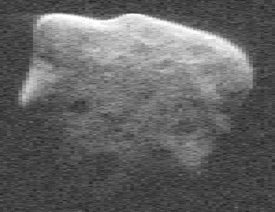
(53319) 1999 JM8
|
| |
| Discovery | |
|---|---|
| Discovered by | LINEAR |
| Discovery date | 13 May 1999 |
| Designations | |
| 1990 HD1 | |
|
Apollo PHA[1] Mars crosser | |
| Orbital characteristics[1] | |
| Epoch 13 January 2016 (JD 2457400.5) | |
| Uncertainty parameter 0 | |
| Observation arc | 9442 days (25.85 yr) |
| Aphelion | 4.4760 AU (669.60 Gm) |
| Perihelion | 0.97524 AU (145.894 Gm) |
| 2.7256 AU (407.74 Gm) | |
| Eccentricity | 0.64220 |
| 4.50 yr (1643.6 d) | |
Average orbital speed | 16.01 km/s |
| 247.69° | |
| 0° 13m 8.508s / day | |
| Inclination | 13.856° |
| 133.70° | |
| 166.76° | |
| Earth MOID | 0.0276419 AU (4.13517 Gm) |
| Jupiter MOID | 0.842693 AU (126.0651 Gm) |
| Physical characteristics | |
| Dimensions | 6.4 km [2] |
Mean radius | 3.5 ± 0.7 km |
| 136 h (5.7 d)[1] | |
| X [1] | |
| 15.2 [1] | |
|
| |
(53319) 1999 JM8 (also written (53319) 1999 JM8) is a Potentially hazardous asteroid, near-Earth asteroid and Mars-crosser asteroid discovered by LINEAR. Radar imaging by Goldstone and Arecibo has revealed the asteroid to have an effective diameter of 6.4 km.[2] Like the asteroid 4179 Toutatis, its rotation speed is unusually slow and possibly chaotic. It is the largest Potentially hazardous object known.
It passed closer than 0.20 AU to the Earth five times in the last century (0.033 AU in 1990), but its closest approach in the 21st century will be in 2075 at 0.256 AU.[1]
See also
References
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 "JPL Small-Body Database Browser: 53319 (1999 JM8)". Jet Propulsion Laboratory. Retrieved 6 April 2016.
- 1 2 Brozovic, M.; Benner, L. A. M.; Nolan, M. C. (2012). "Shape Modeling of Near-Earth Asteroid (53319) 1999 JM8 from Goldstone and Arecibo Radar Images". Asteroids, Comets, Meteors. Bibcode:2012LPICo1667.6183B.
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to (53319) 1999 JM8. |
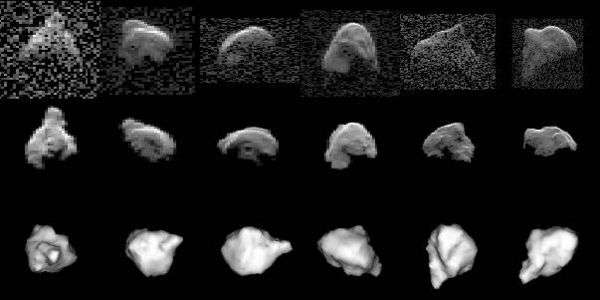
Radar images and computer models of 1999 JM₈
External links
This article is issued from Wikipedia - version of the 9/9/2016. The text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution/Share Alike but additional terms may apply for the media files.