71 Niobe
|
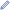
Three-dimensional model of 71 Niobe created based on light-curve. | |
| Discovery | |
|---|---|
| Discovered by | Karl Theodor Robert Luther |
| Discovery date | August 13, 1861 |
| Designations | |
Named after | Niobe |
| Main belt | |
| Orbital characteristics[1] | |
| Epoch December 31, 2006 (JD 2454100.5) | |
| Aphelion | 484.945 Gm (3.242 AU) |
| Perihelion | 339.408 Gm (2.269 AU) |
| 412.176 Gm (2.755 AU) | |
| Eccentricity | 0.177 |
| 1670.455 d (4.57 a) | |
Average orbital speed | 17.80 km/s |
| 13.883° | |
| Inclination | 23.256° |
| 316.094° | |
| 267.445° | |
| Physical characteristics | |
| Dimensions | 83.4 km |
| Mass | 6.1×1017 kg |
| 0.0233 m/s² | |
| 0.0441 km/s | |
| 35.864 ± 0.001 hours[2] | |
| Albedo | 0.305 [3] |
| Temperature | ~168 K |
Spectral type | S |
| 7.30 | |
|
| |
71 Niobe (/ˈnaɪ.əbiː/ NY-ə-bee) is a large, slowly rotating main-belt asteroid. It was discovered by the German astronomer Robert Luther on August 13, 1861, and named after Niobe, a character in Greek mythology. In 1861, the brightness of this asteroid was shown to vary by German astronomer Friedrich Tietjen.[4]
In 2006, it was examined by radar using the Arecibo Observatory radio telescope in Puerto Rico. This was supplemented by optical observations intended to build a lightcurve. The resulting estimated rotation period of 35.6 hours, or 1.48 Earth days, superseded an earlier estimate of the rotation period as 14.3 hours. The radar data produced an estimate of a maximum equatorial diameter of 94 km, which is consistent with earlier estimates based upon infrared data if the shape is assumed to be slightly elongated.[5]
The rotation period was further refined to 35.864 ± 0.001 hours during observations through 2010. Six stellar occultations of this asteroid between 2004 and 2007 produced chords ranging from 13–72 km (8–45 mi), which are statistically consistent with the published maximum diameter estimates.[2]
References
- ↑ Yeomans, Donald K., "71 Niobe", JPL Small-Body Database Browser, NASA Jet Propulsion Laboratory, retrieved 2013-03-30.
- 1 2 Pilcher, Frederick (July 2010), "A New Investigation of the Rotation Period and Size of 71 Niobe", The Minor Planet Bulletin, 37 (3): 98–99, Bibcode:2010MPBu...37...98P
- ↑ Asteroid Data Sets
- ↑ Harwood, Margaret (December 1924), "Variations in the Light of Asteroids", Harvard College Observatory Circular, 269, pp. 1–15, Bibcode:1924HarCi.269....1H.
- ↑ Warner, Brian D.; et al. (December 2006), "Analysis of the lightcurve of 71 Niobe", The Minor Planet Bulletin, 33 (4): 102–103, Bibcode:2006MPBu...33..102W
External links
- 71 Niobe at the JPL Small-Body Database