Electrical capacitance tomography
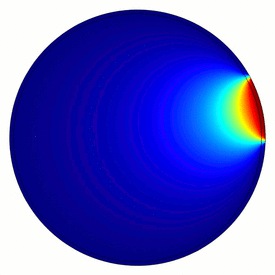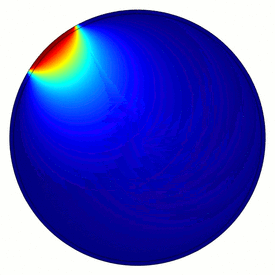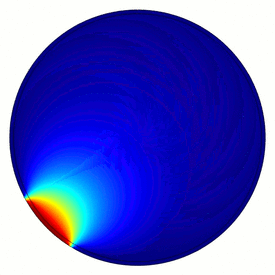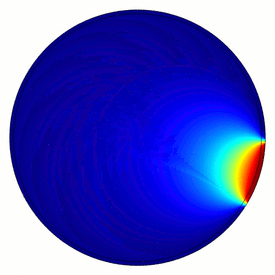
Electrical capacitance tomography (ECT) is a method for determination of the dielectric permittivity distribution in the interior of an object from external capacitance measurements. It is a close relative of electrical impedance tomography[1] and is proposed as a method for industrial process monitoring, although it has yet to see widespread use. Potential applications include the measurement of flow of fluids in pipes [2] and measurement of the concentration of one fluid in another, or the distribution of a solid in a fluid.
Although capacitance sensing methods were in widespread use the idea of using capacitance measurement to form images is attributed to Maurice Beck and co-workers at UMIST in the 1980s.[3]
Although usually called tomography, the technique differs from conventional tomographic methods, in which high resolution images are formed of slices of a material. The measurement electrodes, which are metallic plates, must be sufficiently large to give a measureable change in capacitance. This means that very few electrodes are used and eight or twelve electrodes is common. An N-electrode system can only provide N(N−1)/2 independent measurements. This means that the technique is limited to producing very low resolution images of approximate slices. However, ECT is fast, and relatively inexpensive.
References
- ↑ M Soleimani, W R B Lionheart, Nonlinear image reconstruction in electrical capacitance tomography using experimental data, Meas. Sci. Technol., 16, 2005, pp 1987–1996
- ↑ Jaworski AJ and Dyakowski T, Application of electrical capacitance tomography for measurement of gas–solid flow characteristics in a pneumatic conveying system, Measurement Science and Technology, 12, 2001, pp 1109–19
- ↑ S M Huang, A Plaskowski, C G Xie and M S Beck, Capacitance-based tomographic flow imaging system, Electronics Letters, 24 (7), 1988, pp 418–19.