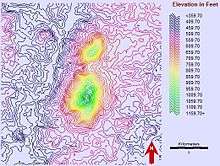
Battle Mountain, Virginia
| Battle Mountain | |
|---|---|
 The western slope of Battle Mountain, Castleton, Virginia | |
| Highest point | |
| Elevation | 1,162 ft (354 m) |
| Prominence | 762 ft (232 m) |
| Coordinates | 38°39′26″N 78°3′36″W / 38.65722°N 78.06000°W |
| Geography | |
| Location | Rappahannock County, Virginia, U.S. |
| Parent range | Blue Ridge Mountains |
| Topo map | USGS Massies Corner, Va. |
| Geology | |
| Age of rock | 704,000,000 years |
| Mountain type | Stratovolcano |
| Volcanic belt | Robertson River Igneous Suite |
| Last eruption |
704 Mya |
Geology

Battle Mountain is an igneous mountain in Rappahannock County, Virginia. The eastern slope is generally considered to reside in the unincorporated town of Amissville, Virginia while the western slope is generally considered to be within Castleton, Virginia. The entire mountain including the summit lies within private property at an elevation of 1,162 ft (354.2 m).[1]
Tectonic Emplacement and Geochronology
It is an extinct volcano dating to the Neoproterozoic and is approximately 704 million years old (+/- 4 million years) as dated using the U-Pb zircon crystal geochronology method. It is a unit of the Robertson River Igneous Suite [2] and is located within the Blue Ridge anticlinorium. This volcanic formation was a result of crustal extensional rifting of the eastern Laurentian margin of the supercontinent Rodinia.[3] This was the beginning of a chain of events that ultimately gave birth to the precursor Atlantic, the Iapetus Ocean at 550 Ma during the Ediacaran–Cambrian transition.[4]
Geochemical Evolution
The volcano is composed of alkali feldspar granitic rock of the Robertson River Igneous Suite. This includes felsic complex material such as biotite, hornblende-biotite, magnetite, and alkali granitic rock including rhyolite on the eastern slopes of Battle Mountain[5] and the adjacent (and geologically related) Little Battle Mountain (elevation 937 feet).
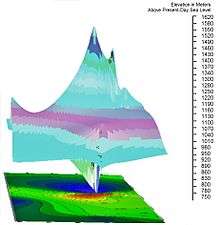



Paleaogeographic Reconstruction
A unique geological feature of Battle Mountain is that the western slope outcrops are composed entirely of alkalai feldspar granite, while the eastern slope up to and including the summit is entirely rhyolitic. This provides strong evidence of a theorized lateral explosive eruption event centered on the eastern slope at approximately 704 Ma as proposed by Woolman (2016). Further mathematical geology evidence which supports this theory includes a paleaogeographic reconstruction of the mountain by Woolman utilizing artificial neural networks and Markov chain geostatistical models including period climate condition-based soil erosion rates, Kirkby's hillslope movement evolution equations and recursive biogeochemical soil erosion rates in felsic granitic conditions. The result was the digital reconstruction image shown on the left, indicating what Battle Mountain may have looked like 704 million years ago on the western slope.

Only Known Volcanic Mountains in Rappahannock County, VA
Battle Mountain and Little Battle Mountain are the only mountains in Rappahannock County which are known to be volcanic in origin, and are among the oldest visibly intact extinct volcanoes in Virginia. White quartz boulders and smaller fragments are common on and around Battle Mountain, a result of molten silica that was contained in the rhyolite lava and granitic magma that formed the volcano. As quartz is extremely hard relative to feldspar granite and rhyolite, it tends to remain present on the surface while the softer granite it was embedded in wears away into the soil.

Role in the War Between the States
In Progress.
Access
The nearest unincorporated town is Amissville, Virginia at approximately 4 miles away. Access to the mountain and the summit must be negotiated with local landowners first as the mountain, including all portions of the July, 1863 battlefield exists entirely on private property.
References
- ↑ "Robertson River Igneous Suite; Battle Mountain Alkali Feldspar Granite - felsite". www.usgs.gov. Retrieved 21 August 2016.
- ↑ Richard P. Tollo and Sara Arav (1992). "The Robertson River Igneous Suite (Blue Ridge Province, Virginia)—Late Proterozoic anorogenic (A-type) granitoids of unique petrochemical affinity. Basement Tectonics 8 (pp. 425-441).". Springer Netherlands. Retrieved 2016-08-07.
- ↑ Richard P. Tollo, John N. Aleinikoff (1996-11-01). "Petrology and U-PB geochronology of the Robertson River Igneous Suite, Blue Ridge province, Virginia - Evidence for multistage magmatism associated with an early episode of Laurentian rifting". American Journal of Science. Retrieved 2016-08-22.
- ↑ Birthdate for the lapetus Ocean? A precise U-Pb zircon and baddeleyite age for the Long Range dikes, southeast Labrador
- ↑ Thomas A. Woolman (2016-04-01). "A Gallium Anomaly Utilized in Palaeogeographic Reconstruction of Battle Mountain, Rappahannock County, Virginia". Kansas Academy of Science. Retrieved 2016-07-14.