Circassia
| Circassia | ||||||||||
| Адыгэ Хэку | ||||||||||
| ||||||||||
|
| ||||||||||
 Circassia in 1750 | ||||||||||
| Capital | Sochi | |||||||||
| Languages | Circassian | |||||||||
| Religion | Islam, Christianity, Traditional | |||||||||
| Government | Confederation | |||||||||
| History | ||||||||||
| • | Established | c. 1500 | ||||||||
| • | Russian–Circassian War | 1763–1864 | ||||||||
| • | Disestablished | 1864 | ||||||||
| ||||||||||
Circassia (Adyghe: Адыгэ Хэку,[1] Russian: Черке́сия, Georgian: ჩერქეზეთი, Arabic: شيركاسيا[2]) is a region in the North Caucasus and along the northeast shore of the Black Sea.[3] It is the ancestral homeland of the Circassian people.
Name

The name Circassia is a Latinisation of Cherkess (modern Turkish: Çerkes), the Turkic name for the Adyghe people, and originated in the 15th century with medieval Genoese merchants and travellers to Circassia.[4][5] The name Cherkess is traditionally applied to the Adyghe by neighbouring Turkic peoples (principally Crimean Tatars[6] and Ottoman Turks[7]).
Another historical name for the country was Zyx or the Zygii. The Zygii have been described by the ancient Greek intellectual Strabo as a nation to the north of Colchis.
At the end of the 15th century a detailed description of Circassia and of its inhabitants was made by Genoese traveller and ethnographer Giorgio Interiano.[8]
Geography
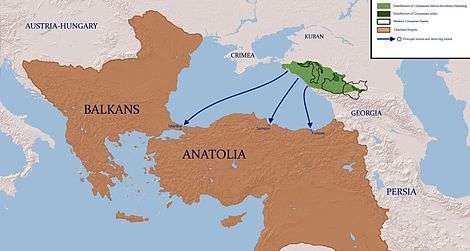
Circassia was located in Eastern Europe, near the northeastern Black Sea coast. Before the Russian conquest of the Caucasus (1763–1864), it covered the entire fertile plateau and the steppe of the northwestern region of the Caucasus, with an estimated population of between 3 and 4 million.
Circassia’s historical great range extended from the Taman Peninsula in the west, to the town of Mozdok in today’s North Ossetia–Alania in the east. Historically, Circassia covered the southern half of today’s Krasnodar Krai, the Republic of Adygea, Karachay-Cherkessia, Kabardino-Balkaria, and parts of North Ossetia–Alania and Stavropol Krai, bounded by the Kuban River on the north which separated it from the Russian Empire.
Sochi is considered by many Circassians as their traditional capital city.[9] According to Circassians, the 2014 Winter Olympic village is built in an area of mass graves of Circassians after their defeat by the Russians in 1864.[10]
History
- 1237 – Historian Rashid-ad-Din in the Persian Chronicles, wrote that the Circassian king Tukar was killed in battle against the Mongols.[11]
- 1333 – In his letter, Pope John XXII (to the king Zichia (Circassia) Verzacht ["Верзахта" in Cyrillic script]), the Rome (Avignon) Pontiff thanks the Governor of Circassians for his assistance in implementing the Christian faith among the Adygs (Circassians).[12] Verzacht's power and status was so high that his example was followed by the rest of the Circassian princes: They took the Roman Catholic faith.
- 1471 – A contract was signed between the ruler of Circassia and the ruler of Caffa, naming another ruler Zichia - "Petrezok, the paramount lord of Zichia".[13] Under the contract, Zichia would supply large quantities of grain in the Cаffа.
- The region was famed for its beautiful women, many of whom were married to the Ottoman sultan and Persian Shahs and had influential positions in the Imperial Harem.
- Most of the population was expelled from their country to the neighboring Ottoman Empire in the late 19th century after the Russian–Circassian War. Today, about 700,000 Circassians remain in historical Circassia in today's Russia. The 2010 Russian Census recorded 718,727 Circassians, of which 516,826 are Kabardians, 124,835 are Adyghe proper, 73,184 are Cherkess and 3,882 Shapsugs.[14] The largest Circassian population resides in Turkey (pop. 1,400,000 – 6,000,000).[15][16] In other countries like Jordan, Syria, Iraq, Iran, Lebanon, Serbia, Egypt and Israel Circassian population also exists, but is considerably smaller [17][18]
- Circassian nationalism has only recently developed and calls for a restoration of the native homelands.
Conquest by Russia
Population
Under Russian and Soviet rule, ethnic and tribal divisions between Circassians (and other peoples) were promoted, resulting in several different statistical names being used for various parts of the Circassian people (Adyghes, Cherkess, Kabardins, Shapsugs). Consequently, there is an effort among Circassians to unite under the name Circassian (Adyghe) in Russian Censuses to reflect and revive the concept of the Circassian nation. The majority of the diaspora already tends to call itself "Circassian".
See also
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Circassia. |
References
- ↑ http://aheku.org/ (Russian)
- ↑ http://www.circassianews.com/ (Arabic)
- ↑
 Chisholm, Hugh, ed. (1911). "Circassia". Encyclopædia Britannica. 6 (11th ed.). Cambridge University Press. pp. 380–381.
Chisholm, Hugh, ed. (1911). "Circassia". Encyclopædia Britannica. 6 (11th ed.). Cambridge University Press. pp. 380–381. - ↑ Latham, R. G. Descriptive Ethnology. London, J. Van Voorst, 1859. p. 50.
- ↑ Latham, R. G. Elements of Comparative Philology. London, Walton and Maberly, 1862. p. 279.
- ↑ Taitbout, De Marigny. Three Voyages in the Black Sea to the Coast of Circassia. London, 1837. pp. 5–6.
- ↑ Guthrie, William, James Ferguson, and John Knox. A New Geographical, Historical and Commercial Grammar and Present State of the Several Kingdoms of the World ... Philadelphia, Johnson & Warner, 1815. P. 549.
- ↑ Biblioteca Italiana.Vita de' Zichi chiamati Ciarcassi di G. Interiano (Latin)
- ↑ Home thoughts from abroad: Circassians mourn the past—and organise for the future. The Economist. 2012-05-26.
- ↑ Spelen zijn op massagraven. Nederlandse Omroep Stichting 2014-02-03
- ↑ Рашид ад-Дин. Сборник летописей. М.-Л., 1952. Т. 2. С. 39
- ↑ Колли Л. Кафа в период владения ею банком св. Георгия (1454—1475) // Известия Таврической Ученой Архивной комиссии. № 47. Симферополь, 1912. С. 86
- ↑ Kressel R. Ph. The Administration of Caffa under the Uffizio di San Giorgio. University of Wisconsin, 1966. P. 396
- ↑ "Russian Census 2010: Population by ethnicity". 2010. Retrieved 2015-12-16.
- ↑ "TURKEY'S CIRCASSIANS DEMAND FREEDOM TO TRAVEL TO ABKHAZIA". 2009. Retrieved 2015-12-16.
- ↑ "Country: Turkey / People groups: Kabardian + Adyge". 2015. Retrieved 2015-12-16.
- ↑ "World: Europe Circassians flee Kosovo conflict". BBC News. 1998-08-02. Retrieved 2008-07-06.
- ↑ "N.J. Circassians join international group to protest Winter Olympics in Russia". NJ.com.
Bibliography
- Bullough, Oliver. Let Our Fame Be Great: Journeys Among the Defiant People of the Caucasus. Allen Lane, 2010. ISBN 978-1846141416
- Jaimoukha, Amjad. The Circassians: A Handbook, London: Routledge, New York: Routledge & Palgrave, 2001. ISBN 978-0700706440
- Jaimoukha, Amjad. Circassian Culture and Folklore: Hospitality, Traditions, Cuisine, Festivals and Music. Bennett & Bloom, 2010. ISBN 978-1898948407
- Richmond, Walter. The Circassian Genocide, Rutgers University Press, 2013. ISBN 9780813560694
- Caucasian highlanders (Повседневная жизнь горцев Cеверного Кавказа в XIX в.). Everyday life of the Caucasian highlanders. The 19th century (In the co-authorship with I. Karpeev). Moscow: Molodaya Gvardiy, 2003. ISBN 5-235-02585-7
- Journal of a residence in Circassia during the years 1837, 1838, and 1839 - Bell, James Stanislaus (English)

