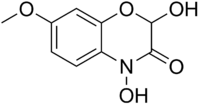
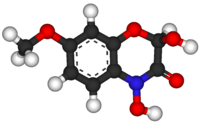
DIMBOA
 | |
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
2,4-Dihydroxy-7-methoxy-1,4-benzoxazin-3-one | |
| Identifiers | |
| 15893-52-4 | |
| 3D model (Jmol) | Interactive image |
| ChemSpider | 2268 |
| PubChem | 2358 |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C9H9NO5 | |
| Molar mass | 211.17 g·mol−1 |
| Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| | |
| Infobox references | |
DIMBOA (2,4-dihydroxy-7-methoxy-1,4-benzoxazin-3-one) is a naturally-occurring hydroxamic acid, a benzoxazinoid. DIMBOA is a powerful antibiotic present in maize and related grasses, particularly wheat.
In maize, DIMBOA functions as natural defense against European corn borer larvae and many other damaging pests, including fungi and bacteria.[1] The exact level of DIMBOA varies between individual plants, but higher concentrations are typically found in young seedlings and the concentration decreases as the plant ages.[2]
References
- ↑ G7113 European Corn Borer: A Multiple-Crop Pest in Missouri, MU Extension
- ↑ Cambier, V; Hance, T; de Hoffmann, E (2000). "Variation of DIMBOA and related compounds content in relation to the age and plant organ in maize". Phytochemistry. 53 (2): 223–229. doi:10.1016/S0031-9422(99)00498-7. PMID 10680175.
This article is issued from Wikipedia - version of the 3/1/2016. The text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution/Share Alike but additional terms may apply for the media files.