Chairman of the Senate of Pakistan
| Chairman of the Senate of Pakistan | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Style |
Mr. Chairman (Informal and within the Senate) Chairman Senate (Formal) |
| Appointer | Elected by the Pakistan Senate |
| Term length | 3 years |
| Formation |
Constitution of Pakistan (12 April 1973) |
| First holder |
Habibullah K. Marwat (12 April 1973) |
| Succession | Second |
| Website | Chairman Senate |
 |
| This article is part of a series on the politics and government of Pakistan |
| Constitution |
|
The Chairman of the Senate of Pakistan (Urdu: ﭽئرمين سينـﭧ; informally as Chairman senate), is the president-chair of the Senate of Pakistan.[1] According to the Constitution of Pakistan, the chairman is a presiding official and that Senate must choose a chairman and deputy chairman for a time interval of three years.[2]
During the President's absence, the chairman senate is empowered with the duties of the presidency; in rare events involving the absence of the chairman, the presidential duties are usually held by Speaker National Assembly.[3] The Chairman of the Senate is the second in the line of succession to the President of Pakistan, ahead of the Speaker National Assembly.[4]
The Chairman of the Senate was Habibullah Marwat while Wasim Sajjad remains the longest-serving chairman. Raza Rabbani, a PPP leader and senior senator from Sindh, is the current Chairman of the Senate, having assumed office on 12 March 2015.[5]
Role and responsibilities
The office of Chairman of the Senate is created by Article 60(1) of the Chapter 2 in Part III of the Constitution of Pakistan:[1]
After the Senate has been duly constituted, it shall, at its first meeting and to the exclusion of any other business, elect from amongst its members a chairman and a Deputy chairman and, so often as the office of chairman or Deputy chairman becomes vacant, the Senate shall elect another member as chairman or, as the case may be, Deputy chairman
The term of office of the chairman or Deputy chairman shall be 3 years from the day on which he enters upon his office.
The main purpose for the creation of the Senate was to give equal representation to all the federating units since the membership of the National Assembly was based on the population of each four province.[6] Equal provincial membership in the Senate, thus, balances the provincial inequality in the National Assembly and dispels doubts and apprehension, if any, regarding deprivation and exploitation.[6]
The role of the Senate is to promote national cohesion and harmony and to alleviate fears of the smaller provinces regarding domination by any one province because of its majority, in the National Assembly.[6]
The Senate act as an legislative institution that represents the provinces and territories of the country and promotes a feeling of equality, peace and good understanding between them, which is so essential for the growth and prosperity of a nation.[6] Thus, the Senate in Pakistan, over the years, has emerged as an essential organ and a stabilizing factor of the federation.[6]
History
After creation of Pakistan on 14 August 1947, the first Constituent Assembly, elected in December 1945 in undivided India, was assigned the task of framing the Constitution of Pakistan. This Assembly passed the Objectives Resolution on 12 March 1949, laying down principles which later became substantive part of the Constitution of Pakistan.[7] However, before it could accomplish the task of framing the constitution, it was dissolved in 1954.[7] Thereafter, the Governor General, convened the Second Constituent Assembly in 1955, which framed and passed the first Constitution of Pakistan on 29 February 1956.[7] That Constitution was promulgated on 23 March 1956, which provided for a parliamentary form of Government with a unicameral legislature.[7] However, from 14 August 1947 to 1 March 1956 the Government of India Act, 1935, was retained as the Constitution of Pakistan.[7]
On 7 October 1958, Martial Law was promulgated and the Constitution abrogated. The Military Government appointed a Constitution Commission in February 1960 which framed the 1962 Constitution.[7] That Constitution provided for a Presidential form of Government with a unicameral legislature. The 1962 Constitution was abrogated on 25 March 1969.[7] The Civil Government, which came to power in December 1971 pursuant to 1970 elections, gave the nation an interim Constitution in the year 1972.[7]
In 1973, the constitutional conventional framed the comprehensive Constitution which was rectify on 12 April and promulgated on 14 August 1973.[7] Retired Senior Justice Habibullah Khan Marwat was elected its first chairman and remained until 1977.[7] The 1973 Constitution also provided a parliamentary system of government with a bicameral legislature: the National Assembly (lower house) and the Senate (upper house). The membership of the Senate, which was originally 45, was raised to 63 in 1977 and to 87 in 1985.[7] In 2002, the membership rose to 100 through the legal framework enforced on 21 August 2002.[7]
Relationship between Constituents of the Parliament
The Parliament of Pakistan consists of the President and the two legislative houses: National Assembly (lower house) and the Senate (upper house).[8]
The President is elected by members of both Houses of the Parliament and the four provincial assemblies.[9] The President may be removed from office or impeached through a resolution, passed by not less than two-thirds of the total membership of the Parliament in a joint sitting of the two Houses, convened for the purpose.[10] In case the office of the president becomes vacant for any reason, the chairman, or if he is unable to perform the functions of the office of the president, the Speaker, acts as president till such time that a president is elected.[1] Same is the case when the president by reason of absence from Pakistan or any other cause is unable to perform his functions.[1]
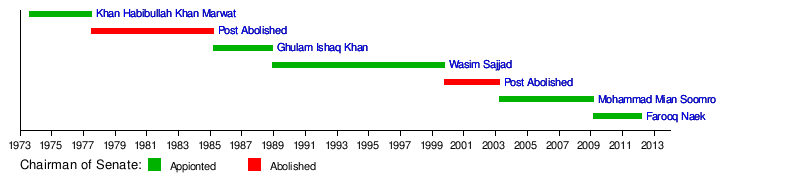
List of Chairman of the Senate
Republican Party/Pakistan Muslim League
| Name | Entered office | Left office | Date of Birth and Death | Political party | Provinces | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Habibullah Khan | 6 August 1973 | 5 August 1975 | 5 December 1978 (aged 77) | Pakistan Peoples Party | Khyber-Pakhtunkhwa |
| 6 August 1975 | 4 July 1977 | |||||
| 2 | Ghulam Ishaq Khan | 21 March 1985 | 20 March 1988 | 27 October 2006 (aged 91) | Independent | Khyber-Pakhtunkhwa |
| 21 March 1988 | 12 December 1988 | |||||
| 3 | Wasim Sajjad | 24 December 1988 | 20 March 1991 | 30 March 1941 | Pakistan Muslim League (N) | Punjab |
| 21 March 1991 | 20 March 1994 | |||||
| 21 March 1994 | 20 March 1997 | |||||
| 21 March 1997 | 12 October 1999 | |||||
| 4 | Mohamad Mian Soomro | 23 March 2003 | 22 March 2006 | 19 August 1950 | Pakistan Muslim League (Q) | Sindh |
| 23 March 2006 | 11 March 2009 | |||||
| 5 | Farooq Naek | 12 March 2009 | 11 March 2012 | 3 January 1950 | Pakistan Peoples Party | Sindh |
| 6 | Nayyar Bukhari | 12 March 2012 | 12 March 2015 | 23 December 1952 | Pakistan Peoples Party | Sindh |
| 7 | Raza Rabbani | 12 March 2015 | 23 July 1952 | Pakistan Peoples Party | Sindh | |
Time Line
See also
References
- 1 2 3 4 5 Article 60(1) of the Chapter 2: Majlis-e-Shoora (Parliament) in Part III of the Constitution of Pakistan.
- ↑ Article 60(2), 63(6–7) of the Chapter 2: Majlis-e-Shoora (Parliament) in Part III of the Constitution of Pakistan.
- ↑ Article 49(1) of the Chapter 1: The President in Part III of the Constitution of Pakistan.
- ↑ Article 49(2) of the Chapter 1: The President in Part III of the Constitution of Pakistan.
- ↑ Senate chairman. "Chairman of the Senate". http://www.senate.gov.pk/. Senate of Pakistan press. Archived from the original on 26 April 2015. Retrieved 29 April 2015. External link in
|website=(help) - 1 2 3 4 5 Senate. "Brief History". http://www.senate.gov.pk/. Senate press release. Retrieved 29 April 2015. External link in
|website=(help) - 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 Senate, pdf. "Senate of Pakistan" (PDF). http://www.senate.gov.pk/. Senate, pdf format. Retrieved 29 April 2015. External link in
|website=(help) - ↑ Article 50 in Chapter 2 of the Part III of the Constitution of Pakistan
- ↑ Article 41(3) in Chapter 1 of the Part III of the Constitution of Pakistan
- ↑ Article 47(1)-47(8) in Chapter 2 of the Part III of the Constitution of Pakistan
