Crozet Islands
| Crozet Islands Îles Crozet |
||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
||||
| Motto: "Liberté, égalité, fraternité" | ||||
| Anthem: La Marseillaise | ||||
 Orthographic projection centred over the Îles Crozet.
|
||||
 One of the Crozet Islands | |
| Geography | |
|---|---|
| Location | Indian Ocean |
| Coordinates | 46°25′S 51°59′E / 46.417°S 51.983°ECoordinates: 46°25′S 51°59′E / 46.417°S 51.983°E |
| Archipelago | Crozet Islands |
| Total islands | 6 |
| Major islands | 3 |
| Area | 352 km2 (136 sq mi) |
| Highest elevation | 1,090 m (3,580 ft) |
| Highest point | Mont Marion-Dufresne |
| Administration | |
| Overseas territory | French Southern and Antarctic Lands |
| District | Crozet Islands |
| Demographics | |
| Population |
18 (winter) 30 (summer) |

The Crozet Islands (French: Îles Crozet; or, officially, Archipel Crozet) are a sub-antarctic archipelago of small islands in the southern Indian Ocean. They form one of the five administrative districts of the French Southern and Antarctic Lands.
History
The Crozet Islands were discovered on 24 January 1772 by the expedition of French explorer Marc-Joseph Marion du Fresne, aboard Le Mascarin. His second-in-command Jules (Julien-Marie) Crozet landed on Île de la Possession, claiming the archipelago for France.[1] The expedition continued east and landed at New Zealand, where Captain Marion and much of his crew were killed and cannibalized by Maori.[2] Crozet survived the disaster, and successfully led the survivors back to their base at Mauritius. In 1776 Crozet met James Cook at Cape Town, at the onset of Cook's third voyage.[2] Crozet shared the charts of his ill-fated expedition, and as Cook sailed eastward he stopped at the islands, naming the western group Marion and the eastern group Crozet.[1] In the following years, sealers visiting the islands referred to both the eastern and western groups as the Crozet Islands, and Marion Island became the name of the larger of the two Prince Edward Islands, which were discovered by Captain Marion on the same expedition.[1]
In the early 19th century, the islands were often visited by sealers, to the extent that the seals had been nearly exterminated by 1835. Subsequently, whaling was the main activity around the islands, especially by the whalers from Massachusetts. In 1841 there were a dozen whaleships around the islands. Within a couple of years this had increased to twenty from the United States alone. Such exploitation was short-lived, and the islands were rarely visited for the rest of the century.
Shipwrecks occurred frequently at the Crozet Islands. The British sealer, Princess of Wales, sank in 1821, and the survivors spent two years on the islands. The Strathmore was wrecked in 1875. In 1887, the French Tamaris was wrecked and her crew stranded on Île des Cochons. They tied a note to the leg of an albatross, which was found seven months later in Fremantle, but the crew was never recovered. Because shipwrecks around the islands were so common, for some time the Royal Navy dispatched a ship every few years to look for stranded survivors. The steamship Australasian also checked for survivors en route to Australia.[3]
Between 1924 and 1955, France administered the islands as a dependency of Madagascar. Crozet Islands became part of the French Southern Territories in 1955. In 1938, the Crozet Islands were declared a nature reserve. In 1961, a first research station was set up, but it was not until 1963 that the permanent station Alfred Faure opened at Port Alfred on Île de la Possession (both named after the first leader of the station). The station is staffed by 18 to 30 people (depending on the season) and does meteorological, biological, and geological research, maintains a seismograph and a geomagnetic observatory (IAGA code: CZT).
Geography
Not including minor islets or rock reefs etc., the Crozet group consists of six islands. From west to east:
| No. | Island or Group (English) | Area | Highest Peak | Location |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| L'Occidental (Western Group) | ||||
| 1 | Île aux Cochons (Pig Island) | 67 km2 (26 sq mi) | Mont Richard-Foy, 770 m (2,526 ft) | 46°06′S 50°14′E / 46.100°S 50.233°E |
| 2 | Île des Pingouins (Penguin Island, literally Auk Island) | 3 km2 (1.2 sq mi) | Mont des Manchots 340 m (1,115 ft) | 46°25′S 50°24′E / 46.417°S 50.400°E |
| 3 | Îlots des Apôtres (Apostle Islets)(1) | 2 km2 (0.8 sq mi) | Mont Pierre, 289 m (948 ft) | 45°57′S 50°25′E / 45.950°S 50.417°E |
| L'Oriental (Eastern Group) | ||||
| 4 | Île de la Possession (Possession Island) | 150 km2 (58 sq mi) | Pic du Mascarin, 934 m (3,064 ft) | 46°24′S 51°46′E / 46.400°S 51.767°E |
| 5 | Île de l'Est (East Island) | 130 km2 (50 sq mi) | Mont Marion-Dufresne, 1,090 m (3,576 ft) | 46°25′S 52°12′E / 46.417°S 52.200°E |
| Îles Crozet (Crozet Islands) | 352 km2 (136 sq mi) | Mont Marion-Dufresne, 1,090 m (3,576 ft) | 45°57' to 46°29'S 50°10' to 52°19'E | |
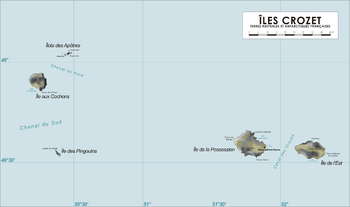
(1) Group of two major islands (Grande Île—Big Island, and Petite Île—Little Island) and about 20 pinnacle rocks.
The Eastern and Western Groups are 94.5 kilometres (58.7 mi) apart (from Île des Pingouins to Île de la Possession)
The Crozet Islands are uninhabited, except for the research station Alfred Faure (Port Alfred) on the East side of Île de la Possession, which has been continuously manned since 1963. Previous scientific stations included La Grande Manchotière and La Petite Manchotière.
Geology
Analysis of magnetic anomalies on the sea floor indicates that the Crozet Plateau formed some 50 million years ago. The islands are of volcanic origin, and basalt. Rock samples indicate volcanic origins going back to at least 8.8 million years.
Climate
The Crozet islands have a maritime-influenced tundra climate (Köppen climate classification, ET). Monthly temperatures average around 2.9 °C (37 °F) and 7.9 °C (46 °F) in winter and summer respectively.[4] Precipitation is high, with over 2,000 mm (78.7 in) per year. It rains on average 300 days a year, and winds exceeding 100 km/h (60 mph) occur on 100 days a year. The temperatures may rise to 18 °C (64.4 °F) in summer and rarely go below −5 °C (23 °F) even in winter.
| Climate data for Alfred Faure (1981–2010) | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Month | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | Year |
| Record high °C (°F) | 22.4 (72.3) |
21.7 (71.1) |
21.2 (70.2) |
19.7 (67.5) |
16.5 (61.7) |
16.0 (60.8) |
14.9 (58.8) |
16.4 (61.5) |
15.4 (59.7) |
17.5 (63.5) |
19.7 (67.5) |
20.7 (69.3) |
22.4 (72.3) |
| Average high °C (°F) | 10.4 (50.7) |
11.0 (51.8) |
10.1 (50.2) |
9.1 (48.4) |
7.2 (45) |
6.1 (43) |
6.0 (42.8) |
5.4 (41.7) |
5.8 (42.4) |
6.8 (44.2) |
7.8 (46) |
9.2 (48.6) |
7.9 (46.2) |
| Daily mean °C (°F) | 7.5 (45.5) |
8.1 (46.6) |
7.4 (45.3) |
6.5 (43.7) |
4.9 (40.8) |
3.8 (38.8) |
3.7 (38.7) |
3.2 (37.8) |
3.3 (37.9) |
4.1 (39.4) |
5.0 (41) |
6.3 (43.3) |
5.3 (41.5) |
| Average low °C (°F) | 4.5 (40.1) |
5.2 (41.4) |
4.8 (40.6) |
3.9 (39) |
2.5 (36.5) |
1.5 (34.7) |
1.4 (34.5) |
0.9 (33.6) |
0.8 (33.4) |
1.3 (34.3) |
2.3 (36.1) |
3.3 (37.9) |
2.7 (36.9) |
| Record low °C (°F) | 0.0 (32) |
0.7 (33.3) |
−0.4 (31.3) |
−1.7 (28.9) |
−2.5 (27.5) |
−3.7 (25.3) |
−5.0 (23) |
−4.7 (23.5) |
−6.6 (20.1) |
−3.9 (25) |
−2.8 (27) |
−1.9 (28.6) |
−6.6 (20.1) |
| Average precipitation mm (inches) | 127.8 (5.031) |
129.1 (5.083) |
146.2 (5.756) |
160.2 (6.307) |
186.2 (7.331) |
131.7 (5.185) |
139.2 (5.48) |
157.3 (6.193) |
163.6 (6.441) |
156.2 (6.15) |
147.9 (5.823) |
142.0 (5.591) |
1,782.5 (70.177) |
| Average precipitation days (≥ 1.0 mm) | 12.97 | 11.64 | 13.37 | 15.89 | 16.54 | 14.85 | 15.81 | 16.04 | 14.75 | 13.86 | 12.92 | 14.88 | 172.91 |
| Mean monthly sunshine hours | 96.6 | 74.7 | 65.4 | 10.9 | 17.1 | 14.8 | 30.8 | 41.9 | 46.1 | 62.1 | 80.1 | 63.2 | 600.4 |
| Source: Meteo climat[5][6] | |||||||||||||
Flora and fauna
The islands are part of the Southern Indian Ocean Islands tundra ecoregion that includes several subantarctic islands. In this cold climate plant life is mainly limited to grasses, mosses and lichens, while the main animals are insects along with large populations of seabirds, seals and penguins.[4]
The Crozet Islands are home to four species of penguins. Most abundant are the macaroni penguin, of which some 2 million pairs breed on the islands, and the king penguin, home to 700,000 breeding pairs; half the world's population.[7] The eastern rockhopper penguin also can be found, and there is a small colony of gentoo penguins. There is also an endemic subspecies of the duck Eaton's pintail. Other birds include black-faced sheathbills, petrels, and albatross, including the wandering albatross.
Mammals living on the Crozet Islands include fur seals, and southern elephant seals. Killer whales have been observed preying upon the seals. The transient killer whales of the Crozet Islands are famous for intentionally beaching (and later un-stranding) themselves while actively hunting the islands' breeding seal population. This is a very rare behaviour, most often seen in the Patagonia region of Argentina, and is thought to be a learned skill passed down through generations of individual orca families.
The Crozet Islands have been a nature reserve since 1938. Introduction of foreign species (mice, rats, and subsequently cats for pest control) has caused severe damage to the original ecosystem. The pigs that had been introduced on Île des Cochons and the goats brought to Île de la Possession—both as a food resource—have been exterminated.
Another on-going concern is overfishing of the Patagonian toothfish and the albatross population is monitored. The waters of the Crozet Islands are patrolled by the French government.
In Popular Culture
A 2012 French film, Les Saveurs du Palais, begins and ends with scenes in the Crozet Islands. The film's protagonist, a grandmotherly chef from the Périgord region of France who signed on as cook for the research station, had once been the personal chef to President Mitterrand.
Gallery
 The Marion Dufresne off the "port" of Crozet. East Island in the background.
The Marion Dufresne off the "port" of Crozet. East Island in the background. One of the penguin colonies of the islands
One of the penguin colonies of the islands The Eastern Group
The Eastern Group Crozet Islands causing a Von Karman Vortex street to form under low clouds.
Crozet Islands causing a Von Karman Vortex street to form under low clouds.
See also
- Administrative divisions of France
- French overseas departments and territories
- Islands controlled by France in the Indian and Pacific oceans
- Kerguelen Islands
- List of Antarctic and sub-Antarctic islands
- List of volcanoes in French Southern and Antarctic Lands
- Prince Edward Islands
References
- 1 2 3 Mills, William J (2003). Exploring Polar Frontiers: A Historical Encyclopedia, Volume 1. ABC-CLIO. pp. 166–167. Retrieved 26 September 2016.
- 1 2 Hough, Richard (1995). Captain James Cook: A Biography. W. W. Norton & Company. pp. 259–260. ISBN 978-0393315196.
- ↑ "THE CROZET ISLANDS.". The Express And Telegraph. XXVI, (7,584). South Australia. 21 March 1889. p. 3 (Second Edition.). Retrieved 4 May 2016 – via National Library of Australia.
- 1 2 "Southern Indian Ocean Islands tundra". Terrestrial Ecoregions. World Wildlife Fund. Retrieved 2012-01-10.
- ↑ "Moyennes 1981/2010: France (Terres Australes)" (in French). Météoclimat. Retrieved June 14, 2015.
- ↑ "STATION Alfred Faure" (in French). Météoclimat. Retrieved June 14, 2015.
- ↑ Bost, Charles-André (31 October 2015). "King penquins face longer commute". New Scientist. 228 (3045): 17.
Further reading
- LeMasurier, W. E.; Thomson, J. W., eds. (1990). Volcanoes of the Antarctic Plate and Southern Oceans. American Geophysical Union. ISBN 0-87590-172-7.
- Church, Ian (1985). Survival on the Crozet Islands: The Wreck of the Strathmore in 1875. Waikanae, New Zealand: Heritage Press. ISBN 0-908708-02-5.
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Crozet Islands. |
| Wikispecies has information related to: Category:Crozet Islands nonmarine fauna |
- South Atlantic & Subantarctic Islands site, Crozet Islands page
- Further information
- Further information
- TAAF

