Castle of Bouka
Coordinates: 38°57′04″N 20°45′22″E / 38.95113°N 20.75610°E
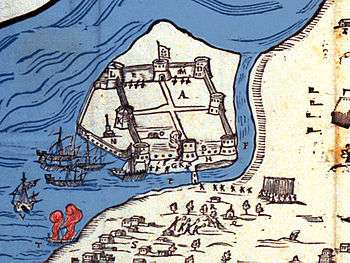
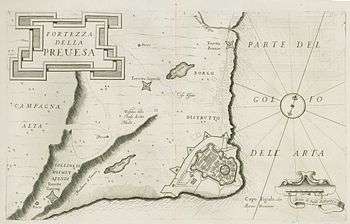
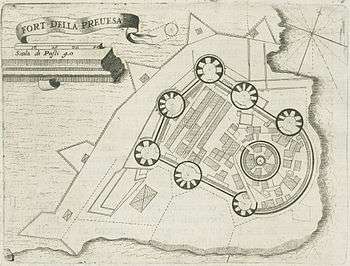
The castle of Bouka (Greek: Κάστρο της Μπούκας, from the Italian word bocca) was the first major Ottoman fortification of Preveza, in northwestern Greece. It was constructed by the Ottomans in 1478 and controlled the straits of the Ambracian Gulf.[1][2] In 1701, the Venetians blew the castle up before they handed Preveza over to the Ottomans, according to the terms of the Treaty of Karlowitz.[3]
The castle of Bouka was standing upon the site which today is called "Paliosaraga" (Παλιοσάραγα, "Old Seraglio"). The summer seraglio of Ali Pasha of Yannina was built on the castle's remains, during the early 1810s.[4] After Preveza's liberation by the Greek Army in 1912, an army supply unit was based on the site of the castle.[5] Today, there are very few remains of the castle of Bouka, despite the fact that the site has generally not been built up.[1]
History
The castle was built by the Ottomans in 1478, fifteen years after their definite occupation of the region of Preveza and Riniassa.[2] The date of the castle's construction is also mentioned in the Short Chronicle number 71.7: ἔκτισεν τὴν Πρέβεζαν ἐπὶ ἔτους ‚ςϡπς΄, "he fortified Preveza in the year 6986 [Anno Mundi]". The year 6986 Anno Mundi corresponds to 1.9.1477-31.8.1478 in the Gregorian calendar. The construction of the castle at the mouth of the Ambracian Gulf was immediately recognized by Leonardo III Tocco, Count of Cephalonia, in a manuscript letter written on 31 March 1478, as a danger for the Republic of Venice. Because of this, he sent his relative, Bogordo di Tocco, to Venice in order to seek its assistance.[1][2] In this letter the castle is mentioned as "castello ala bucca delo gulfo" ("castle at the mouth/entrance of the gulf").[6]
The castle was presumably strengthened by the Ottomans in 1486-87, as well as in 1495 in order to ward off the imminent danger from the West, due to the conquering plans of the French king Charles VIII, which, however, were eventually abandoned. The castle was also improved in 1530, in 1553 during the reign of Suleiman the Magnificent, and by the Venetians, after they conquered Preveza in 1684.[2] The castle was demolished by the Venetians in 1701, before surrendering the area to the Ottomans, in accordance to the provisions of the Treaty of Karlowitz and other bilateral agreements.[3]
Immediately after the demolition of the castle of Bouka and the handing over of Preveza, the Ottomans started constructing a large castle in order to defend the town and the straits of the Ambracian Gulf. The new stronghold was built one kilometre north of the demolished castle, at a distance of a cannon-shot from it, and it is now known as St. Andrew's Castle (its name during the late Ottoman times was Iç Kale).[3]
References
- 1 2 3 Nikos D. Karabelas, 2010, The castle of Bouka (1478-1701), [in Greek].
- 1 2 3 4 Nikos D. Karabelas, 2015, The Ottoman conquest of Preveza and its first castle
- 1 2 3 Nikos D. Karabelas, 2012, The first phase of the castle of İç kale in Preveza, pp. 48-49.
- ↑ Nikos D. Karabelas, 2009, Henry Holland in Preveza, pp. 155-156, subnote 34
- ↑ Regional District of Preveza, www.preveza.gr, Castle of Bouka (in Greek), accessed on 18.11.2013
- ↑ According to Nikos D. Karabelas, 2015, p. 978: A letter by Leonardo III Tocco addressed to Filippo Foscari, member of a powerful Venetian family, written in Lefkas on 31 March 1478, filed in the Archivio di Stato di Venezia, Scuola di Santa Maria del Rosario, b. 29, Processo X, ff. 25r. The letter has been published apart from Karabelas, in the following papers: Professor Dr. Chryssa Maltezou, Προσωπογραφικά βυζαντινής Πελοποννήσου και ξενοκρατούμενου ελληνικού χώρου (με αφορμή τον φάκελο Foscari της Βενετίας), Βυζαντινά Σύμμεικτα vol. 5, 1983, pp. 1-27; Spyros N. Asonitis, Το Νότιο Ιόνιο κατά τον Όψιμο Μεσαίωνα. Κομητεία Κεφαλληνίας, Δουκάτο Λευκάδας, Αιτωλοακαρνανία, Athens, 1985, p. 212, subnote 152.
Sources
- Nikos D. Karabelas, 2010: The castle of Bouka (1478-1701). Fortified Preveza through sources, in: Preveza B. Proceedings of the Second International Symposium for the History and Culture of Preveza (16–20 September 2009), Preveza, 2010, vol. I, pp. 395–433; Editors: Marina Vrelli-Zachou, Christos Stavrakos; Publishers: University of Ioannina, Municipality of Preveza, Actia Nicopolis Foundation; ISBN 978-960-99475-0-3 / ISBN 978-960-99475-1-0
- Nikos D. Karabelas, 2012: Ottoman Fortifications in Preveza in 1702. The First Phase of the Castle of İç Kale, Journal of the Center for Ottoman Studies, Ankara University (OTAM) 32, Ankara, 2012, pp. 47–66
- Nikos D. Karabelas, 2015: The Ottoman conquest of Preveza and its first castle, Proceedings of the XVIth Congress of Turkish History (20–24 September 2010), Ankara, 2015, vol. 4.2, pp. 967–998; Publisher: Türk Tarih Kurumu; ISBN 978-975-16-2982-1 / ISBN 978-975-16-2988-3
Gallery
 Woodcut of the Castle of Bouka by Francesco Genesio, 1538
Woodcut of the Castle of Bouka by Francesco Genesio, 1538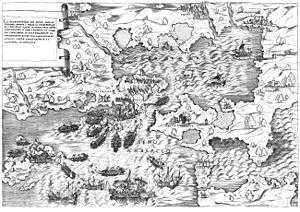 Etching of the Castle of Bouka by Antonio Salamanca, 1540 c.
Etching of the Castle of Bouka by Antonio Salamanca, 1540 c.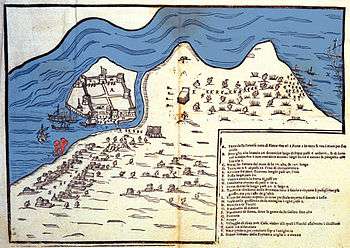 Plan of the castle of Bouka. Engraving by Giovanni Orlandi, 1605
Plan of the castle of Bouka. Engraving by Giovanni Orlandi, 1605 Etching of the Castle of Bouka by Giuseppe Longhi, 1684 c.
Etching of the Castle of Bouka by Giuseppe Longhi, 1684 c. Etching of the Castle of Bouka by Giovanni Giacomo de Rossi, 1687
Etching of the Castle of Bouka by Giovanni Giacomo de Rossi, 1687 Woodcut of the Castle of Bouka by Leonhard Loschge, 1687
Woodcut of the Castle of Bouka by Leonhard Loschge, 1687 Etching of the Castle of Bouka by Vincenzo Coronelli, 1688
Etching of the Castle of Bouka by Vincenzo Coronelli, 1688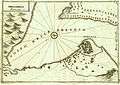 Etching of the Castle of Bouka by Vincenzo Coronelli, 1707
Etching of the Castle of Bouka by Vincenzo Coronelli, 1707 Etching of the Castle of Bouka by Vincenzo Coronelli, 1707
Etching of the Castle of Bouka by Vincenzo Coronelli, 1707
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Castle of Bouka. |