Chromogranin A
| CHGA | |||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| |||||||||||||||
| Identifiers | |||||||||||||||
| Aliases | CHGA, CGA, chromogranin A | ||||||||||||||
| External IDs | OMIM: 118910 MGI: 88394 HomoloGene: 976 GeneCards: CHGA | ||||||||||||||
| RNA expression pattern | |||||||||||||||
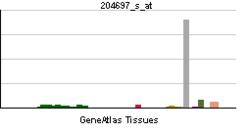 | |||||||||||||||
| More reference expression data | |||||||||||||||
| Orthologs | |||||||||||||||
| Species | Human | Mouse | |||||||||||||
| Entrez | |||||||||||||||
| Ensembl |
|
||||||||||||||
| UniProt | |||||||||||||||
| RefSeq (mRNA) | |||||||||||||||
| RefSeq (protein) | |||||||||||||||
| Location (UCSC) | Chr 14: 92.92 – 92.94 Mb | Chr 12: 102.55 – 102.57 Mb | |||||||||||||
| PubMed search | [1] | [2] | |||||||||||||
| Wikidata | |||||||||||||||
| View/Edit Human | View/Edit Mouse |
Chromogranin A or parathyroid secretory protein 1 (gene name CHGA) is a member of the granin family of neuroendocrine secretory proteins, i.e., it is located in secretory vesicles of neurons and endocrine cells such as islet beta cell secretory granules in pancreas. In humans, chromogranin A protein is encoded by the CHGA gene.[3]
Tissue distribution
Examples of cells producing chromogranin A (ChgA) are chromaffin cells of the adrenal medulla, paraganglia, enterochromaffin-like cells and beta cells of the pancreas. It is present in islet beta cell secretory granules.
Function
Chromogranin A is the precursor to several functional peptides including vasostatin-1, vasostatin-2, pancreastatin, catestatin and parastatin. These peptides negatively modulate the neuroendocrine function of the releasing cell (autocrine) or nearby cells (paracrine).
Chromogranin A induces and promotes the generation of secretory granules such as those containing insulin in pancreatic islet beta cells.
Clinical significance
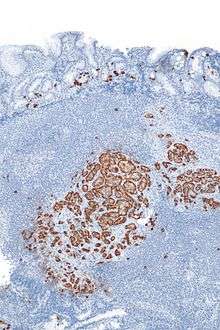
Chromogranin A is elevated in pheochromocytomas.[4] It has been identified as autoantigen in type 1 diabetes.[5] A peptide fragment of ChgA located in the Vasostatin-1, namely ChgA29-42 has been identified as the antigenic epitope recognized by diabetogenic BDC2.5 T cells from type 1 diabetes prone NOD mice.[6][7]
It is used as an indicator for pancreas and prostate cancer[8] and in carcinoid syndrome.[9] It might play a role in early neoplasic progression. Chromogranin A is cleaved by an endogenous prohormone convertase to produce several peptide fragments. See chromogranin A GeneRIFs for references. In immunohistochemistry it can be used to identify a range of neuroendocrine tumours and is highly specific for both benign and malignant cells of this type.[10]
There are considerable differences in the amino acid composition between different animals. Commercial assays for measuring human CGA can usually not be used for measuring CGA in samples from other species. Some specific parts of the molecule have a higher degree of amino acid homology and methods where the antibodies are directed against specific epitopes can be used to measure samples from different animals.[11] Region-specific assays measuring defined parts of CGA, CGB and SG2 can be used for measurements in samples from cats and dogs.[12][13][14]
References
- ↑ "Human PubMed Reference:".
- ↑ "Mouse PubMed Reference:".
- ↑ Helman LJ, Ahn TG, Levine MA, Allison A, Cohen PS, Cooper MJ, Cohn DV, Israel MA (August 1988). "Molecular cloning and primary structure of human chromogranin A (secretory protein I) cDNA". The Journal of Biological Chemistry. 263 (23): 11559–63. PMID 3403545.
- ↑ Cotesta D, Caliumi C, Alò P, Petramala L, Reale MG, Masciangelo R, Signore A, Cianci R, D'Erasmo E, Letizia C (2005). "High plasma levels of human chromogranin A and adrenomedullin in patients with pheochromocytoma". Tumori. 91 (1): 53–8. PMID 15850005.
- ↑ Stadinski BD, Delong T, Reisdorph N, Reisdorph R, Powell RL, Armstrong M, Piganelli JD, Barbour G, Bradley B, Crawford F, Marrack P, Mahata SK, Kappler JW, Haskins K (March 2010). "Chromogranin A is an autoantigen in type 1 diabetes". Nature Immunology. 11 (3): 225–31. doi:10.1038/ni.1844. PMC 3166626
 . PMID 20139986.
. PMID 20139986. - ↑ Nikoopour E, Sandrock C, Huszarik K, Krougly O, Lee-Chan E, Masteller EL, Bluestone JA, Singh B (April 2011). "Cutting edge: vasostatin-1-derived peptide ChgA29-42 is an antigenic epitope of diabetogenic BDC2.5 T cells in nonobese diabetic mice". Journal of Immunology. 186 (7): 3831–5. doi:10.4049/jimmunol.1003617. PMID 21357258.
- ↑ Nikoopour E, Cheung R, Bellemore S, Krougly O, Lee-Chan E, Stridsberg M, Singh B (April 2014). "Vasostatin-1 antigenic epitope mapping for induction of cellular and humoral immune responses to chromogranin A autoantigen in NOD mice". European Journal of Immunology. 44 (4): 1170–80. doi:10.1002/eji.201343986. PMID 24443235.
- ↑ Wu JT, Erickson AJ, Tsao KC, Wu TL, Sun CF (April 2000). "Elevated serum chromogranin A is detectable in patients with carcinomas at advanced disease stages". Annals of Clinical and Laboratory Science. 30 (2): 175–8. PMID 10807161.
- ↑ Nikou GC, Lygidakis NJ, Toubanakis C, Pavlatos S, Tseleni-Balafouta S, Giannatou E, Mallas E, Safioleas M (2005). "Current diagnosis and treatment of gastrointestinal carcinoids in a series of 101 patients: the significance of serum chromogranin-A, somatostatin receptor scintigraphy and somatostatin analogues". Hepato-Gastroenterology. 52 (63): 731–41. PMID 15966194.
- ↑ Leong, Anthony S-Y; Cooper, Kumarason; Leong, F Joel W-M (2003). Manual of Diagnostic Cytology (2 ed.). Greenwich Medical Media, Ltd. pp. 159–160. ISBN 1-84110-100-1.
- ↑ Stridsberg, M (1 June 2000). "Characterisation of N-terminal chromogranin A and chromogranin B in mammals by region-specific radioimmunoassays and chromatographic separation methods". Journal of Endocrinology. 165 (3): 703–714. doi:10.1677/joe.0.1650703.
- ↑ Stridsberg M, Pettersson A, Hagman R, Westin C, Höglund O (2014). "Chromogranins can be measured in samples from cats and dogs". BMC Research Notes. 7 (1): 336. doi:10.1186/1756-0500-7-336. PMID 24899097.
- ↑ Höglund OV, Hagman R, Stridsberg M (27 March 2015). "Chromogranin A and cortisol at intraoperative repeated noxious stimuli: Surgical stress in a dog model" (PDF). SAGE Open Medicine. 3 (0): 2050312115576432. doi:10.1177/2050312115576432. PMID 26770773.
- ↑ Srithunyarat T, Höglund OV, Hagman R, Olsson U, Stridsberg M, Lagerstedt AS, Pettersson A (2 August 2016). "Catestatin, vasostatin, cortisol, temperature, heart rate, respiratory rate, scores of the short form of the Glasgow composite measure pain scale and visual analog scale for stress and pain behavior in dogs before and after ovariohysterectomy". BMC Research Notes. 9 (1): 381. doi:10.1186/s13104-016-2193-1. PMID 27484122.
Further reading
- Hendy GN, Bevan S, Mattei MG, Mouland AJ (February 1995). "Chromogranin A". Clinical and Investigative Medicine. Médecine Clinique Et Experimentale. 18 (1): 47–65. PMID 7768066.
- Iacangelo AL, Eiden LE (August 1995). "Chromogranin A: current status as a precursor for bioactive peptides and a granulogenic/sorting factor in the regulated secretory pathway". Regulatory Peptides. 58 (3): 65–88. doi:10.1016/0167-0115(95)00069-N. PMID 8577930.
- Curry WJ, Barkatullah SC, Johansson AN, Quinn JG, Norlen P, Connolly CK, McCollum AP, McVicar CM (October 2002). "WE-14, a chromogranin a-derived neuropeptide". Annals of the New York Academy of Sciences. 971: 311–6. doi:10.1111/j.1749-6632.2002.tb04485.x. PMID 12438141.
- Curry WJ, Shaw C, Johnston CF, Thim L, Buchanan KD (April 1992). "Isolation and primary structure of a novel chromogranin A-derived peptide, WE-14, from a human midgut carcinoid tumour". FEBS Letters. 301 (3): 319–21. doi:10.1016/0014-5793(92)80266-J. PMID 1577173.
- Tamamura H, Ohta M, Yoshizawa K, Ono Y, Funakoshi A, Miyasaka K, Tateishi K, Jimi A, Yajima H, Fujii N (July 1990). "Isolation and characterization of a tumor-derived human protein related to chromogranin A and its in vitro conversion to human pancreastatin-48". European Journal of Biochemistry / FEBS. 191 (1): 33–9. doi:10.1111/j.1432-1033.1990.tb19090.x. PMID 2165909.
- Konecki DS, Benedum UM, Gerdes HH, Huttner WB (December 1987). "The primary structure of human chromogranin A and pancreastatin". The Journal of Biological Chemistry. 262 (35): 17026–30. PMID 2445752.
- Sekiya K, Ghatei MA, Minamino N, Bretherton-Watt D, Matsuo H, Bloom SR (February 1988). "Isolation of human pancreastatin fragment containing the active sequence from a glucagonoma". FEBS Letters. 228 (1): 153–6. doi:10.1016/0014-5793(88)80606-9. PMID 2830133.
- Helman LJ, Ahn TG, Levine MA, Allison A, Cohen PS, Cooper MJ, Cohn DV, Israel MA (August 1988). "Molecular cloning and primary structure of human chromogranin A (secretory protein I) cDNA". The Journal of Biological Chemistry. 263 (23): 11559–63. PMID 3403545.
- Wilson BS, Phan SH, Lloyd RV (February 1986). "Chromogranin from normal human adrenal glands: purification by monoclonal antibody affinity chromatography and partial N-terminal amino acid sequence". Regulatory Peptides. 13 (3-4): 207–23. doi:10.1016/0167-0115(86)90040-6. PMID 3704195.
- Deftos LJ, Murray SS, Burton DW, Parmer RJ, O'Connor DT, Delegeane AM, Mellon PL (May 1986). "A cloned chromogranin A (CgA) cDNA detects a 2.3Kb mRNA in diverse neuroendocrine tissues". Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications. 137 (1): 418–23. doi:10.1016/0006-291X(86)91226-X. PMID 3718511.
- Hagn C, Schmid KW, Fischer-Colbrie R, Winkler H (October 1986). "Chromogranin A, B, and C in human adrenal medulla and endocrine tissues". Laboratory Investigation; A Journal of Technical Methods and Pathology. 55 (4): 405–11. PMID 3762065.
- Murray SS, Deaven LL, Burton DW, O'Connor DI, Mellon PL, Deftos LJ (January 1987). "The gene for human chromogranin A (CgA) is located on chromosome 14". Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications. 142 (1): 141–6. doi:10.1016/0006-291X(87)90462-1. PMID 3814131.
- Cetin Y, Aunis D, Bader MF, Galindo E, Jörns A, Bargsten G, Grube D (March 1993). "Chromostatin, a chromogranin A-derived bioactive peptide, is present in human pancreatic insulin (beta) cells". Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. 90 (6): 2360–4. doi:10.1073/pnas.90.6.2360. PMC 46086
 . PMID 8096340.
. PMID 8096340. - Mouland AJ, Bevan S, White JH, Hendy GN (March 1994). "Human chromogranin A gene. Molecular cloning, structural analysis, and neuroendocrine cell-specific expression". The Journal of Biological Chemistry. 269 (9): 6918–26. PMID 8120054.
- Maruyama K, Sugano S (January 1994). "Oligo-capping: a simple method to replace the cap structure of eukaryotic mRNAs with oligoribonucleotides". Gene. 138 (1-2): 171–4. doi:10.1016/0378-1119(94)90802-8. PMID 8125298.
- Simon-Chazottes D, Wu H, Parmer RJ, Rozansky DJ, Szpirer J, Levan G, Kurtz TW, Szpirer C, Guenet JL, O'Connor DT (July 1993). "Assignment of the chromogranin A (Chga) locus to homologous regions on mouse chromosome 12 and rat chromosome 6". Genomics. 17 (1): 252–5. doi:10.1006/geno.1993.1316. PMID 8406464.
- Mahata SK, Kozak CA, Szpirer J, Szpirer C, Modi WS, Gerdes HH, Huttner WB, O'Connor DT (April 1996). "Dispersion of chromogranin/secretogranin secretory protein family loci in mammalian genomes". Genomics. 33 (1): 135–9. doi:10.1006/geno.1996.0171. PMID 8617499.
- Strub JM, Goumon Y, Lugardon K, Capon C, Lopez M, Moniatte M, Van Dorsselaer A, Aunis D, Metz-Boutigue MH (November 1996). "Antibacterial activity of glycosylated and phosphorylated chromogranin A-derived peptide 173-194 from bovine adrenal medullary chromaffin granules". The Journal of Biological Chemistry. 271 (45): 28533–40. doi:10.1074/jbc.271.45.28533. PMID 8910482.