History of suits
The man's suit of clothes, in the sense of a lounge or business or office suit, is a set of garments which are crafted from the same cloth. This article discusses the history of the lounge suit, often called a business suit when made in dark colours and of conservative cut.
The current styles were founded in a period of sartorial revolution during the early 19th century. This sharply changed the elaborately embroidered and jeweled formal clothing into the simpler clothing of the Regency period (1811–20), which gradually evolved to the stark formality of the Victorian era (1837-1901). It was in the search for more comfort that the loosening of rules gave rise in the late 19th century to the modern lounge suit.
Men's suits
.jpg)
The suit is a traditional form of men's formal clothes in the Western world. For some four hundred years, suits of matching coat, trousers, and waistcoat have been in and out of fashion. The modern lounge suit's derivation is visible in the outline of the brightly coloured, elaborately crafted royal court dress of the 17th century (suit, wig, knee breeches), which was shed because of the French Revolution. This evolution is seen more recently in British tailoring's use of steam and padding in moulding woolen cloth, the rise and fall in popularity of the necktie, and the gradual disuse of waistcoats and hats in the last fifty years.
The modern lounge suit appeared in the late 19th century, but traces its origins to the simplified, sartorial standard of dress established by the English king Charles II in the 17th century. In 1666, the restored monarch, Charles II, per the example of King Louis XIV's court at Versailles, decreed that in the English Court men would wear a long coat, a waistcoat (then called "petticoat"), a cravat (a precursor of the necktie), a wig, and knee breeches (trousers), and a hat.
Regency
In the early 19th century, British dandy Beau Brummell redefined and adapted this style, then popularised it, leading European men to wearing well-cut, tailored clothes, adorned with carefully knotted neckties. The simplicity of the new clothes and their sombre colours contrasted strongly with the extravagant, foppish styles just before. Brummell's influence introduced the modern era of men's clothing which now includes the modern suit and necktie. Moreover, he introduced a whole new era of grooming and style, including regular (daily) bathing as part of a man's toilette.[1]
In this regency period, the predominant upper-class clothing introduced by Brummell for day wear was a tightly fitting, dark coloured tailcoat with non-matching (usually pale) trousers, pale waistcoat, white shirt and cravat and tall boots.
Victorian
Towards the start of the Victorian period, the frock coat, initially not just black, became popular, and quickly became the standard daily clothing for gentlemen. From the middle of the 19th century, a new (then informal) coat, the morning coat, became acceptable. It was a less formal garment, with a cut away front, making it suitable for wearing while riding. Morning dress and the frock coat garments were not suits, because they were worn with trousers that didn't match in color or fabric; a matching waistcoat and trousers were considered informal and could be described using the short-lived term ditto suit.[2] The frock coat was still the standard garment for all formal or business occasions, and a tailcoat was worn in the evenings.
Towards the end of the 19th century, the modern lounge suit was born as a very informal garment meant only to be worn for sports, in the country, or at the seaside.

Parallel to this, the dinner jacket was invented and came to be worn for informal evening events. It was descended from white tie (the dress code associated with the evening tailcoat) but quickly became a full new garment, the dinner jacket, with a new dress code, initially known as 'dress lounge' and later black tie. When it was imported to the United States, it became known as the tuxedo. The 'dress lounge' was originally worn only for small private gatherings and white tie ('White tie and tails') was still worn for large formal events. The 'dress lounge' slowly became more popular for larger events as an alternative to full evening dress in white tie.
Edwardian

The beginning of the Edwardian era in the early 20th century brought a steady decline in the wearing of frock coats as the morning coat rose in relative formality, first becoming acceptable for businessmen, then becoming standard dress even in town. The lounge suit was slowly accepted as being correct outside its original settings, and during Edwardian times gradually began to be seen in town. While still reserved for private gatherings, usually with no ladies, black tie became more common.
In North America, the "sack suit", a cut of lounge suit, saw a large rise in popularity, and, except for the shoulders, it is unfitted, loose, and informal, as it has no darts.
Inter-war
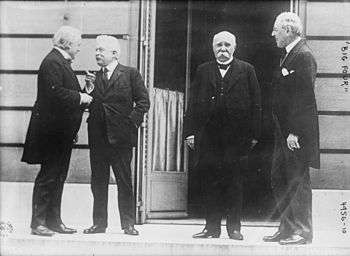
After the end of the first World War, most men adopted the short lounge coated suit. Long coats quickly went out of fashion for everyday wear and business, and the morning coat gained its current classification of "formal". During the 1920s, short suits were always worn except on formal occasions in the daytime, when a morning coat would be worn. Older, more conservative men continued to wear a frock coat, or "Prince Albert coat" as it was known. In America, for evening occasions, the short dinner jacket virtually replaced the long "full dress" tails, which was perceived as "old hat" and was only worn by old conservative men. In Britain, black tie became acceptable as a general informal alternative to white tie, though at the time the style and accessories of black tie were still very fluid.
In the 1920s men began wearing wide, straight-legged trousers with their suits. These trousers normally measured 23 inches around the cuff. Younger men often wore even wider-legged trousers which were known as "Oxford bags." Trousers also began to be worn cuffed shortly after World War I and this style persisted until World War II. Trousers first began to be worn creased in the 1920s. Trousers were worn very highly waisted throughout the 1920s and this fashion remained in vogue until the 1940s. Single-breasted suits were in style throughout the 1920s and the double-breasted suit was mainly worn by older more conservative men. In the 1920s, very fashionable men would often wear double-breasted waistcoats (with four buttons on each side) with single-breasted coats. Lapels on single-breasted suits were fashionably worn peaked and were often wide. In the early 1930s these styles continued and were often even further exaggerated.
Before 1935 (and again in the 1970s) men preferred snugly tailored coats and waistcoats. In 1935, a complete change in style occurred. Loose fitting coats were introduced, trousers began to be tapered at the bottom and suit coats began to have tapered arms. These new trends were only reluctantly accepted by men at first. At first the waistcoat continued to be made in the traditional fitted and snug style. By 1940, the waistcoat began to be made in a loose style which made it uncomfortable to wear. In fashion magazines of the day, men complained how these new vests continually rode up when they happen to sit down or bend over. Fashionable men changed their preference to the double-breasted suit coat at this time and it would remain in fashion for the next two decades.
By this time, morning dress was being replaced by day time semi-formal, known in America as the stroller. This was quite popular, but has actually been outlived by the morning coat. Since the 1950s it has been used as a black version of the lounge suit as an informal look to the dinner jacket. In modern times the black lounge suit has become popular to wear during the day.
Post-war
Throughout the 1940s and 1950s the trend was to simplify and modernize the suit as much as possible. For example, by the 1960s the size of the lapel had shrunk to a very small size. Suit coats were also cut as straight as possible without any indication of a waistline. Cloth rationing changed styles significantly, contributing to a large reduction in the popularity of many cuts, such as the double-breasted suit.
The New York Times Style Magazine explains one iconic suit of the era, the gray flannel suit:
Back in 1955, when denim was the height of rebelliousness, Sloan Wilson's novel The Man in the Gray Flannel Suit turned a men's classic into a synonym for drab, middle-class conformity . . . Flannel had humble beginnings — the name is reputedly derived from "gwlanen," Welsh for woolen cloth — and was used for underwear in the 19th century. In the 1880s white flannel was worn for summer sports; by the 1920s the more seasonless gray had become a favorite. When the Prince of Wales wore gray flannel trousers on his 1924 trip to America, they were aped by collegiates on both sides of the Atlantic. Cary Grant and Fred Astaire then carried the trend through to the 1940s. The archetypal square of the postwar era was later described by Esquire's style encyclopedia as a neat, circumspect, conservative man who carried an attaché case and regarded a pink button-down shirt as his one sartorial fling.[3]
In the late 1960s and early 1970s the Nehru jacket style was worn by a few in the United States — Johnny Carson for example.
In the 1970s, a snug-fitting suit coat became popular once again and this style permitted the return of the waistcoat. This new three-piece suit style became associated with disco music and its culture, specifically popularised by the film Saturday Night Fever, where the tight waistcoat was basic to that fashion. The tight three-piece suit was equated with the discothèque culture. The socially conservative backlash against disco music culture ended the popularity of snug-fitting three piece suits.
In the late 1970s, several brands, most notably Haggar, started to introduce the concept of "suit separates", separately sized coats and pants allowing a man to purchase the appropriate coat and pant size. "The concept of 'Custom Fit Suits' was a Haggar innovation allowing gentlemen to purchase jackets and pants separately, by size, which eliminated the need for tailoring the pant." '[4]
The 1980s saw a trend towards the simplification of the suit once again. The jacket became looser and the waistcoat was completely dispensed with. A few suit makers continued to make waistcoats, but these tended to be cut very low and often had only four buttons. The waistline on the suit coat went down again in the 1980s to a position well below the waist. By 1985-1986, three-piece suits were on the way out and making way for cut double-breasted suits and two piece single-breasted.
The late 1990s saw the return to popularity of the three-button two-piece suit, which then went back out of fashion some time in the first decade of the 21st Century.
Women's suits

The earliest women's suits were riding habits, which consisted of a tailored coat or jacket and matching skirt from the 1660s. Practical and sturdy, riding habits were worn not only on horseback, but also for travel and other daytime pursuits. Jacket-and-skirt ensembles not intended for riding appeared in the later 19th century. Both riding habits and walking suits reflected the skirt and sleeve styles of the day. Until the 1910s, coat and skirt ensembles were usually described as "costumes" rather than suits, and the term "suit", as applied to such sets, was not usual until after the First World War.[5]
In the first half of the 20th century, the skirted suit became the common daytime city costume for women, in the workplace and out; dressmaker suits featured softer fabrics and "feminine" details, and cocktail suits were worn for semi-formal occasions in mid-century.
Under the influence of Dress for Success, a working woman's uniform of skirted suit, tailored shirt, and floppy tie evolved in the 1970s and 1980s. Pantsuits (women's suits with trousers) were introduced by designer André Courrèges in 1964 but were only gradually accepted as formal business attire.
Recent Influence of casual dress
Over the past half-century, the wearing of suits has become far less common than it once was and is now usually reserved for formal and business activities. During the 1990s, many businesses in North America adopted casual dress codes, beginning with "casual Fridays" and then extending to the entire business week. The abandonment of a uniform dress code has led to considerable confusion over what is considered appropriate business wear. More recently, some businesses have reinforced the wearing of suits, although they may never again be as common as they once were. A similar trend has occurred in Europe.
Contemporary trends
Although the man's tailored suit is commonly perceived as the ultimate conservative costume of Western culture, extravagant variations on the tailored suit have been adopted by many subcultures over the last century as a matter of fashion or social identity. As early as 1922, Emily Post addressed what she termed the "freak American suit" in her influential guide Etiquette:
- You will see it everywhere, on Broadway of every city and Main Street of every town, on the boardwalks and beaches of coast resorts, and even in remote farming villages. It comes up to hit you in the face year after year in all its amazing variations: waist-line under the arm pits, "trick" little belts, what-nots in the cuffs; trousers so narrow you fear they will burst before your eyes, pockets placed in every position, buttons clustered together in a tight little row or reduced to one. Such progressive styles may not reflect the international tastes or etiquette.
Some of the non-traditional tailored suit styles of the past century include:
- The Jazz suit of the early 1920s were extremely high-waisted and snug-fitting and were worn with trousers which were quite high-waisted and trouser legs were short and revealed the wearer's socks.
- The Zoot suit of the late 1930s and 1940s.
- The Western suit, a form of western wear featuring a tailored jacket with "western" details such as pointed yokes or arrowhead pockets.
- The Nudie suit, a highly decorated form of western wear.
- The Beatle suit, inspired by Pierre Cardin's collarless jackets, derived from Edwardian suits.
- The Mod suit, a fashion of the 1960s. Characteristics include a very slim cut, narrow lapels, three or four buttons and a strongly tapered waist. Usually single-breasted. The cloth generally consists in part of mohair.
- The Safari suit, a fashion of the 1970s. Patterned after military dress uniforms worn in hot climates, it consisted of (long, but sometimes short) trousers and short-sleeved jacket with patch pockets of a light suiting fabric, typically of beige or pastel shades of blue and green. It was worn with a short-sleeved shirt, mostly of open neck design, but occasionally with a tie. Another style associated with this was the leisure suit, which had a long-sleeved shirt-like jacket.
- The Disco suit, a fashion of the 1970s with exaggerated lapels and flared trousers and usually necktie omitting, often in white or brightly coloured polyester fabric, the jacket was based on the jackets popular in the 1930s.
- The Mandarin suit or Nehru Jacket, a simpler style worn with no necktie, has become increasingly popular in the late 1990s and first decade of the 21st century.
- The Power suit of the mid-1980s and early 1990s. It's a double breasted suit characterized by sharp cuts, wide shoulder pads and a stiff rigidity.
See also
Bibliography
- Antongiavanni, Nicholas: The Suit, HarperCollins Publishers, New York, 2006. ISBN 0-06-089186-6
- Byrd, Penelope: The Male Image: men's fashion in England 1300-1970. B. T. Batsford Ltd, London, 1979. ISBN 0-7134-0860-X
- Croonborg, Frederick: The Blue Book of Men's Tailoring. Croonborg Sartorial Co., New York and Chicago, 1907
- Cunnington, C. Willett; Cunnington, Phillis (1959): Handbook of English Costume in the 19th Century, Plays Inc, Boston, 1970 reprint
- Devere, Louis: The Handbook of Practical Cutting on the Centre Crown System (London, 1866) revised and edited by R. L. Shep. R. L. Shep, Mendocino, California, 1986. ISBN 0-914046-03-9
- Doyle, Robert: The Art of the Tailor, Sartorial Press Publications, Stratford, Ontario, 2005. ISBN 0-9683039-2-7
- Druessedow, Jean L. (editor): Men's Fashion Illustration from the Turn of the Century Reprint. Originally published: New York: Jno J. Mitchell Co. 1910. Dover Publications, 1990 ISBN 0-486-26353-3
- Mansfield, Alan; Cunnington, Phillis: Handbook of English Costume in the 20th Century 1900-1950, Plays Inc, Boston, 1973
- Stephenson, Angus (editor): The Shorter Oxford Dictionary. Oxford University Press, New York, 2007
- Unknown author: The Standard Work on Cutting Men's Garments. 4th ed. Originally pub. 1886 by Jno J Mitchell, New York. ISBN 0-916896-33-1
- Vincent, W. D. F.: The Cutter's Practical Guide. Vol II "All kinds of body coats". The John Williamson Company, London, circa 1893.
- Waugh, Norah: The Cut of Men's Clothes 1600-1900, Routledge, London, 1964. ISBN 0-87830-025-2
- Whife, A. A (ed): The Modern Tailor Outfitter and Clothier. The Caxton Publishing Company Ltd, London, 1951
References
- ↑ Johnson, Birth of the Modern
- ↑ "Ditto Suits". fashionencyclopaedia.com. Retrieved 15 July 2013.
- ↑ New York Times Style Magazine, Bryan, Robert E. "Gray Matters,"
- ↑ The Haggar Family & Corporation, Haggar, Ed R. June, 1999
- ↑ "Costume by John Redfern". Search the Collections. V&A Museum. Retrieved 14 February 2013.