Commander (United States)
_Mustin_(DDG_89)_berthed_at_the_Allegheny_Pier_on_Naval_Air_Station_(NAS)_Pensacola.jpg)
.jpg)
In the United States, commander is a military rank that is also sometimes used as a military billet title, depending on the branch of service. It is also used as a rank or title in some organizations outside the military, particularly in police and law enforcement.
Rank
History
The commander rank started out as "Master and Commander" in 1674 within the British Navy for the officer responsible for sailing a ship under the Captain and some times second-in-command. Sub-captain, under-captain, rector and master-commanding was also used for the same position. With the Master and Commander also serving as captain of smaller ships, the British Navy subsumed as the third and lowest of three grades of captain given the various sizes of ships. The American Continental Navy adopted the tri-graded captain ranks. Captain 2nd Grade, or Master Commandant, became Commander in 1838.[1]
Naval



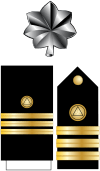

In the United States Navy, the United States Coast Guard, the United States Public Health Service Commissioned Corps, and the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration Commissioned Officer Corps, commander (abbreviated "CDR") is a mid-grade officer rank, with the pay grade of O-5. Commander ranks above lieutenant commander (O-4) and below captain (O-6). Commander is equivalent to the rank of lieutenant colonel in the other uniformed services.[2] Notably, it is the first rank at which the holder wears an embellished cap, whereas officers of the other services are entitled to embellishment at O-4 rank. Promotion to commander in the US Navy is governed by Department of Defense policies derived from the Defense Officer Personnel Management Act (DOPMA) of 1980 or its companion Reserve Officer Personnel Management Act (ROPMA). DOPMA/ROPMA guidelines suggest that 70% of lieutenant commanders should be promoted to commander after serving a minimum of three years at their present rank and after attaining 15-17 years of cumulative commissioned service, although this percentage may vary and be appreciably less for certain officer designators (i.e., primary "specialties") dependent on defense budgets, force structure and needs of the service.
A commander in the U.S. Navy may command a frigate, destroyer, submarine, aviation squadron or small shore activity, or may serve on a staff afloat or ashore (typically as an action officer or as an executive officer to a flag officer or general officer), or a larger vessel afloat (as either a department head or executive officer). An officer in the rank of commander who commands a vessel may also be referred to as "captain" as a courtesy title, or informally referred to as "skipper". Commanding officers of aviation squadrons and shore activities may also be informally referred to as "skipper" but never as "captain."[3]
Although it exists largely as a maritime training organization, the U.S. Maritime Service also has the grade of commander. The commission is appointed by the President via the Secretary of Transportation, making it a federally recognized rank with a corresponding paygrade.
In addition to its use as a rank title, the U.S. Navy also uses commander as a "position title" for senior captains or flag officers in command of multiple independent units, each with their own "commanding officer". For example, the senior officer in a U.S. Navy aviation squadron is the "commanding officer" (CO) because he or she is in command of that singular unit. That officer's immediate superior in command (ISIC) will likely be an air group or air wing "commander", with the latter being responsible for multiple squadrons. This is in keeping with the naval tradition of "commanding officers" commanding single units, but "commanders" commanding multiple units.
U.S. police ranks
The Los Angeles Police Department was one of the first American police departments to use this rank. A commander in the LAPD is equivalent to an inspector in other U.S. police departments (such as the New York City Police Department); the LAPD rank was originally called inspector as well, but was changed in 1974 to commander after senior officers voiced a preference for the more military-sounding rank. A commander is the third-highest rank in the force, above the rank of captain and below deputy chief. Duties are as commanding officer of Community Affairs, Internal Affairs, Governmental Liaison, Narcotics, Organized Crime and Vice, Criminal Intelligence, Detective Services, and other departments.[4]
The San Francisco Police Department also has a Commander rank. Like the LAPD, it is above Captain and below Deputy Chief.
The Metropolitan Police Department of the District of Columbia uses the rank of commander. The rank falls between those of inspector and assistant chief.
The Rochester Police Department uses the rank of commander. Higher than captain and below deputy chief, the rank is achieved by appointment. Commander is the rank held by the two patrol division heads and other commanders fill various administrative roles. The Saint Paul Police Department is another police force that uses the rank of commander. In the Saint Paul Police Department, commanders serve as the chief of the district/unit that they oversee.
Many police departments in the Midwest use the rank of commander. It is equivalent to a lieutenant in most other departments, being above a sergeant and below a deputy chief or captain. Commander is also used as a title in certain circumstances, such as the commander of a squad of detectives, who would usually be of the rank of lieutenant.
Commander is also utilized by larger sheriff's departments in the United States, with the rank usually falling between chief deputy and captain, three positions removed from the sheriff.
Commander as an appointment
U.S. Army and Marine Corps
In the United States Army and United States Marine Corps, the term "commander" is officially applied to the commanding officer of a unit; hence, there are company commanders, battalion commanders, brigade commanders, and so forth. At the highest levels of U.S. military command structure, "commander" also refers to what used to be called commander-in-chief, or CINC, until October 24, 2002, although the term CINC is still used in casual speech. The soldier in charge of a tank, for example the M1 Abrams, is also called its "commander".
U.S. Air Force
In the Air Force, the term "commander" (abbreviated "CC") is officially applied to the commanding officer of an Air Force unit; hence, there are squadron commanders, group commanders, wing commanders, numbered air force (NAF) commanders, major command commanders and so forth. In rank, a squadron commander is typically a lieutenant colonel, although some smaller squadrons may be commanded by a major.
A group commander is typically a mid-grade colonel, while a wing commander is typically a senior colonel or a brigadier general.
A numbered air force commander is normally a lieutenant general, although some may be in the rank of major general, especially in the Air Force Reserve or Air National Guard. The Major command commanders are normally in the rank of general or lieutenant general.
See also
| Look up commander (united states) in Wiktionary, the free dictionary. |
References
- ↑ Oliver, Raymond (August 1983). "Commander". The Story Behind Names of Different Rank. Office of History, Sacramento Air Logistics Center, McClellan AFB. Retrieved May 27, 2015.
- ↑ "Officer Ranks Insignia". Department of Defense. US Government. Retrieved May 27, 2015.
- ↑ Commander rank- Retrieved 2014-5-25
- ↑ LAPD rank- Retrieved 2014-05-25
| United States uniformed services commissioned officer and officer candidate ranks | ||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pay grade / branch of service | Officer candidate |
O-1 | O-2 | O-3 | O-4 | O-5 | O-6 | O-7 | O-8 | O-9 | O-10 | O-11 (Obs.) |
Special grade | |
| Insignia | |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |
| CDT / OC | 2LT | 1LT | CPT | MAJ | LTC | COL | BG | MG | LTG | GEN | GA[3] | GAS[3] | ||
| Midn / Cand | 2ndLt | 1stLt | Capt | Maj | LtCol | Col | BGen | MajGen | LtGen | Gen | [5] | [5] | ||
| MIDN / OC | ENS | LTJG | LT | LCDR | CDR | CAPT | RDML | RADM | VADM | ADM | FADM[3] | AN[3] | ||
| Cadet / OT / OC | 2d Lt | 1st Lt | Capt | Maj | Lt Col | Col | Brig Gen | Maj Gen | Lt Gen | Gen | GAF[3] | [5] | ||
| CDT / OC | ENS | LTJG | LT | LCDR | CDR | CAPT | RDML | RADM | VADM | ADM | [5] | [5] | ||
| [OC] | ENS | LTJG | LT | LCDR | CDR | CAPT | RADM | RADM | VADM | ADM | [5] | [5] | ||
| OC | ENS | LTJG | LT | LCDR | CDR | CAPT | RDML | RADM | VADM | [4] | [5] | [5] | ||
| [1] No universal insignia for officer candidate rank; Navy candidate insignia shown [2]Official 1945 proposal for General of the Armies insignia; John J. Pershing's GAS insignia: [3] Rank used for specific officers in wartime only, not permanent addition to rank structure [4] Grade is authorized by the U.S. Code for use but has not been created [5] Grade has never been created or authorized | ||||||||||||||
| United States warrant officer ranks | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| W-1 | W-2 | W-3 | W-4 | W-5 | |
| Army |
WO1 |
CW2 |
CW3 |
CW4 |
CW5 |
| Marine Corps |
WO1 |
CWO2 |
CWO3 |
CWO4 |
CWO5 |
| Navy |
WO1[1] |
CWO2 |
CWO3 |
CWO4 |
CWO5 |
| Air Force |
WO1[1] |
CWO2[1] |
CWO3[1] |
CWO4[1] |
CWO5[1] |
| Coast Guard |
WO1[1] |
CWO2 |
CWO3 |
CWO4 |
[2] |
| PHS Corps |
[2] | [2] | [2] | [2] | [3] |
| NOAA Corps |
[3] | [3] | [3] | [3] | [3] |
| [2] Grade is authorized for use by U.S. Code but has not been created [3] Grade never created or authorized | |||||