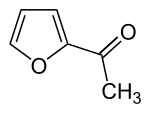
2-Acetylfuran
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
1-(Furan-2-yl)ethan-1-one | |
| Other names
1-(Furan-2-yl)ethanone 1-(2-Furanyl)-ethanone 2-Acetylfuran Acetyl furan 2-Furyl methyl ketone | |
| Identifiers | |
| 1192-62-7 | |
| 3D model (Jmol) | Interactive image |
| ChEBI | CHEBI:59983 |
| ChemSpider | 13849 |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.013.416 |
| PubChem | 14505 |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C6H6O2 | |
| Molar mass | 110.11 g·mol−1 |
| Appearance | Low melting solid |
| Density | 1.0975 at 20 °C |
| Melting point | 30 °C (86 °F; 303 K) |
| Boiling point | 168 to 169 °C (334 to 336 °F; 441 to 442 K) |
| Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
2-Acetylfuran is a low melting solid or high boiling liquid, depending on temperature.[1][2] The solid melts at 30 °C and has a density of 1.0975 g/ml at 20 °C, while the normal boiling point of the liquid is 168–169 °C.[3] 2-Acetylfuran is a useful intermediate in the synthesis of fine chemicals and pharmaceuticals, and is used in the production of the generic cephalophosphorin antibiotic cefuroxime.[4]
Synthesis
2-Acetylfuran was prepared by Ashina in 1914 via the reaction of the methyl Grignard reagent on 2-furonitrile.[5] Modern industrial synthesis generally involves the Friedel–Crafts acylation of furan with acetic anhydride.
Applications
Pharmaceuticals
A one-pot synthesis of an intermediate to the HIV integrase inhibitor S-1360 was based on the Friedel-Crafts alkylation of 2-acetylfuran with 4-fluorobenzyl chloride using zinc chloride catalyst.[6]
Reaction of 2-acetylfuran with aqueous sodium nitrite gave 2-furanyloxoacetic acid, an intermediate to Cefuroxime, a second-generation cephalosporin antibiotic.[7]
References
- ↑ Howard D. Hartough; Kosak, Alvin I. (1948). "Acylation of thiophene and furan by means of boron trifluoride. VII". Journal of the American Chemical Society. 70: 867. doi:10.1021/ja01182a510.
- ↑ Walther Borsche; Leditschke, Heinrich; Lange, Karl (1938). "Cleavage of the furan ring by primary aromatic amines and hydrochloric acid". Berichte der Deutschen Chemischen Gesellschaft [Abteilung] B: Abhandlungen. 71B: 957–66.
- ↑ Y. Asahina; Murayama, Y. (1914). "Ethereal oil of Elsholtzia cristata Willdenow (Lablatae)". Archiv der Pharmazie. 252: 435–48. doi:10.1002/ardp.19142520609.
- ↑ Rong-geng Wang; Liu, Cheng-ping; Zhu, Kun-peng; Du, Hai-lin; Liu, Lie-yi (2004). "Side chain of cefuroxime: (Z)-2-methoxyimino-2-(fury-2-yl)acetic acid ammonium salt". Jingxi Yu Zhuanyong Huaxuepin. 12 (17): 10–11.
- ↑ Asahina, Y.; Murayama, Y. (1914). "Ethereal oil of Elsholtzia cristata Willdenow (Lablatae)". Archiv der Pharmazie. 252: 435–48. doi:10.1002/ardp.19142520609.
- ↑ Kenji Izumi; Kabaki, Mikio; Uenaka, Masaaki; Shimizu, Sumio (2007). "One-Step Synthesis of 5-(4-Fluorobenzyl)-2-furyl Methyl Ketone: A Key Intermediate of HIV-Integrase Inhibitor S-1360". Organic Process Research & Development. 11 (6): 1059–1061. doi:10.1021/op700117q.
- ↑ Rui-min Lv; Zhang, Zhi-de; Zhang, Zhi-cheng (2005). "The research for the synthesis of 2-methoxyimino-2-furylacetic acid". Shandong Huagong. 34 (6): 5–8.