Dōgojima
| Native name: <span class="nickname" ">島後 Dōgo | |
|---|---|
 Coastline of Dōgo | |
 | |
| Geography | |
| Location | Sea of Japan |
| Coordinates | 36°14′N 133°17′E / 36.233°N 133.283°ECoordinates: 36°14′N 133°17′E / 36.233°N 133.283°E |
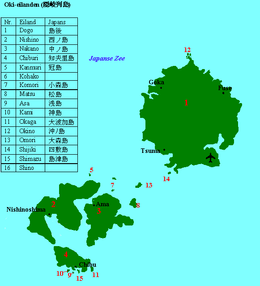
| Archipelago | Oki Islands |
| Area | 241.58 km2 (93.27 sq mi) |
| Coastline | 211 km (131.1 mi) |
| Highest elevation | 607.7 m (1,993.8 ft) |
| Highest point | Mount Daimanji |
| Administration | |
|
Japan | |
| Prefectures | Shimane Prefecture |
| District | Oki District |
| Town | Okinoshima |
| Demographics | |
| Population | 14,849 (2013) |
| Ethnic groups | Japanese |
Dōgo (島後) is one of the Oki Islands in the Sea of Japan.[1]
The island, 241.58 km² in area, has a population of approximately 14,849 persons. The island is administered by the town of Okinoshima in Shimane Prefecture. Much of the island is within the borders of Daisen-Oki National Park.
Geography
Dōgo is the largest of the Oki Islands. It is located approximately 80 kilometres (43 nmi) north of Honshu coast. The island is of volcanic origin, and is roughly circular, with an approximate diameter of 20 kilometres (12 mi), with its highest point at the summit of Mount Daimanji at 608 metres (1,995 ft) above sea level.[2]
The climate of Dōgo is classified as a humid subtropical climate (Köppen climate classification Cfa) with very warm summers and cool winters. Precipitation is abundant throughout the year.
History
The Oki Islands have been inhabited since the Japanese Paleolithic era, and numerous artifacts from the Jomon, Yayoi and Kofun periods have been found by archaeologists. The island of Dōgo is mentioned in the Nara period chronicles Kojiki and Nihon Shoki, and Dōgo was the location of the capital of ancient Oki Province.[3]
Dōgo was used as a place of exile from the Nara period, but is well known as the place of exile for ex-Emperor Go-Toba, who died on Nakanoshima in 1239, and for Emperor Go-Daigo, who was exiled to Nishinoshima from 1331-1333 [4] The island became tenryo territory directly under the control of the Tokugawa shogunate in the Edo period.
After the Meiji restoration, the Oki Islands became part of Tottori Prefecture in 1871, but were transferred to Shimane Prefecture in 1881.[5]
In 1892, Lafcadio Hearn visited Dōgojima, spending a month there, and writing about his experiences in Glimpses of Unfamiliar Japan. Dōgo was visited by the American naturalist Charles Henry Gilbert in 1906.[6]
A lighthouse was erected on Cape Saigō in the southeast of the island in 1921. This lighthouse remained the only lighthouse in the Oki Islands until the 1950s.[7]
On October 1, 2004, the town of Saigō merged with three neighboring villages to unify the island under the administration of the new town of Okinoshima.
Transportation
Dōgo is connected by regular ferry service from Saigo Port to points on mainland Japan. Oki Airport connects the island with Osaka (Itami) Airport, and Izumo by air.
Economy
The economy of the island is based on agriculture and commercial fishing. Seasonal tourism also plays a role in the local economy.
References
- ↑ Teikoku's Complete Atlas of Japan, Teikoku-Shoin Co., Ltd., Tokyo, ISBN 4-8071-0004-1
- ↑ Map of Dogo
- ↑ http://www.town.nishinoshima.shimane.jp/english/about.nishinoshima.htm
- ↑ Ancient Tales and Folk-lore of Japan - A Story of Oki Islands
- ↑ Shimane Prefecture - History
- ↑ HighBeam Research - Charles Henry Gilbert (1859-1928), naturalist-in-charge: the 1906 North Pacific expedition of the Steamer Albatross
- ↑ University of North Carolina - Lighthouses of Japan: Shimane
External links
![]() Media related to Dōgo at Wikimedia Commons
Media related to Dōgo at Wikimedia Commons