6144 Kondojiro
| Discovery | |
|---|---|
| Discovered by | K. Endate, K. Watanabe |
| Discovery site | Kitami |
| Discovery date | 14 March 1994 |
| Designations | |
| MPC designation | 6144 |
Named after | Jiro Kondo |
| 1994 EQ3, 1937 JF, 1937 JQ, 1984 FW1 | |
| Jupiter-crosser asteroid | |
| Orbital characteristics[1] | |
| Epoch 13 January 2016 (JD 2457400.5) | |
| Uncertainty parameter 0 | |
| Observation arc | 22150 days (60.64 yr) |
| Aphelion | 6.47345 AU (968.414 Gm) (Q) |
| Perihelion | 3.03222 AU (453.614 Gm) (q) |
| 4.75283 AU (711.013 Gm) (a) | |
| Eccentricity | 0.36202 (e) |
| 10.36 yr (3784.66 d) | |
| 34.71927° (M) | |
| 0° 5m 42.435s / day (n) | |
| Inclination | 5.88716° (i) |
| 117.14167° (Ω) | |
| 96.127254° (ω) | |
| Earth MOID | 2.03358 AU (304.219 Gm) |
| Jupiter MOID | 0.204605 AU (30.6085 Gm) |
| Jupiter Tisserand parameter | 2.867 |
| Physical characteristics | |
| Dimensions | 32.9±5.1 km[2] |
| 4.0±2 h[1][3] | |
| 0.044±0.009[2] | |
| D[4] | |
| 11.6 | |
|
| |
6144 Kondojiro (1994 EQ3) is an asteroid discovered on March 14, 1994 by Kin Endate and Kazuro Watanabe at the Kitami Observatory in eastern Hokkaidō, Japan. It is named after Jiro Kondo, a Japanese Egyptologist and professor of archaeology at Waseda University.
Orbit and classification
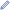
.png)
The orbit of 6144 Kondojiro compared to that of Jupiter and the inner planets
The orbit of 6144 Kondojiro is unusual for a number of reasons, including:
- An eccentricity greater than 0.3,
- A semi-major axis between that of an outer main-belt asteroid (3.2 AU < a < 4.6 AU) and a Jupiter trojan (4.6 AU < a < 5.5 AU),
- A relatively low inclination for a Jupiter-crossing minor planet, and
- A lack of proper orbital elements due to recurring perturbations by Jupiter.
It is difficult to classify an object with such a peculiar orbit using a conventional definition. Despite this, the Minor Planet Center (MPC) lists it as a main-belt asteroid,[5] even though both the orbital and physical properties of 6144 Kondojiro suggest that it may be an extinct comet rather than a true asteroid.[4]
See also
References
- 1 2 "JPL Small-Body Database Browser: 6144 Kondojiro (1994 EQ3)". 14 August 2015. Retrieved 19 November 2015.
- 1 2 J. Licandro, 2015, "Size and albedo distributions of asteroids in cometary orbits using WISE data"
- ↑ Behrend, Raoul. "Asteroids and comets rotation curves – (6144) Kondojiro". Geneva Observatory. Retrieved 6 January 2016.
- 1 2 M. Ishiguro, 2014, "Physical Properties of Asteroids in Comet-like Orbits in Infrared Asteroid Survey Catalogs"
- ↑ "IAU Minor Planet Center - (6144) Kondojiro". Minor Planet Center. Retrieved 19 November 2015.
External links
- Orbital simulation from JPL (Java) / Ephemeris
- 6144 Kondojiro at the JPL Small-Body Database
This article is issued from Wikipedia - version of the 9/10/2016. The text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution/Share Alike but additional terms may apply for the media files.