Coenzyme F420
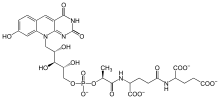
Structure of Coenzyme F420
Coenzyme F420 or 8-hydroxy-5-deazaflavin is a coenzyme involved in redox reactions in methanogens,[1] in many Actinobacteria, and sporadically in other bacterial lineages. It is a flavin derivative. The coenzyme is a substrate for coenzyme F420 hydrogenase,[2] 5,10-methylenetetrahydromethanopterin reductase and methylenetetrahydromethanopterin dehydrogenase.[3][4]
A particularly rich natural source of F420 is Mycobacterium smegmatis, in which several dozen enzymes use F420 instead of the related cofactor FMN used by homologous enzymes in most other species.[5]
See also
References
- ↑ Deppenmeier U (2002). "Redox-driven proton translocation in methanogenic Archaea". Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 59 (9): 1513–33. doi:10.1007/s00018-002-8526-3. PMID 12440773.
- ↑ Fox JA, Livingston DJ, Orme-Johnson WH, Walsh CT (1987). "8-Hydroxy-5-deazaflavin-reducing hydrogenase from Methanobacterium thermoautotrophicum: 1. Purification and characterization". Biochemistry. 26 (14): 4219–27. doi:10.1021/bi00388a007. PMID 3663585.
- ↑ Hagemeier CH, Shima S, Thauer RK, Bourenkov G, Bartunik HD, Ermler U (2003). "Coenzyme F420-dependent methylenetetrahydromethanopterin dehydrogenase (Mtd) from Methanopyrus kandleri: a methanogenic enzyme with an unusual quarternary [sic] structure". J. Mol. Biol. 332 (5): 1047–57. doi:10.1016/S0022-2836(03)00949-5. PMID 14499608.
- ↑ GD; Geerts, WJ; Keltjens, JT; Van Der Drift, C; Vogels, GD (1991). "Purification and properties of 5,10-methylenetetrahydromethanopterin dehydrogenase and 5,10-methylenetetrahydromethanopterin reductase, two coenzyme F420-dependent enzymes, from Methanosarcina barkeri". Biochim. Biophys. Acta. 1079 (3): 293–302. doi:10.1016/0167-4838(91)90072-8. PMID 1911853.
- ↑ Selengut JD, Haft DH (2010). "Unexpected abundance of coenzyme F(420)-dependent enzymes in Mycobacterium tuberculosis and other actinobacteria.". J Bacteriol. 192 (21): 5788–98. doi:10.1128/JB.00425-10. PMC 2953692
 . PMID 20675471.
. PMID 20675471.
External links
This article is issued from Wikipedia - version of the 5/24/2016. The text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution/Share Alike but additional terms may apply for the media files.