Ciguayo language
| Ciguayo | |
|---|---|
| Siwayo | |
| Native to | Dominican Republic |
| Region | Samaná Peninsula |
| Ethnicity | Ciguayos |
| Extinct | 16th century |
|
unclassified (one of the pre-Arawakan languages of the Greater Antilles) | |
| Language codes | |
| ISO 639-3 |
None (mis) |
Linguist list |
0yv |
| Glottolog | None |
|
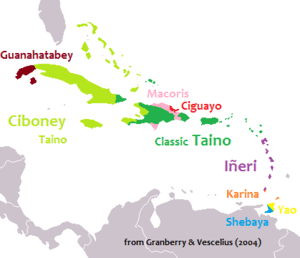
Precolombian languages of the Antilles.
Ciguayo
Ciboney Taíno, Classic Taíno, and Iñeri were Arawakan, Karina and Yao were Cariban. Guanahatabey, Macorix, and Ciguayo are unclassified. | |
Ciguayo (Siwayo) was the language of the Samaná Peninsula of Hispaniola (now the Dominican Republic) at the time of the Spanish Conquest. The Ciguayos appear to have predated the agricultural Taino who inhabited much of the island. The language appears to have been moribund at the time of Spanish contact, and within a century it was extinct.[1][2]
Little is known of Ciguayo apart from it being a distinct language from Taino and neighboring Macorix. The only attested words are "gold", tuob (presumably [tuˈob] or [ˈtwob]) and a few place names such as Quizquella (presumably [kisˈkeja]). This makes it unlikely that the language is Arawakan or Cariban, as languages of those families have simple V and CV syllable structures even in loanwords that were originally CCV or CVC. Granberry & Vescelius (2004) speculate that the closest parallels might be in the Tolan languages of Honduras.[3]
See also
References
- ↑ Granberry, Julian (2012). "Lenguas indígenas del caribe" (PDF). Cuba Arqueológica. 5 (1): 5–11.
- ↑ Guitar, Lynne (2005). "Following Linguistic Trails across Half a Millennium Provides New Answers to Old Questions". H-LatAm (H-Net).
- ↑ Granberry, Julian, & Gary Vescelius (2004). Languages of the Pre-Columbian Antilles. Tuscaloosa, AL: University of Alabama Press. ISBN 0-8173-5123-X.