleksandr Danilovich Aleksandrov (1912–1999)
- László Fejes Tóth (1915–2005)
- Edwin Evariste Moise (1918–1998)
- Aleksei Pogorelov (1919–2002) - differential geometry
- Magnus Wenninger (1919–) - polyhedron models
- Jean-Louis Koszul (1921–)
- Isaak Yaglom (1921–1988)
- Benoît Mandelbrot (1924–2010) - fractal geometry
- Katsumi Nomizu (1924–2008) - affine differential geometry
- Michael S. Longuet-Higgins (1925–2016)
- John Leech (mathematician) (1926–1992)
- Alexander Grothendieck (1928–2014) - algebraic geometry
- Branko Grünbaum (1929–) - discrete geometry
- Michael Atiyah (1929–)
- Geoffrey Colin Shephard (~1930–)
- Norman W. Johnson (1930–)
- John Milnor (1931–)
- Roger Penrose (1931–)
- Yuri Manin (1937–) - algebraic geometry and diophantine geometry
- Vladimir Arnold (1937–2010) - algebraic geometry
- Ernest Vinberg (1937–)
- J. H. Conway ( 1937–) - sphere packing, recreational geometry
- Robin Hartshorne (1938–) - geometry, algebraic geometry
- Phillip Griffiths (1938–) - algebraic geometry, differential geometry
- Enrico Bombieri (1940–) - algebraic geometry
- Robert Williams (geometer) (1942–)
- Peter McMullen (1942–)
- Richard S. Hamilton (1943–) - differential geometry, Ricci flow, Poincaré conjecture
- Mikhail Gromov (1943–)
- Roger Burrows (1945–) - applied close packing theory in education
- Rudy Rucker (1946–)
- William Thurston (1946–2012)
- Shing-Tung Yau (1949–)
- Michael Freedman (1951–)
- Egon Schulte (1955–) - polytopes
- George W. Hart (1955–) - sculptor
- Károly Bezdek (1955–) - Discrete geometry, sphere packing, Euclidean geometry, non-Euclidean geometry
- Simon Donaldson (1957–)
- Grigori Perelman (1966–) - Poincaré conjecture
- Maryam Mirzakhani (1977–)
Geometers in art
 God as architect of the world, 1220–1230, from Bible moralisée |
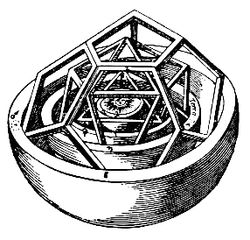 Kepler's Platonic solid model of planetary spacing in the Solar system from Mysterium Cosmographicum (1596) |
 The Ancient of Days, 1794, by William Blake,with the compass as a symbol for divine order |
 Newton (1795), by William Blake; here, Newton is depicted critically as a "divine geometer".[2] |
References
- ↑ Bill Casselman. "One of the Oldest Extant Diagrams from Euclid". University of British Columbia. Retrieved 2008-09-26.
- ↑ "Newton, object 1 (Butlin 306) "Newton"". William Blake Archive. September 25, 2013.
This article is issued from Wikipedia - version of the 12/2/2016. The text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution/Share Alike but additional terms may apply for the media files.