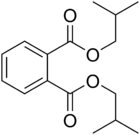
Diisobutyl phthalate
 | |
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
Bis(2-methylpropyl) benzene-1,2-dicarboxylate | |
| Other names
Diisobutyl phthalate Diisobutyl ester of phthalic acid 1,2-benzenedicarboxylic acid bis(2-methylpropyl)ester Di(isobutyl) 1,2-benzenedicarboxylate DIBP DiBP Palatinol IC | |
| Identifiers | |
| 84-69-5 | |
| 3D model (Jmol) | Interactive image |
| ChEBI | CHEBI:79053 |
| ChemSpider | 6524 |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.001.412 |
| EC Number | 201-553-2 |
| KEGG | C15205 |
| PubChem | 6782 |
| RTECS number | TI1225000 |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C16H22O4 | |
| Molar mass | 278.35 g/mol |
| Appearance | Colorless viscous liquid |
| Density | 1.038 g/cm3 |
| Melting point | −37 °C (−35 °F; 236 K) |
| Boiling point | 320 °C (608 °F; 593 K) |
| 1 mg/l at 20 °C | |
| log P | 4.11 |
| Vapor pressure | 0.01 Pa at 20 °C |
| Hazards | |
| Main hazards | Harmful (Xn), Dangerous for the environment (N) |
| R-phrases | R50/53;R62;R63 |
| S-phrases | S36/37;S61 |
| NFPA 704 | |
| Flash point | 185 °C (365 °F; 458 K) c.c. |
| 400 °C (752 °F; 673 K) | |
| Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| | |
| Infobox references | |
Diisobutyl Phthalate (DIBP) is prepared by esterification process of isobutanol and phthalic anhydride. Its structural formula is C6H4(COOCH2CH(CH3)2)2. Refractive index is 1.488 - 1.492 (20 °C, D).
DIBP is an odorless plasticizer and has excellent heat and light stability. It is the lowest cost plasticizer for cellulose nitrate. DIBP has lower density and freezing point than DBP (dibutyl phthalate, CAS No.: 84-74-2). It has similar properties as dibutyl phthalate and can be used as a substitute for it.
DIBP is used in nitro cellulose plastic, nail polish, explosive material, lacquer manufacturing and used with methyl methacrylate applications.
The concentration of a metabolite of DIBP (Mono-isobutyl phthalate or MIBP) has been steadily increasing in the urine of Americans over the period 1999-2008.[1] Prenatal maternal exposure is associated with substantial harm to intellectual development in children.[2]
Contamination
Products in Taiwan made from Hebo Natural Products Limited (禾博天然產物有限公司) of China contained ginger contaminated with DIBP, some 80,000 nutritional supplement capsules made with imported ginger powder were seized by the Public Health Department of Taiwan in June 2011.[3] In addition, soybean extract and olive leaf extract, both in powder form, were contaminated with DIBP and DBP. Concentration of DIBP in the ginger extract powder was found to be 33,100 parts per million (ppm), that of DIBP in the soybean extract powder, 41 ppm, and that of DIBP and DBP in the olive leaf extract powder, 768 ppm and 441 ppm, respectively.[4]
See also
- Phthalates
- Dibutyl phthalate (DBP)
References
- ↑ Center for Disease Control Fourth National Report on Human Exposure to Environmental Chemicals, Updated Tables, February 2011 CDC Exposure Report.
- ↑ Persistent Associations between Maternal Prenatal Exposure to Phthalates on Child IQ at Age 7 Years. PLOS ONE
- ↑ http://www.etaiwannews.com/etn/news_content.php?id=1627491&lang=eng_news&cate_rss=TAIWAN_eng
- ↑ http://www.chinapost.com.tw/taiwan/national/national-news/2011/06/15/306275/Plasticizer-found.htm China Post
External links
- International Chemical Safety Card 0829
- Human Health Hazard Assessment
- Diisobutyl phthalate degradation by Fenton treatment
