Cyanase
| cyanase | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
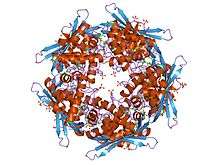 Structure of the cyanase from E. coli with the di-anion oxalate bound at the enzyme active site | |||||||||
| Identifiers | |||||||||
| EC number | 4.2.1.104 | ||||||||
| CAS number | 37289-24-0 | ||||||||
| Databases | |||||||||
| IntEnz | IntEnz view | ||||||||
| BRENDA | BRENDA entry | ||||||||
| ExPASy | NiceZyme view | ||||||||
| KEGG | KEGG entry | ||||||||
| MetaCyc | metabolic pathway | ||||||||
| PRIAM | profile | ||||||||
| PDB structures | RCSB PDB PDBe PDBsum | ||||||||
| Gene Ontology | AmiGO / EGO | ||||||||
| |||||||||
| Cyanate lyase, C-terminal domain | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Identifiers | |||||||||
| Symbol | Cyanate_lyase | ||||||||
| Pfam | PF02560 | ||||||||
| InterPro | IPR003712 | ||||||||
| SCOP | 1dw9 | ||||||||
| SUPERFAMILY | 1dw9 | ||||||||
| CDD | cd00559 | ||||||||
| |||||||||
In molecular biology, cyanase (EC 4.2.1.104, also known as cyanate hydratase or cyanate lyase) is an enzyme which catalyses the reaction of cyanate with bicarbonate to produce ammonia and carbon dioxide. The systematic name of this enzyme is carbamate hydro-lyase.
Reaction
Cyanase catalyzes the conversion of cyanate to carbamate (H2NCOO−), which then spontaneously decomposes to carbon dioxide and ammonia:[1]
- cyanate (OCN−) + HCO3− + H+ carbamate (H2NCOO−) + CO2
- carbamate (H2NCOO−) + H+ NH3 + CO2 (spontaneous)
The resulting net reaction is:
- cyanate (OCN−) + HCO3− + 2 H+ NH3 + 2 CO2
Function and structure
Some bacteria can overcome the toxicity of environmental cyanate by degrading it via this enzyme.[2] Cyanate hydratase is found in bacteria and plants. The cyanate hydratase monomer is composed of two domains. The N-terminal domain shows structural similarity to the DNA-binding alpha-helix bundle motif. The C-terminal domain has an 'open fold' with no structural homology to other proteins. The dimer structure reveals the C-terminal domains to be intertwined, and a decamer is formed by a pentamer of these dimers. The active site of the enzyme is located between dimers and is composed of residues from four adjacent subunits of the homodecamer.[3]
References
- ↑ "IUBMB Enzyme Nomenclature: EC 4.2.1.104".
- ↑ Sung YC, Fuchs JA (October 1988). "Characterization of the cyn operon in Escherichia coli K12". J. Biol. Chem. 263 (29): 14769–75. PMID 3049588.
- ↑ Walsh MA, Otwinowski Z, Perrakis A, Anderson PM, Joachimiak A (May 2000). "Structure of cyanase reveals that a novel dimeric and decameric arrangement of subunits is required for formation of the enzyme active site". Structure. 8 (5): 505–14. doi:10.1016/S0969-2126(00)00134-9. PMC 3366510
 . PMID 10801492.
. PMID 10801492.
This article incorporates text from the public domain Pfam and InterPro IPR003712