Field cricket
| Field cricket | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Common black cricket, Gryllus assimilis | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Arthropoda |
| Class: | Insecta |
| Order: | Orthoptera |
| Suborder: | Ensifera |
| Family: | Gryllidae |
| Subfamily: | Gryllinae Saussure, 1893 |
| Genera | |
| |
Field crickets are insects of order Orthoptera. These crickets are in subfamily Gryllinae of family Gryllidae.
They hatch in spring, and the young crickets (called nymphs) eat and grow rapidly. They shed their skin (molt) eight or more times before they become adults.
Field crickets eat a broad range of feeds: seeds, plants, or insects (dead or alive). They are known to feed on grasshopper eggs, pupae of Lepidoptera (moths and butterflies) and Diptera (flies). Occasionally they may rob spiders of their prey. Field crickets also eat grass.
"Field cricket" is a common name for Gryllus assimilis, G. bimaculatus, G. campestris, G. firmus, G. pennsylvanicus, G. rubens, and G. texensis, along with other members of various genera including Acheta, Gryllodes, Gryllus, and Teleogryllus.
Acheta domesticus, the House cricket, and Gryllus bimaculatus are raised in captivity for use as live food for exotic pets.
Identification
Field crickets are normally 15–25 millimetres (0.6–1.0 in) in size, depending on the species, and can be black, red or brown in color.[1] While both males and females have very similar basic body plans, each has its own distinguishing feature(s).
Females can be identified by the presence of an ovipositor, a spike-like appendage, about 0.75 inches (19 mm) long, on the hind end of the abdomen between two cerci. This ovipositor allows the female to bury her fertilized eggs into the ground for protection and development. In some female field crickets, species can be distinguished by comparing the length of the ovipositor to the length of the body (i.e. G. rubens has a longer ovipositor than G.texensis[2]).
Males are distinguished from females by the absence of an ovipositor. At the end of the abdomen there are simply two cerci. Unlike females, however, males are able to produce sounds or chirps. Thus, males can be identified through sound while females cannot.
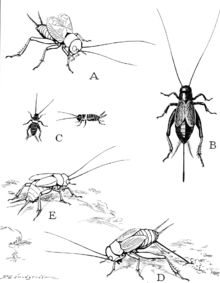
Diagram A shows the male cricket with its wings raised for the purpose of chirping. Diagram B shows the female cricket, identified via the long protruding ovipositor at the end of the abdomen. D and E show the female using the ovipositor to deposit the fertilized eggs into the ground. Diagram C shows a topical and side view of nymphs with no protrusion at the hind of the abdomen.
Behavior
In mid to late summer, males begin chirping. The acoustical properties of their calling song provide an indication of past and present health. Females evaluate each song and move towards the one they prefer. When the male senses a female is near, he will produce a softer courting song. After mating, the female will search for a place to lay her eggs, preferably in warm, damp soil.
Field crickets prefer to live outdoors, but will move inside when environmental conditions become unfavorable. Their method of entry into buildings include open doors and windows as well as cracks in poorly fitted windows, foundations, or siding.
Unlike House crickets, which can adapt themselves to indoor conditions, the field cricket will die by early winter. Consequently, field crickets in temperate regions exhibit diapause.
Tribes and genera
Subfamily has the following 7 tribes and 30 genera, not placed within those tribes:[3]
|
Tribe Cephalogryllini Otte & Alexander, 1983
Tribe Cophogryllini Ichikawa, Murai & Honda, 2000
Tribe Eurygryllodini Gorochov, 1990
Tribe Gryllini Laicharting, 1781
|
Tribe Modicogryllini Otte & Alexander, 1983
|
Tribe Sciobiini Randell, 1964
Tribe Turanogryllini Otte, 1987
Genera Incertae sedis
|
References
- ↑ "Field Cricket". InsectIdentification.org. 2005. Retrieved January 15, 2009.
- ↑ Gray, D.A.,Walker, T.J.,Conley, B.E., Cade, W.H. 2001. "A Morphological Means of Distinguishing Females of the Cryptic Field Cricket Species, Gryllus Rubens and G. Texensis (Orthoptera: Gryllidae)". Florida Entomologist, 84:314-315
- ↑ "Subfamily Gryllinae Laicharting, 1781". Orthoptera Species File. Retrieved 11 June 2015.