Doriprismatica sedna
| Doriprismatica sedna | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Doriprismatica sedna | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Mollusca |
| Class: | Gastropoda |
| (unranked): | clade Heterobranchia clade Euthyneura clade Nudipleura clade Nudibranchia |
| Superfamily: | Doridoidea |
| Family: | Chromodorididae |
| Genus: | Doriprismatica |
| Species: | D. sedna |
| Binomial name | |
| Doriprismatica sedna (Ev. Marcus & Er. Marcus, 1967) | |
| Synonyms[1] | |
| |
Doriprismatica sedna is a species of colorful sea slug, a dorid nudibranch, a marine gastropod mollusk in the family Chromodorididae.[1]
Taxonomy
This species has previously been placed in the genus Glossodoris Ehrenberg, 1831, but it was recently transferred to genus Doriprismatica by Johnson & Gosliner in 2012.[2][3]
Distribution
It was originally described from the Eastern Pacific, records from the Caribbean are considered the result of a recent introduction, presumably human-induced.[3] The indigenous distribution of Doriprismatica sedna includes Eastern Pacific: from the Gulf of California to the Galapagos Islands and non-indigenous in Western Atlantic: Florida, Belize, Bahamas[4] and Panama.[3]
Description

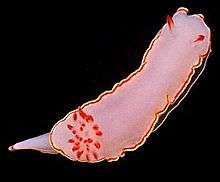
The body is oval.[3] Mantle margin is ruffled.[3] The foot and mantle of this seaslug has three different colors at the border: white, red and yellow on the outer border.[5] Background color is white with two colored bands (inner red and outer yellow) bordering the foot and mantle.[3] Upper half of the rhinophoral clubs and tips of the branchial leaves of the gill are red.[3][5] It is up to 65 mm long.[3] mm.[6]
Habitat
It was found on mangrove roots covered with sponges in Panama.[3] Minimum recorded depth is 1 m.[6] Maximum recorded depth is 29 m.[6]

The diet of Doriprismatica sedna was studied by Verdín Padilla et al. (2010)[7] on the Pacific coast of Mexico.[3] By examining the stomach content and feces, they found that this species feeds exclusively on spiculated demosponges and exhibits a variable diet, which includes 17 different species:[3] Mycale psila, Microciona sp., Myxilla incrustans, Lissodendoryx isodictialis, Haliclona caerulea, Haliclona turquoisia, Callyspongia californica, Cliona californiana, Cliona amplicavata, Cliona flavifodina, Cliona papillae, Pione mazatlanensis, Pione carpenteri, Tethya taboga, Aaptos niger, Geodia media and Dysidea uriae.[7]
References
This article incorporates Creative Commons (CC-BY-4.0) text from the reference[3]
- 1 2 Bouchet, P. (2012). Doriprismatica sedna. Accessed through: World Register of Marine Species at http://www.marinespecies.org/aphia.php?p=taxdetails&id=597380 on 2012-06-17
- ↑ Johnson R. F & Gosliner T. M. (2012). "Traditional taxonomic groupings mask evolutionary history: A molecular phylogeny and new classification of the chromodorid nudibranchs". PLoS One 7: e33479. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0033479
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 Goodheart J. A., Ellingson R. A., Vital X. G., Galvão Filho H. C., McCarthy J. B., Medrano S. M., Bhave V. J., García-Méndez K., Jiménez L. M., López G. & Hoover C. A. (2016). "Identification guide to the heterobranch sea slugs (Mollusca: Gastropoda) from Bocas del Toro, Panama". Marine Biodiversity Records 9(1): 56. doi:10.1186/s41200-016-0048-z
- ↑ Miller M. D. 1999. The Slug Site. http://slugsite.us/bow/nudiwk50.html
- 1 2 Rudman, W.B., 2000 (October 10) Glossodoris sedna (Marcus & Marcus, 1967). [In] Sea Slug Forum. Australian Museum, Sydney. Available from http://www.seaslugforum.net/factsheet.cfm?base=glossedn
- 1 2 3 Welch J. J. (2010). "The "Island Rule" and Deep-Sea Gastropods: Re-Examining the Evidence". PLoS ONE 5(1): e8776. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0008776.
- 1 2 Verdín Padilla C. J., Carballo J. L. & Camacho M. L. (2010). "A qualitative assessment of sponge-feeding organisms from the Mexican Pacific Coast". Open Marine Biology Journal 4: 39–46. PDF
Further reading
- Bertsch H. (1977) The Chromodoridinae nudibranchs from the Pacific coast of America.- Part I. Investigative methods and supra-specific taxonomy. The Veliger 20(2): 107-118.
- Rudman W.B. (1984) The Chromodorididae (Opisthobranchia: Mollusca) of the Indo-West Pacific: a review of the genera. Zoological Journal of the Linnean Society 81 (2/3): 115-273. page(s): 152
- Rudman W.B. (1985) The Chromodorididae (Opisthobranchia: Mollusca) of the Indo-West Pacific: Chromodoris aureomarginata, C. verrieri and C. fidelis colour groups. Zoological Journal of the Linnean Society 83: 241-299. page(s): 295
- Rudman W.B. (1990) The Chromodorididae (Opisthobranchia: Mollusca) of the Indo-West Pacific: further species of Glossodoris, Thorunna and the Chromodoris aureomarginata colour group. Zoological Journal of the Linnean Society 100: 263-326 page(s): 324
- Turgeon, D.; Quinn, J.F.; Bogan, A.E.; Coan, E.V.; Hochberg, F.G.; Lyons, W.G.; Mikkelsen, P.M.; Neves, R.J.; Roper, C.F.E.; Rosenberg, G.; Roth, B.; Scheltema, A.; Thompson, F.G.; Vecchione, M.; Williams, J.D. (1998). Common and scientific names of aquatic invertebrates from the United States and Canada: mollusks. 2nd ed. American Fisheries Society Special Publication, 26. American Fisheries Society: Bethesda, MD (USA). ISBN 1-888569-01-8. IX, 526 + cd-rom pp. page(s): 127
- Debelius, H. & Kuiter, R.H. (2007) Nudibranchs of the world. ConchBooks, Frankfurt, 360 pp. ISBN 978-3-939767-06-0 page(s): 197
- Rosenberg, G., F. Moretzsohn, and E. F. García. 2009. Gastropoda (Mollusca) of the Gulf of Mexico, Pp. 579–699 in Felder, D.L. and D.K. Camp (eds.), Gulf of Mexico–Origins, Waters, and Biota. Biodiversity. Texas A&M Press, College Station, Texas.