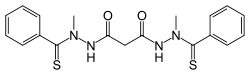
Elesclomol
 | |
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| ATC code | none |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number |
488832-69-5 |
| PubChem (CID) | 300471 |
| ChemSpider |
265501 |
| UNII |
6UK191M53P |
| ChEBI |
CHEBI:79369 |
| ChEMBL |
CHEMBL1972860 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C19H20N4O2S2 |
| Molar mass | 400.518 g/mol |
| |
| | |
Elesclomol (INN, codenamed STA-4783) is a drug that triggers apoptosis (programmed cell death) in cancer cells. It is being developed by Synta Pharmaceuticals and GlaxoSmithKline as a chemotherapy adjuvant, and has received both fast track and orphan drug status from the U.S. Food and Drug Administration for the treatment of metastatic melanoma.[1] Synta Pharmaceuticals announced on February 26, 2009 the suspension of all clinical trials involving Elesclomol due to safety concerns.[2] In March 2010, Synta announced that the FDA had approved resuming clinical development of elesclomol, and that they expected to initiate one or more clinical trials for elesclomol in the second half of the year.[3]
In a small, randomized phase II study, elesclomol was shown to significantly increase progression-free survival in people with metastatic melanoma when given in addition to paclitaxel (Taxol).[4][5]
Mechanism of action
Elesclomol induces oxidative stress by provoking a buildup of reactive oxygen species within cancer cells.[6] Elesclomol requires a redox active metal ion to function. The Cu(II) complex is 34 times more potent than the Ni(II) complex and 1040-fold more potent than the Pt(II) complex.[7]
Discovery
Elesclomol was first synthesized at Shinogi BioResearch in Lexington, MA. It's efficiency against cancer was discovered by scientists at Shionogi BioResearch. “It was pure chemist’s joy,” Synta's Chen said. “Homemade, random, and clearly made for no particular purpose. It was the only one that worked on everything we tried.”[8]
References
- ↑ "Synta And GlaxoSmithKline Announce Elesclomol Granted Orphan Drug Designation By The FDA" (Press release). Medical News Today. January 30, 2008. Retrieved November 30, 2008.
- ↑ "Synta Pharmaceuticals press release". February 26, 2009.
- ↑ "Synta Announces Elesclomol Clinical Development to Resume". March 2, 2010.
- ↑ "Prous Science Molecule of the Month: Elesclomol". Thomson Reuters. December 2007. Retrieved November 30, 2008.
- ↑ Qu Y, Wang J, Sim MS, et al. (June 2010). "Elesclomol, counteracted by Akt survival signaling, enhances the apoptotic effect of chemotherapy drugs in breast cancer cells". Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 121 (2): 311–21. doi:10.1007/s10549-009-0470-6. PMID 19609669.
- ↑ Kirshner JR, He S, Balasubramanyam V, et al. (August 2008). "Elesclomol induces cancer cell apoptosis through oxidative stress". Mol Cancer Ther. 7 (8): 2319–27. doi:10.1158/1535-7163.MCT-08-0298. PMID 18723479.
- ↑ Yadav AA, Patel D, Hasinoff BB (Sep 2013). "Molecular mechanisms of the biological activity of the anticancer drug elesclomol and its complexes with Cu(II), Ni(II) and Pt(II)". J Inorg Biochem. 126: 1–6. doi:10.1016/j.jinorgbio.2013.04.013. PMID 23707906.
- ↑ "The Treatment - Why is it so difficult to develop drugs for cancer?". The New Yorker. May 17, 2010. Retrieved September 13, 2014.