Argon plasma coagulation
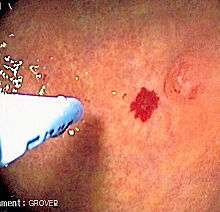
Argon plasma coagulation or APC is a medical endoscopic procedure used primarily to control bleeding from certain lesions in the gastrointestinal tract, and also sometimes to debulk tumours in the case of patients for whom surgery is not recommended. It is administered during esophagogastroduodenoscopy or colonoscopy.
APC involves the use of a jet of ionized argon gas (plasma) that is directed through a probe passed through the endoscope. The probe is placed at some distance from the bleeding lesion, and argon gas is emitted then ionized by a high voltage discharge (approx 6kV).[1] High-frequency electric current is then conducted through the jet of gas, resulting in coagulation of the bleeding lesion on the other end of the jet. As no physical contact is made with the lesion, the procedure is safe if the bowel has been cleaned of colonic gases,[2][3] and can be used to treat bleeding in parts of the gastrointestinal tract with thin walls, such as the cecum. The depth of coagulation is usually only a few millimetres.
APC is used to treat the following conditions:
- angiodysplasiae, anywhere in the GI tract
- gastric antral vascular ectasia, or watermelon stomach
- colonic polyps, after polypectomy
- radiation proctitis
- esophageal cancer
One of the complications of cirrhosis is constriction and twisting of blood vessels (varix) due to portal hypertension, including esophageal varices, gastric varices, and intestinal varices. The most common cause of death in cirrhosis is bleeding from varicies. Closing off these varices with laser coagulation is one of the treatments that has been attempted.[4] It appears that endoscopic banding ligation in combination with argon plasma coagulation is one of the most successful approaches.[4]
See also
References
- ↑ http://www.mibalongastrico.comwww.gastrointestinalatlas.com/English/Colon_and_Rectum/Radiation_Colitis/radiation_colitis.html[][]
- ↑ Ladas, SD; Karamanolis, G; Ben-Soussan, E (2007). "Colonic gas explosion during therapeutic colonoscopy with electrocautery". World journal of gastroenterology. 13 (40): 5295–8. doi:10.3748/wjg.v13.i40.5295. PMID 17879396.
- ↑ Ben-Soussan, E; Antonietti, M; Savoye, G; Herve, S; Ducrotté, P; Lerebours, E (2004). "Argon plasma coagulation in the treatment of hemorrhagic radiation proctitis is efficient but requires a perfect colonic cleansing to be safe". European journal of gastroenterology & hepatology. 16 (12): 1315–8. doi:10.1097/00042737-200412000-00013. PMID 15618838.
- 1 2 Shi, KQ; et al. (August 2013). "Secondary prophylaxis of variceal bleeding for cirrhotic patients: a multiple-treatments meta-analysis.". European journal of clinical investigation. 43 (8): 844–54. PMID 23725530.