Doug Ring with the Australian cricket team in England in 1948
| Personal information | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Full name | Douglas Thomas Ring | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Born |
14 October 1918 Hobart, Tasmania, Australia | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Died |
23 June 2003 (aged 84) Melbourne, Victoria, Australia | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Height | 1.83 m (6 ft 0 in) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Batting style | Right-hand | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Bowling style | leg spin | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Role | Specialist bowler, lower order batsman | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| International matches on tour | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| National side | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Test debut | 14 August 1948 v England | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Last Test | 14 August 1948 v England | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Tour statistics | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Source: [1][2], 12 December 2007 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Doug Ring was a member of Donald Bradman's famous Australian cricket team which toured England in 1948. Bradman's men went undefeated in their 34 matches; this unprecedented feat by a Test side touring England earned them the sobriquet The Invincibles.
A leg spinner, Ring was not prominent in the team's success. Regarded as the last bowler to be selected for the team, Ring played in only the Fifth Test, taking one wicket for 44 runs (1/44) for the match and scoring nine runs in his only innings after replacing off spinner Ian Johnson, who was dropped for poor form. Along with Ron Hamence and Colin McCool, neither of whom played in a Test during the tour, Ring called himself "ground staff" because of the paucity of the trio's on-field duties in the major matches and they often sang ironic songs about their status.
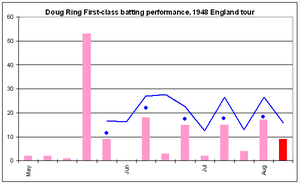
For the entire tour, Ring took 60 first-class wickets at a bowling average of 21.81, the most expensive among Australia's frontline bowlers. As England agreed to have a new ball available 55 overs after the start of each innings in the Tests—more frequently than usual—fast bowling dominated over spin, and Ring was used primarily in the non-Test tour matches. Outside the Tests, only Bill Johnston bowled more overs, and Ring was used to relieve the workload on Bradman's pace spearheads to keep them fresh for the Tests. Ring scored 150 first-class runs at a batting average of 16.66 during the tour, and a top-score of 53 was his only effort beyond 50.
Background
Ring made his Test debut in last international match of the 1947–48 Australian season, the Fifth Test against India. Australia rested a few of its players and some fringe cricketers such as Ring and Sam Loxton were given a debut so that their ability could be evaluated before the tour of England. Ring took six wickets for the match and was selected for the tour along with Loxton, who scored 80.[3]
Early tour
Australia traditionally fielded its first-choice team in the tour opener, which was customarily against Worcestershire.[4] Ring was omitted from this match, despite having replaced Colin McCool to make his Test debut in the fifth and final match against India in Australia during the 1947–48 season that preceded the tour of England; Ring had taken six wickets for 120 runs (6/120).[5] Fellow leg spinner McCool and off spinner Ian Johnson—who had been regular Test players since World War II—were the two slow bowlers picked as Australia started their campaign with an innings victory.[6]
Ring was called into the team for the second tour match against Leicestershire. He made two runs with the bat before being run out as Australia ended on 448. Ring took two top order wickets to leave the hosts at 3/56 before returning to take three late wickets as Leicestershire lost their last four wickets without addition to be all out for 130. Ring ended with 5/45.[7] Made to follow on, Leicestershire scored 147 and lost by an innings. Ring failed to add to his wicket tally in the county's second innings, conceding 26 runs.[7] Ring was rested for the next match against Yorkshire, on a damp pitch that suited slower bowling. It was the closest Australia came to defeat on the tour, as they scraped home by four wickets in a low scoring affair.[1][8][9] The Australians travelled to London to play Surrey at The Oval, and Ring made two in the tourists' 632. He then took 3/34 in the first innings, removing Arthur McIntyre, Alec Bedser and Jim Laker. He bowled five wicketless overs in the second innings as Surrey were defeated by an innings.[10] Ring then took 1/18 and 0/52 from a total of 44 overs as Australia amassed 4/414 declared and defeated Cambridge University by an innings.[1]
In the following match, Australia crushed Essex by an innings and 451 runs, its largest winning margin for the summer.[9] On the first day, Australia set a world record by scoring 721, the most first-class runs made in a single day's play,[11] but Ring was unable to contribute to the surfeit of scoring, making only one. He bowled 18 overs and conceded a total of 35 runs without success as the hosts were bowled out for 83 and 187.[1] This was followed by another innings victory, this time over Oxford University. After having failed to score more than two runs in any of his first three innings of the tour, Ring came to the wicket at 7/317 and scored 53, adding 87 runs in partnership with fellow Victorian Sam Loxton before being bowled. After Australia were out for 431, Ring took a match total of 1/51, removing Geoffrey Keighley as the hosts made 185 and 156.[12]
The next match was against the Marylebone Cricket Club at Lord's. The MCC fielded seven players who would represent England in the Tests,N-[1] and were basically a full strength Test team, while Australia fielded their first-choice team. It was a chance for both teams to gain a psychological advantage. At this point of the tour, Ring had only taken ten wickets at an average of 28.30,[1] while McCool had taken 17 at 14.35. McCool retained the first-choice leg spinner's position and took 4/35 as Australia won by an innings.[9][13]
Ring was rested for Australia'a first non-victory of the tour, a rain-affected draw against Lancashire.[14] He returned for the match against Nottinghamshire at Trent Bridge, which was also drawn.[1][9] Ring took 2/31 in the first innings, both of his victims being stumped, as the hosts made 179, before making an unbeaten nine in Australia's reply of 400. He then shouldered the heaviest workload as Nottinghamshire made 8/299 in the second innings, the highest score against the Australians thus far on the tour. Ring bowled 43 overs and took 4/104. He removed Joe Hardstaff junior, who had made the first century against Australia for the season,[15] triggering a collapse that saw the loss of four wickets for 27 runs to leave the hosts at 8/289. He also dismissed future Test batsman Reg Simpson for 70. The hosts were 32 runs short of making Australia bat again, but held on for a draw as time ran out.[16]
Against Hampshire,[1][9] Ring took 1/19 as the home team made 195 after being put into bat on a drying pitch.[17][18] He made a duck as Australia collapsed to 117 to trail by 78 runs, the first time the tourists had conceded a first innings lead during the English summer.[1][18] Ring was not required to bat in the Australian second innings, as Hampshire were bowled out for 103 in 42.5 overs and Australia then reached their target of 182 to win by eight wickets.[17] Ring had a final chance to push for Test selection in the innings win over Sussex, the last match before the First Test. He bowled only two wicketless overs as the pacemen skittled the hosts for 86, and did not bat as Australia amassed 5/549 declared. He then took three consecutive wickets as Sussex fell from 5/98 to 8/109 before eventually being bowled out for 138. Ring ended with 3/42 from 13 overs.[9]
Test omission
Ring's performances were not enough for him to take McCool's place in Bradman's first-choice team.[19] Instead, Bill Johnston, who had taken 10/40 against Yorkshire and 11/117 against Hampshire on damp surfaces,[19] was given the place on the opening morning of the First Test when rain appeared likely.[4][19][20] Johnston then took nine wickets in Australia's victory, cementing his position in the team.[19] This left Ring jostling with the other spinners—Johnson and McCool—for one spot in the Test team.
After the First Test, Ring returned to action as Australia completed an innings victory over Northamptonshire. He took 1/31 in the hosts' first innings of 119, before making an unbeaten 16 in partnering McCool in an unbroken stand of 39 as Australia declared at 8/352. In the second innings, he took four of the last five wickets and ended with 4/31 as Northamptonshire collapsed from 5/142 to be all out for 169.[21] This was followed by a drawn match against Yorkshire, in which Ring scored three runs and was not asked to bowl in the first innings. Yorkshire were bowled out for 206 from 90.1 overs; Bradman called on Ernie Toshack and Johnston to bowl 81.1 overs and did not entrust the other bowlers with substantial work.[22] Ring then took 1/22 in the second innings as the match petered out into a draw.[1][22]
Ring was overlooked for the Second Test at Lord's as Bradman retained the same XI, despite the incumbent spinner Johnson managing only 1/85 in the First Test. Australia won convincingly by 409 runs.[19][23] The next match was against Surrey, starting the day after the finish of the Test. Ring took 3/51 from 21.2 overs in the first innings, leading the way in terms of wickets and overs; most of the Test bowlers were given a light workload. He then contributed an unbeaten 15 in Australia's first innings of 389. After Australia took a first innings lead of 168, Ring bowled another 24 overs in the second innings and took 1/54. He twice dismissed Jack Parker, who had top-scored in each innings with 76 and 81. Australia then chased down the 122 runs for victory in less than an hour, to complete a 10-wicket win.[1][9][24]
In the match against Gloucestershire immediately before the Third Test,[9][25] Ring did not bat as Australia reached 7/774 declared, which was their highest score of the tour and which underpinned an innings victory. Ring took two wickets in the space of three runs, including Test batsman Charlie Barnett, to end with 2/83 in 25 overs as the hosts made 279. After stand-in captain Lindsay Hassett enforced the follow on—Bradman had rested himself—Ring removed Test batsmen Barnett and George Emmett to leave Gloucestershire at 2/20. After resting he resumed bowling with the score at 4/93 and took three more wickets, as the hosts fell to 9/109 and then 132 all out. Ring took 5/47 and bowled the most overs (25) in the second innings. Johnson, however, took 11/100 in the match and retained his place in the team for the Third Test at Old Trafford.[25][26] The Test was drawn amid inclement weather.[9][23][27]
Ring then played against Middlesex in Australia's only match before the Fourth Test. He took one wicket in each innings for a match total of 2/57. After only scoring two in the first innings, Ring opened the batting with McCool in the second innings, with a target of only 22 runs. They promptly reached the target without loss, with Ring unbeaten on 15.[1][9][28] This was not enough for Ring to force his way into the team for the Fourth Test at Headingley. Australia persisted with the same bowling attack and posted 3/404 in the second innings, setting a world record for the highest successful run-chase to win a Test.[27][29][30] Former Australian Test leg spinner Bill O'Reilly criticised the Australians for using only one spinner, pointing out that he and Chuck Fleetwood-Smith, a left-arm wrist spinner, had taken 17 wickets between them during the last Anglo-Australian Test at Headingley in 1938.[31] O'Reilly cited the 1934 Headingley Test the same venue in 1934 in which he and Clarrie Grimmett had significant success for Australia, and said that at least one of McCool or Ring, should have played alongside Johnson.[31] England had been at 2/423 in their first innings, before collapsing to be 496 all out;[29] O'Reilly blamed Australia's lack of early success on the absence of a leg spinner, attributing England's collapse to inept batting.[32]
Immediately after the Headingley Test, Ring scored four as Australia amassed 456 against Derbyshire. He bowled the most overs in the first innings, taking 3/73 from 24 overs as the hosts made 240. He then took 0/23 from six overs after Australia enforced the follow on and ultimately won the match by an innings.[9][33] In the next match against Glamorgan, Ring led the bowling with 3/34, including the wicket of opposition captain Wilf Wooller as the hosts folded for 197. Ring did not bat, as rain ended the match early, with Australia's score at 3/215.[1][9][34] Ring was then rested for the match against Warwickshire, which Australia won by nine wickets.[1][9]
Bradman recalled Ring as Australia faced and drew with Lancashire for the second time on the tour. Ring scored 17 not out as Australia made 321; he then dismissed Test players Ken Cranston (who was captaining Lancashire) and Dick Pollard, to end with 2/25 in the first innings. In the county's second innings Ring bowled 22 of the 57 overs during which Australia reduced Lancashire to 7/199 before time ran out. He took 2/88, including the wicket of Cranston for the second time.[9][14] In a non-first-class match against Durham, the last fixture before the Fifth Test, Ring made an unbeaten single as Australia scored 282. He then took 1/24 as the hosts fell to 5/73 in their first innings, before rain washed out the match.[9][35]
Fifth Test
After taking only seven wickets at 61.00 in the first four Tests, Johnson was dropped for the Fifth Test at The Oval;[36] Ring replaced him as the team's spinner.[37] English skipper Norman Yardley won the toss and elected to bat on a rain-affected pitch, which was regarded as a surprising move by the majority of the press corps. Precipitation in the previous week caused an extremely wet outfield, which meant that the Test could not start until midday had passed.[38][39] Former Australian Test batsman Jack Fingleton speculated that the Australians would have bowled if they had won the toss.[38]
Along with the effects of the rain on the pitch, the humid conditions assisted the Australian fast bowlers, who were able to make the ball bounce at variable heights.[39] Led by Lindwall, who took 6/20, Australia skittled England for 52, and Ring did not get a chance to bowl. Ring then made nine before being caught by Jack Crapp in the slips as Australia replied with 389.[37][40] England started their second innings 337 runs in arrears late on day two and resumed at 1/54 the next morning.[37] During the first session, Ring bowled a tidy spell of 13 overs as Denis Compton and Len Hutton added only 67 runs for the session.[41] Ring did not bowl consistently or accurately, and although the batsman hit him regularly, they did not place their shots, which often went to the fielders.[42] There were four men in the off side ring and they had much work to do as Hutton hit the ball there repeatedly.[43] The English batsmen progressed steadily although Ring had one confident appeal for lbw against Compton.[44] Later in the day, Ring dismissed debutant Allan Watkins for two to take his only wicket of the match.[37] Watkins lofted a delivery from Ring to the leg side straight into the hands of Hassett, who did not need to move from his position on the boundary,[41] leaving England at 6/167. The hosts were eventually bowled out early on the fourth morning for 188, sealing defeat by an innings and 149 runs. Ring had taken 1/44 after sending down the most overs in the innings (28), including 13 maidens.[37][39]
Later tour matches
After the Fifth Test seven matches remained on Bradman's quest to go through a tour of England without defeat.[9] Australia rested Ring for the match against Kent, which Australia won by an innings.[45] This was followed by a game against the Gentlemen of England, the leading amateurs in the country. Ring was not required to bat as Australia amassed 5/610 before declaring. He then bowled the most overs in the first innings, sending down 25.3 and taking the wickets of English Test batsmen Bill Edrich, Trevor Bailey and Freddie Brown. Ring ended with 3/74 as the hosts were bowled out for 245. Australia enforced the follow on and Ring again shouldered the heaviest workload. He removed Reg Simpson to break the opening stand of 60. The Gentlemen progressed to 3/217 before Ring dismissed Edrich for 128, followed by George Mann for a duck without further addition to the score. Ring then bowled Yardley and dismissed Wilf Wooller soon after, leaving the hosts at 7/240; they were eventually all out for 284, which sealed an innings victory for Australia. Ring ended with 5/70 from 32 overs.[9][46] The following match against Somerset followed a similar pattern. Ring did not bat as Australia declared at 5/560. He then took 2/17 in the first innings and was not required to bowl in the second innings as the hosts collapsed for 115 and 71 to cede another innings victory.[1][9][47][48]
Ring was rested for the match against the South of England. Australia declared at 7/522 before the hosts made 298; rain ended the match before the second innings could start.[1][49] Australia's biggest challenge in the post-Test tour matches was against the Leveson-Gower's XI. During the previous Australian tour of England in 1938, this team was effectively a full-strength England outfit, but this time Bradman insisted that only six current England Test players be allowed to play for the hosts.[50][51] Bradman then fielded a full-strength team.[50] He made only one change from the team that won the Fifth Test, dropping Ring for Johnson. Australia led by 312 runs on the first innings before persistent rain ended the match.[37][52]
The tour ended with two non-first-class matches against Scotland. In the first, Ring made an unbeaten three as Australia scored 236. He bowled five overs without success in the first innings, before removing four of the first five batsmen in the second innings and ending with 4/20.[53] Scotland made 85 and 111 to lose by an innings.[1][9] In the second match, Ring was the costliest bowler in the first innings, conceding 42 runs without success in Scotland's 178. After Australia declared at 6/407, Ring took the leading figures of 4/30, including the wickets of both openers as Australia ended the tour with another innings triumph.[1][53]
Role
Although the 1948 tour of England was an unprecedented triumph for the Australians, Ring's leg spin was not prominent in the success. He jostled with McCool and Johnson for a position as Bradman selected only one specialist spinner in the Tests.[19][23][27][29][37] Headlined by Lindwall, Miller and Johnston, the faster bowlers dominated the bowling attack.[54] With a new ball allowed at intervals of 55 overs in Tests, a period that usually elapsed sooner than the 200 runs stipulated under the usual rule of the time, spinners were given few opportunities and made little impact in the big matches. Bradman and his fellow tour selectors—vice-captain Lindsay Hassett and Arthur Morris—picked a pace-dominated attack to exploit the more frequently shiny ball, as a new ball swings and seams more for fast bowlers, while slower bowlers can impart more spin with a worn ball.[55] In its summary of the tour, Wisden said that Ring "was never a trump card in the pack".[56] Such was the strength of the bowling that Ring's 60 first-class wickets at an average of 21.81 made him the most expensive of the regular bowlers on the tour.[57] Among the seven frontline bowlers, Ring's strike rate of 54.26 was the second least incisive and his economy rate of 40.20 was the second most expensive. Although McCool was less economical, he had the second highest strike rate, and while Toshack had the worst strike rate, he was the second most economical of the Australians in the first-class fixtures.[2]
Ring did most of his work in the non-Test first-class matches, in which he sent down 3,088 deliveries. This was second only to Johnston, who bowled 3,251. In contrast, Lindwall and Miller sent down only 2,105 and 1,749 deliveries outside the Tests respectively, as Bradman sought to preserve them for hostile bursts with the new ball against England.[2][54] Along with Lindwall, Ring was the equal third highest wicket-taker in first-class matches excluding the Tests, with 59 scalps, doing a large part of the work in the county matches so that the leading bowlers could conserve energy for the Tests.[58]
Ring had limited opportunities with the bat. Along with Toshack and Johnston, he invariably batted in the bottom three positions.N-[2] This was because Australia's other frontline bowlers tended to be capable with the bat; Lindwall, Miller, and McCool all made Test centuries and more than nine triple-figure first-class scores, with the latter pair averaging over 30 in Tests. Johnson passed fifty on 21 occasions in his first-class career, six of them in Tests.[59] The strength of the batting side meant that Ring batted only 14 times in his 19 first-class matches on the tour, as Australia often batted only once and won by an innings, and several times declared their first innings closed before Ring could bat.[1][2][9] Ring scored 150 runs at 16.66, an aggregate and average better than only Toshack's. He passed 50 only once, and his tour batting average was lower than his career benchmark of 23.25.[60] Ring also took 12 catches.[2]
Ring and fellow fringe members of the squad McCool and Ron Hamence, would refer themselves as the "ground-staff", as it was unlikely that the tour selectors would include them in the Test team during the tour.[61][62] The trio were known to sing ironic songs about the paucity of their on-field duties during the tour.[63]
Notes
Statistical notes
n-[1]
a
This statement can be verified by consulting the scorecards for the Tests and MCC match, as listed here.[19][20][23][27][29][37]
n-[2]
a
This statement can be verified by consulting all of the scorecards for the matches, as listed here.[6][7][10][12][14][16][17][19][20][21][22][23][24][25][27][28][29][33][34][35][37][45][48][52][53][64][65][66][67][68][69][70][71][72]
General notes
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 "Player Oracle DT Ring 1948". CricketArchive. Retrieved 2008-12-18.
- 1 2 3 4 5 "Batting and bowling averages Australia tour of England, Apr-Sep 1948 - First-class matches". Cricinfo. Retrieved 2008-12-10.
- ↑ Piesse, pp. 156, 335.
- 1 2 Haigh, Gideon (2007-05-26). "Gentrifying the game". Cricinfo. Retrieved 2007-06-01.
- ↑ "Australia v India". CricketArchive. Retrieved 2008-09-29.
- 1 2 "Worcestershire v Australians". CricketArchive. Retrieved 2008-12-18.
- 1 2 3 "Leicestershire v Australians". CricketArchive. Retrieved 2008-12-18.
- ↑ Fingleton, pp. 53–55.
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 "Matches, Australia tour of England, Apr-Sep 1948". Cricinfo. Retrieved 2008-07-16.
- 1 2 "Surrey v Australians". CricketArchive. Retrieved 2008-12-18.
- ↑ "Australians in England, 1948". Wisden Cricketers' Almanack (1949 ed.). Wisden. pp. 221–222.
- 1 2 "Oxford University v Australians". CricketArchive. Retrieved 2008-12-18.
- ↑ "Player Oracle CL McCool 1948". CricketArchive. Retrieved 2008-12-18.
- 1 2 3 "Lancashire v Australians". CricketArchive. Retrieved 2008-12-18.
- ↑ "Australians in England, 1948". Wisden Cricketers' Almanack (1949 ed.). Wisden. pp. 225–226.
- 1 2 "Nottinghamshire v Australians". CricketArchive. Retrieved 2008-12-18.
- 1 2 3 "Hampshire v Australians". CricketArchive. Retrieved 2008-12-18.
- 1 2 "Australians in England, 1948". Wisden Cricketers' Almanack (1949 ed.). Wisden. pp. 226–227.
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 "1st Test England v Australia at Nottingham Jun 10–15 1948". Cricinfo. Retrieved 2007-12-12.
- 1 2 3 "MCC v Australians". CricketArchive. Retrieved 2008-12-18.
- 1 2 "Northamptonshire v Australians". CricketArchive. Retrieved 2008-12-18.
- 1 2 3 "Yorkshire v Australians". CricketArchive. Retrieved 2008-12-18.
- 1 2 3 4 5 "2nd Test England v Australia at Lord's Jun 24–29 1948". Cricinfo. Retrieved 2007-12-12.
- 1 2 "Surrey v Australians". CricketArchive. Retrieved 2008-12-18.
- 1 2 3 "Gloucestershire v Australians". CricketArchive. Retrieved 2007-12-26.
- ↑ Perry, p. 176.
- 1 2 3 4 5 "3rd Test England v Australia at Manchester Jul 8-13 1948". Cricinfo. Retrieved 2007-12-12.
- 1 2 "Middlesex v Australians". CricketArchive. Retrieved 2008-12-18.
- 1 2 3 4 5 "4th Test England v Australia at Leeds Jul 22-27 1948". Cricinfo. Retrieved 2007-12-12.
- ↑ "Fourth Test Match England v Australia". Wisden Cricketers' Almanack. Wisden. 1949. Retrieved 2008-07-02.
- 1 2 O'Reilly, p. 110.
- ↑ O'Reilly, pp. 119–122.
- 1 2 "Derbyshire v Australians". CricketArchive. Retrieved 2007-12-26.
- 1 2 "Glamorgan v Australians". CricketArchive. Retrieved 2008-12-18.
- 1 2 "Durham v Australians". CricketArchive. Retrieved 2008-12-18.
- ↑ "Player Oracle IWG Johnson 1948". CricketArchive. Retrieved 2008-12-18.
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 "5th Test England v Australia at The Oval Aug 14–18 1948". Cricinfo. Retrieved 2007-12-12.
- 1 2 Fingleton, p. 183.
- 1 2 3 "Fifth Test Match England v Australia". Wisden Cricketers' Almanack. Wisden. 1949. Retrieved 2008-07-02.
- ↑ Arlott, p. 130.
- 1 2 Fingleton, p. 189.
- ↑ O'Reilly, p. 154.
- ↑ Arlott, p. 134.
- ↑ O'Reilly, p. 155.
- 1 2 "Kent v Australians". CricketArchive. Retrieved 2008-12-18.
- ↑ "Gentlemen v Australians". CricketArchive. Retrieved 2008-12-18.
- ↑ "Australians in England, 1948". Wisden Cricketers' Almanack (1949 ed.). Wisden. pp. 256–257.
- 1 2 "Somerset v Australians". CricketArchive. Retrieved 2008-12-18.
- ↑ "Australians in England, 1948". Wisden Cricketers' Almanack (1949 ed.). Wisden. pp. 257–258.
- 1 2 Perry (2005), pp. 253–254.
- ↑ Fingleton, pp. 207–209.
- 1 2 "H.D.G. Leveson-Gower's XI v Australians". CricketArchive. Retrieved 2008-12-18.
- 1 2 3 "Scotland v Australians". CricketArchive. Retrieved 2008-12-18.
- 1 2 "Batting and bowling averages The Ashes, 1948 - Australia". Cricinfo. Retrieved 2008-12-10.
- ↑ Perry (2005), p. 223.
- ↑ "Australians in England". Wisden Cricketers' Almanack (1949 ed.). Wisden. p. 207.
- ↑ "Australians in England". Wisden Cricketers' Almanack (1949 ed.). Wisden. p. 214.
- ↑ Perry (2005), pp. 223–227.
- ↑ Cashman, pp. 152, 175, 199, 258.
- ↑ Cashman, p. 258.
- ↑ "Doug Ring". The Daily Telegraph. 2003-06-25. Retrieved 2008-09-30.
- ↑ Donald Bradman referred to these players as the "Groundbowlers" in an appreciation of McCool for the 1959 testimonial year granted by Somerset."Colin McCool's Testimonial Year-1959: An Appreciation by Sir Donald Bradman". Somerset County Cricket Club Year Book (1958-59 ed.). Somerset County Cricket Club. p. 95.
- ↑ Fingleton, p. 196.
- ↑ "Yorkshire v Australians". CricketArchive. Retrieved 2008-12-18.
- ↑ "Cambridge University v Australians". CricketArchive. Retrieved 2008-12-18.
- ↑ "Essex v Australians". CricketArchive. Retrieved 2008-12-18.
- ↑ "Sussex v Australians". CricketArchive. Retrieved 2008-12-18.
- ↑ "Warwickshire v Australians". CricketArchive. Retrieved 2008-12-18.
- ↑ "Lancashire v Australians". CricketArchive. Retrieved 2008-12-18.
- ↑ "Gentlemen v Australians". CricketArchive. Retrieved 2007-12-26.
- ↑ "South of England v Australians". CricketArchive. Retrieved 2008-12-18.
- ↑ "Scotland v Australians". CricketArchive. Retrieved 2008-12-18.
References
- Arlott, John (1949). Gone to the Test Match: Being Primarily an Account of the Test Series of 1948. London: Longmans. OCLC 219797846.
- Cashman, Richard; Franks, Warwick; Maxwell, Jim; Sainsbury, Erica; Stoddart, Brian; Weaver, Amanda; Webster, Ray (1997). The A–Z of Australian Cricketers. Melbourne, Victoria: Oxford University Press. ISBN 0-9756746-1-7.
- Fingleton, Jack (1949). Brightly Fades the Don. London: Collins. OCLC 2943894.
- O'Reilly, W. J. (1949). Cricket Conquest: The Story of the 1948 Test Tour. London: Werner Laurie. OCLC 220353891.
- Perry, Roland (2000). Captain Australia: A History of the Celebrated Captains of Australian Test Cricket. Milsons Point, New South Wales: Random House Australia. ISBN 1-74051-174-3.
- Perry, Roland (2001). Bradman's Best: Sir Donald Bradman's Selection of the Best Team in Cricket History. Milsons Point, New South Wales: Random House Australia. ISBN 0-09-184051-1.
- Perry, Roland (2002). Bradman's Best Ashes Teams: Sir Donald Bradman's Selection of the Best Ashes Teams in Cricket History. Milsons Point, New South Wales: Random House Australia. ISBN 1-74051-125-5.
- Perry, Roland (2005). Miller's Luck: The Life and Loves of Keith Miller, Australia's Greatest All-rounder. Milsons Point, New South Wales: Random House. ISBN 978-1-74166-222-1.
- Piesse, Ken (2003). Cricket's Colosseum: 125 Years of Test Cricket at the MCG. South Yarra, Victoria: Hardie Grant Books. ISBN 1-74066-064-1.
- Pollard, Jack (1990). From Bradman to Border: Australian Cricket 1948–89. North Ryde, New South Wales: Harper Collins. ISBN 0-207-16124-0.