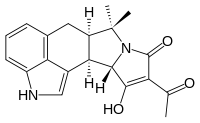
Cyclopiazonic acid
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
(6aR,11aS,11bR)-10-Acetyl-11-hydroxy-7,7-dimethyl-2,6,6a,7,11a,11b-hexahydro-9H-pyrrolo[1',2':2,3]isoindolo[4,5,6-cd]indol-9-one | |
| Identifiers | |
| 18172-33-3 | |
| 3D model (Jmol) | Interactive image |
| ChEBI | CHEBI:22450 |
| ChEMBL | ChEMBL480627 |
| ChemSpider | 21106432 |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.162.058 |
| 5350 | |
| PubChem | 65261 |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C20H20N2O3 | |
| Molar mass | 336.39 g·mol−1 |
| Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| | |
| Infobox references | |
Cyclopiazonic acid (CPA) is a toxic fungal secondary metabolite.[1] Chemically, CPA is related to ergoline alkaloids. CPA was originally isolated from Penicillium cyclopium and subsequently from other fungi including Penicillium griseofulvum, Penicillium camemberti, Penicillium commune, Aspergillus flavus, and Aspergillus versicolor. CPA only appears to be toxic in high concentrations. Biologically, CPA is a specific inhibitor of SERCA ATPase in intracellular Ca2+ storage sites.[2]
References
- ↑ Holzapfel, C. W. (1968). "The isolation and structure of cyclopiazonic acid, a toxic metabolite of Penicillium cyclopium Westling". Tetrahedron. 24 (5): 2101–2119. doi:10.1016/0040-4020(68)88113-X. PMID 5636916.
- ↑ Sosa, M. J.; Córdoba, J. J.; Díaz, C; Rodríguez, M; Bermúdez, E; Asensio, M. A.; Núñez, F (2002). "Production of cyclopiazonic acid by Penicillium commune isolated from dry-cured ham on a meat extract-based substrate". Journal of food protection. 65 (6): 988–92. PMID 12092733.
This article is issued from Wikipedia - version of the 6/15/2016. The text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution/Share Alike but additional terms may apply for the media files.